Abstract
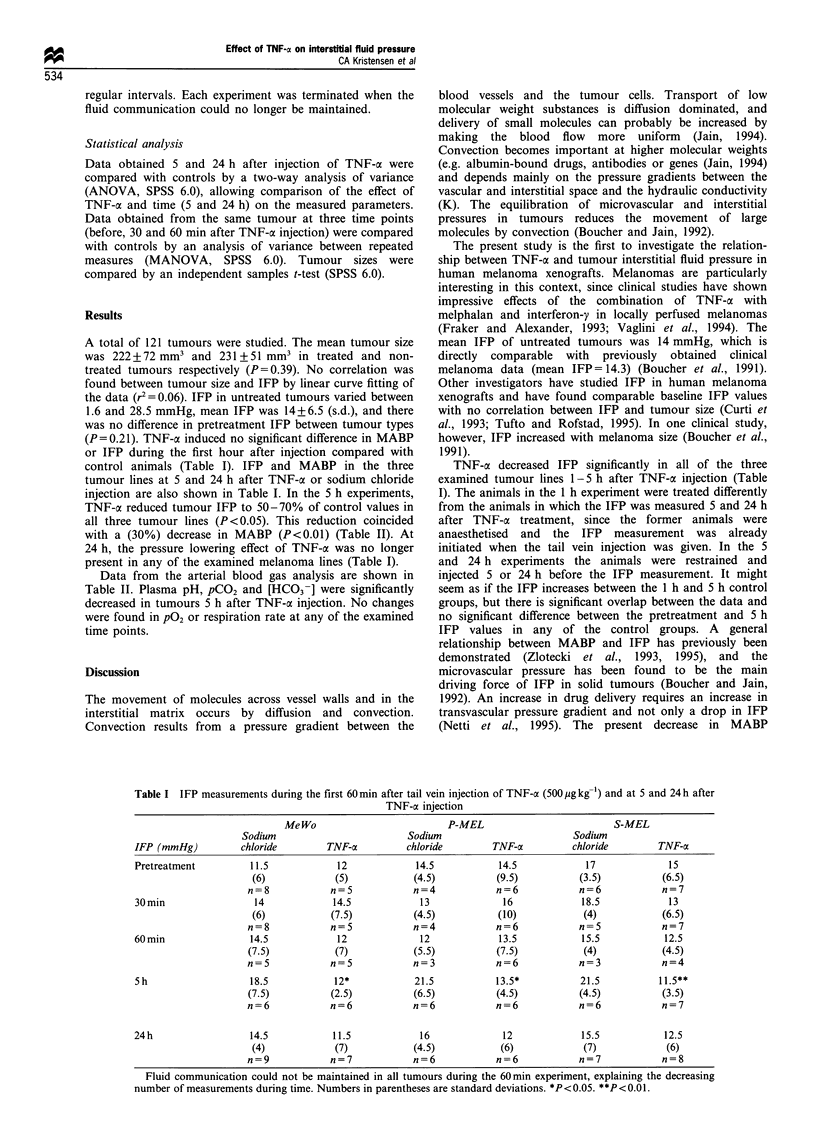
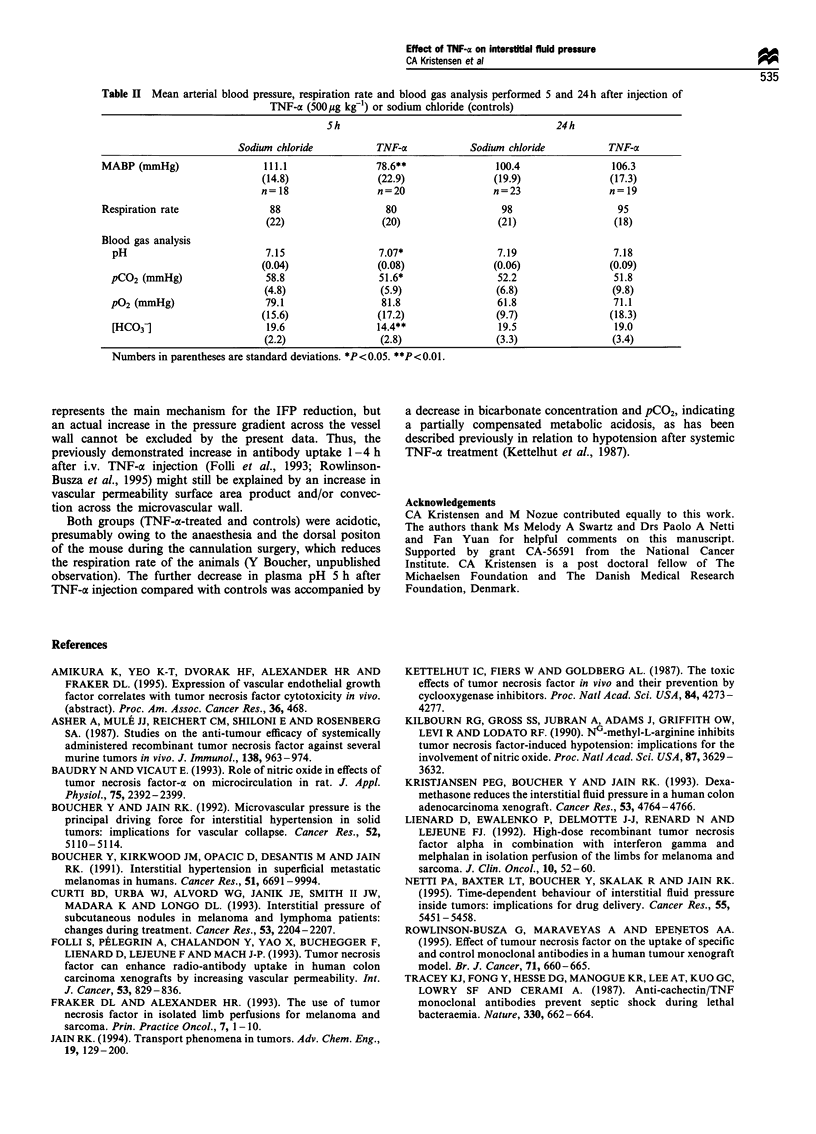
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) reduced the interstitial fluid pressure (IFP) to 54-64% (P < 0.05) and the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) to 70% (P < 0.01) of control values after 5 h in three human melanoma tumour lines transplanted to nude mice.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asher A., Mulé J. J., Reichert C. M., Shiloni E., Rosenberg S. A. Studies on the anti-tumor efficacy of systemically administered recombinant tumor necrosis factor against several murine tumors in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):963–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry N., Vicaut E. Role of nitric oxide in effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on microcirculation in rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993 Dec;75(6):2392–2399. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.75.6.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher Y., Jain R. K. Microvascular pressure is the principal driving force for interstitial hypertension in solid tumors: implications for vascular collapse. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):5110–5114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher Y., Kirkwood J. M., Opacic D., Desantis M., Jain R. K. Interstitial hypertension in superficial metastatic melanomas in humans. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6691–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curti B. D., Urba W. J., Alvord W. G., Janik J. E., Smith J. W., 2nd, Madara K., Longo D. L. Interstitial pressure of subcutaneous nodules in melanoma and lymphoma patients: changes during treatment. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2204–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folli S., Pèlegrin A., Chalandon Y., Yao X., Buchegger F., Lienard D., Lejeune F., Mach J. P. Tumor-necrosis factor can enhance radio-antibody uptake in human colon carcinoma xenografts by increasing vascular permeability. Int J Cancer. 1993 Mar 12;53(5):829–836. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettelhut I. C., Fiers W., Goldberg A. L. The toxic effects of tumor necrosis factor in vivo and their prevention by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4273–4277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Gross S. S., Jubran A., Adams J., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Lodato R. F. NG-methyl-L-arginine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced hypotension: implications for the involvement of nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3629–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristjansen P. E., Boucher Y., Jain R. K. Dexamethasone reduces the interstitial fluid pressure in a human colon adenocarcinoma xenograft. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4764–4766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienard D., Ewalenko P., Delmotte J. J., Renard N., Lejeune F. J. High-dose recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha in combination with interferon gamma and melphalan in isolation perfusion of the limbs for melanoma and sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Jan;10(1):52–60. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netti P. A., Baxter L. T., Boucher Y., Skalak R., Jain R. K. Time-dependent behavior of interstitial fluid pressure in solid tumors: implications for drug delivery. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 15;55(22):5451–5458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlinson-Busza G., Maraveyas A., Epenetos A. A. Effect of tumour necrosis factor on the uptake of specific and control monoclonal antibodies in a human tumour xenograft model. Br J Cancer. 1995 Apr;71(4):660–665. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufto I., Rofstad E. K. Interstitial fluid pressure in human melanoma xenografts. Relationship to fractional tumor water content, tumor size, and tumor volume-doubling time. Acta Oncol. 1995;34(3):361–365. doi: 10.3109/02841869509093990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaglini M., Belli F., Ammatuna M., Inglese M. G., Manzi R., Prada A., Persiani L., Santinami M., Santoro N., Cascinelli N. Treatment of primary or relapsing limb cancer by isolation perfusion with high-dose alpha-tumor necrosis factor, gamma-interferon, and melphalan. Cancer. 1994 Jan 15;73(2):483–492. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940115)73:2<483::aid-cncr2820730238>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotecki R. A., Baxter L. T., Boucher Y., Jain R. K. Pharmacologic modification of tumor blood flow and interstitial fluid pressure in a human tumor xenograft: network analysis and mechanistic interpretation. Microvasc Res. 1995 Nov;50(3):429–443. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1995.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotecki R. A., Boucher Y., Lee I., Baxter L. T., Jain R. K. Effect of angiotensin II induced hypertension on tumor blood flow and interstitial fluid pressure. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2466–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


