Abstract
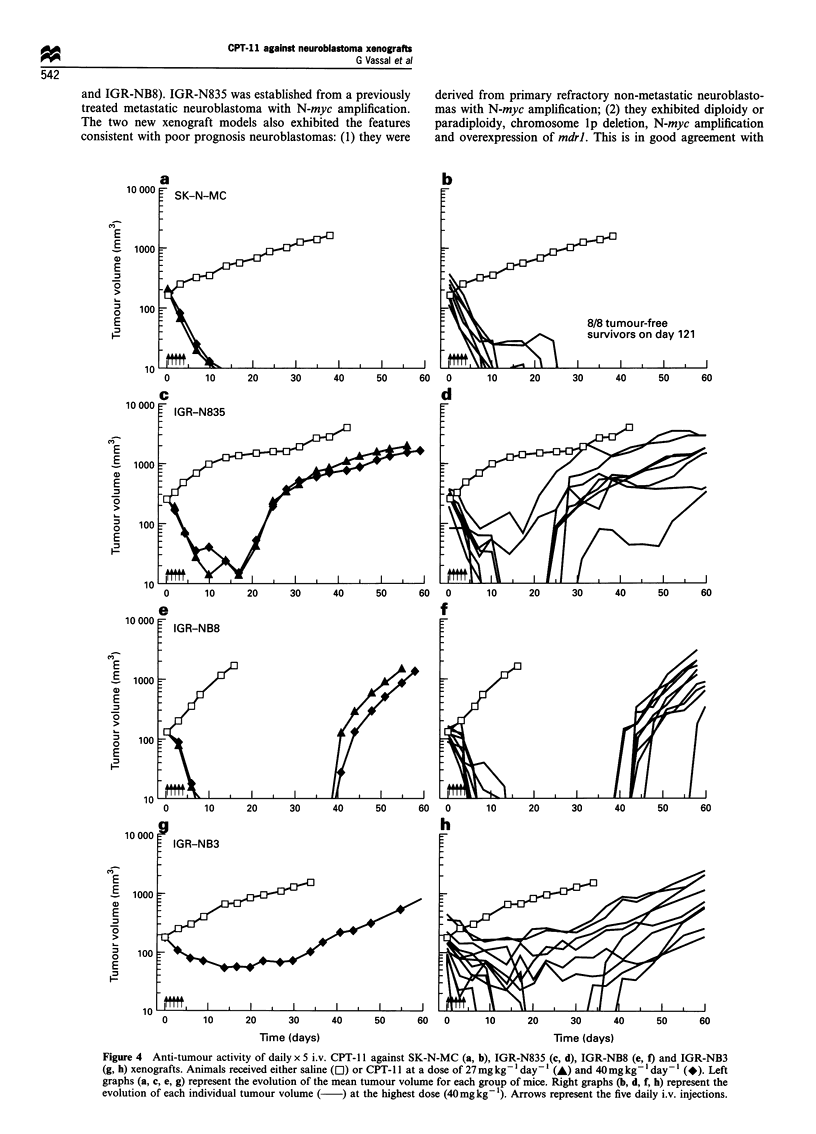
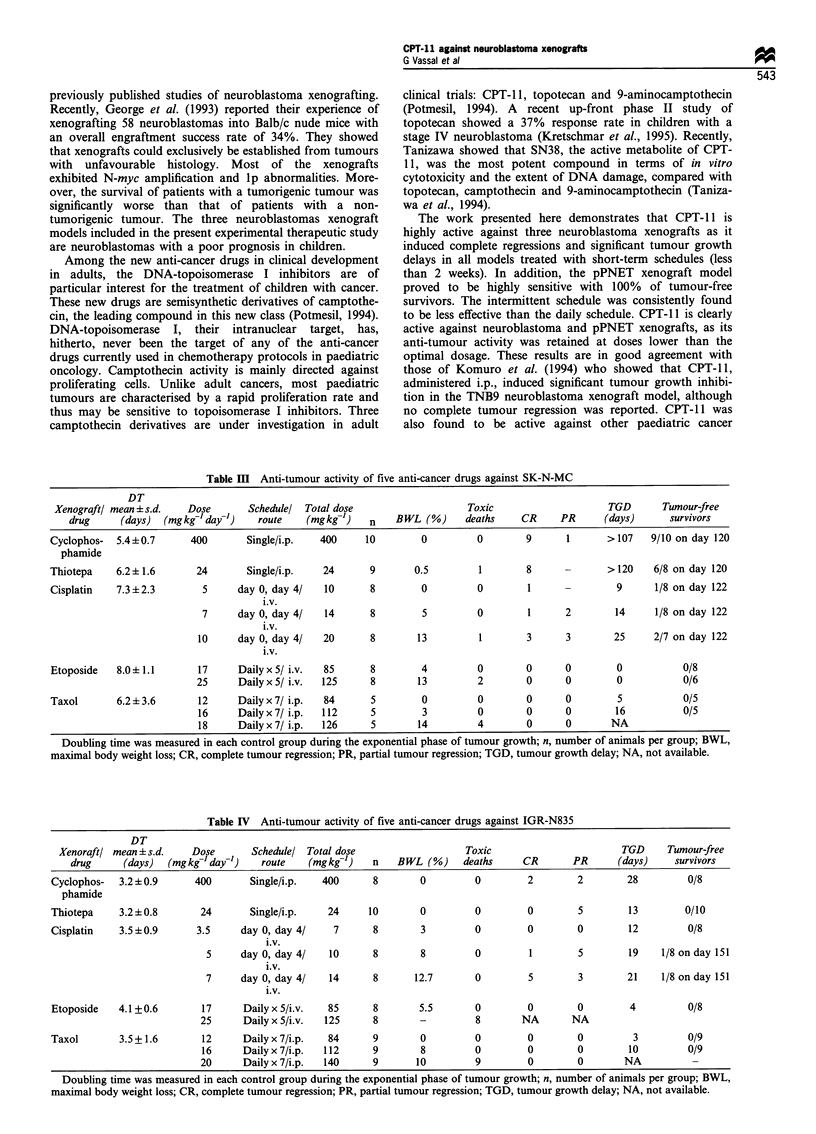
The anti-tumour activity of CPT-11, a topoisomerase I inhibitor, was evaluated in four human neural-crest-derived paediatric tumour xenografts; one peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumour (pPNET) (SK-N-MC) and three neuroblastomas. Two models, SK-N-MC and IGR-N835, were established in athymic mice from a previously established in vitro cell line. Two new neuroblastoma xenograft models, IGR-NB3 and IGR-NB8, were derived from previously untreated non-metastatic neuroblastomas. They exhibited the classic histological features of immature neuroblastoma along with N-myc amplification, paradiploidy, chromosome 1p deletions and overexpression of the human mdr 1 gene. These tumour markers have been shown to be poor prognostic factors in children treated for neuroblastoma. CPT-11 was tested against advanced stage subcutaneous tumours. CPT-11 was administered i.v. using an intermittent (q4d x 3) and a daily x 5 schedule. The optimal dosage and schedule was 40 mg kg-1 daily for 5 days. At this highest non-toxic dose, CPT-11 induced 100% tumour-free survivors on day 121 in mice bearing the pPNET SK-N-MC xenograft. For the three neuroblastoma xenografts, 38-100% complete tumour regressions were observed with a tumour growth delay from 38 to 42 days, and anti-tumour activity was clearly sustained at a lower dosage (27 mg kg-1 day-1). The efficacy of five anti-cancer drugs commonly used in paediatric oncology or in clinical development was evaluated against SK-N-MC and IGR-N835. The sensitivity of these two xenografts to cyclophosphamide, thiotepa and cisplatin was of the same order of magnitude as that of CPT-11, but they were refractory to etoposide and taxol. In conclusion, CPT-11 demonstrated significant activity against pPNET and neuroblastoma xenografts. Further clinical development of CPT-11 in paediatric oncology is warranted.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abigerges D., Chabot G. G., Armand J. P., Hérait P., Gouyette A., Gandia D. Phase I and pharmacologic studies of the camptothecin analog irinotecan administered every 3 weeks in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1995 Jan;13(1):210–221. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettan-Renaud L., Bayle C., Teyssier J. R., Benard J. Stability of phenotypic and genotypic traits during the establishment of a human neuroblastoma cell line, IGR-N-835. Int J Cancer. 1989 Sep 15;44(3):460–466. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Helson L., Spengler B. A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2643–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourhis J., Bénard J., Hartmann O., Boccon-Gibod L., Lemerle J., Riou G. Correlation of MDR1 gene expression with chemotherapy in neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Sep 20;81(18):1401–1405. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.18.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boven E., Winograd B., Fodstad O., Lobbezoo M. W., Pinedo H. M. Preclinical phase II studies in human tumor lines: a European multicenter study. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;24(3):567–573. doi: 10.1016/s0277-5379(98)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan H. S., Haddad G., Thorner P. S., DeBoer G., Lin Y. P., Ondrusek N., Yeger H., Ling V. P-glycoprotein expression as a predictor of the outcome of therapy for neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 5;325(23):1608–1614. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112053252304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Lin H. H., Weissman B. E. A functional analysis of tumor suppressor activity for peripheral neuroepitheliomas by monochromosome transfer. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 2;10(3):577–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Desmaze C., Melot T., Peter M., Kovar H., Joubert I., de Jong P., Rouleau G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Sur une nouvelle technique d'analyse du caryotype humain. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 May 17;272(20):2638–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandis E., Da Silva J., Riou G., Bénard I. Coactivation of the MDR1 and MYCN genes in human neuroblastoma cells during the metastatic process in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2256–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. T., Dracopoli N. C., White P. S., Merrill P. T., Griffith R. C., Housman D. E., Brodeur G. M. Loss of heterozygosity for the short arm of chromosome 1 in human neuroblastomas: correlation with N-myc amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. S., Schold S. C., Jr, Bigner D. D. Chemotherapy of subcutaneous and intracranial human medulloblastoma xenografts in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):224–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George B. A., Yanik G., Wells R. J., Martin L. W., Soukup S., Ballard E. T., Gartside P. S., Lampkin B. C. Growth patterns of human neuroblastoma xenografts and their relationship to treatment outcome. Cancer. 1993 Dec 1;72(11):3331–3339. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931201)72:11<3331::aid-cncr2820721132>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Kanda N., Inaba T., Hanada R., Nagahara N., Muchi H., Yamamoto K. Cytogenetic findings and prognosis in neuroblastoma with emphasis on marker chromosome 1. Cancer. 1989 Jan 1;63(1):126–132. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<126::aid-cncr2820630120>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes F. A., Thompson E. I., Meyer W. H., Kun L., Parham D., Rao B., Kumar M., Hancock M., Parvey L., Magill L. Therapy for localized Ewing's sarcoma of bone. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Feb;7(2):208–213. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton P. J., Cheshire P. J., Hallman J. C., Bissery M. C., Mathieu-Boué A., Houghton J. A. Therapeutic efficacy of the topoisomerase I inhibitor 7-ethyl-10-(4-[1-piperidino]-1-piperidino)-carbonyloxy-camptothecin against human tumor xenografts: lack of cross-resistance in vivo in tumors with acquired resistance to the topoisomerase I inhibitor 9-dimethylaminomethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2823–2829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton P. J., Cheshire P. J., Hallman J. D., 2nd, Lutz L., Friedman H. S., Danks M. K., Houghton J. A. Efficacy of topoisomerase I inhibitors, topotecan and irinotecan, administered at low dose levels in protracted schedules to mice bearing xenografts of human tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(5):393–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00686188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Lihou M. G., Liu L. F. Arrest of replication forks by drug-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA cleavable complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 15;49(18):5077–5082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C. A., Relling M. V., Weitman S. D., Ravindranath Y., Vietti T. J., Strother D. R., Ragab A. H., Pratt C. B. Phase I trial of paclitaxel in children with refractory solid tumors: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Dec;11(12):2324–2329. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.12.2324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato Y., Furuta T., Aonuma M., Yasuoka M., Yokokura T., Matsumoto K. Antitumor activity of a camptothecin derivative, CPT-11, against human tumor xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1991;28(3):192–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00685508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro H., Li P., Tsuchida Y., Yokomori K., Nakajima K., Aoyama T., Kaneko M., Kaneda N. Effects of CPT-11 (a unique DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor) on a highly malignant xeno-transplanted neuroblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23(6):487–492. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950230607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung F., Hayes F. A., Krischer J., Mahoney D., Jr, Leventhal B., Brodeur G., Berry D. H., Dubowy R., Toledano S. Clinical trial of etoposide (VP-16) in children with recurrent malignant solid tumors. A phase II study from the Pediatric Oncology Group. Invest New Drugs. 1988 Apr;6(1):31–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00170776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto T., Nitta K., Tanaka T., Uehara N., Baba H., Takeuchi M., Yokokura T., Sawada S., Miyasaka T., Mutai M. Antitumor activity of 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxy-camptothec in, a novel water-soluble derivative of camptothecin, against murine tumors. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):5944–5947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner B. H., LaQuaglia M. P., Bonilla M. A., Lindsley K., Rosenfield N., Yeh S., Eddy J., Gerald W. L., Heller G., Cheung N. K. Highly effective induction therapy for stage 4 neuroblastoma in children over 1 year of age. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Dec;12(12):2607–2613. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.12.2607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda N., Fukuoka M., Kusunoki Y., Matsui K., Takifuji N., Kudoh S., Negoro S., Nishioka M., Nakagawa K., Takada M. CPT-11: a new derivative of camptothecin for the treatment of refractory or relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Aug;10(8):1225–1229. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.8.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méresse V., Vassal G., Michon J., De Cervens C., Courbon B., Rubie H., Perel Y., Landman J., Chastagnier P., De Valck C. Combined continuous infusion etoposide with high-dose cyclophosphamide for refractory neuroblastoma: a phase II study from the Société Française d'Oncologie Pédiatrique. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Apr;11(4):630–637. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.4.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip T., Ghalie R., Pinkerton R., Zucker J. M., Bernard J. L., Leverger G., Hartmann O. A phase II study of high-dose cisplatin and VP-16 in neuroblastoma: a report from the Société Française d'Oncologie Pédiatrique. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Jun;5(6):941–950. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.6.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Tanizawa A., Kohn K. W. Mechanisms of topoisomerase I inhibition by anticancer drugs. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;29B:73–92. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potmesil M. Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1431–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanizawa A., Fujimori A., Fujimori Y., Pommier Y. Comparison of topoisomerase I inhibition, DNA damage, and cytotoxicity of camptothecin derivatives presently in clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Jun 1;86(11):836–842. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.11.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruo T., Matsuzaki T., Matsushita M., Saito H., Yokokura T. Antitumor effect of CPT-11, a new derivative of camptothecin, against pleiotropic drug-resistant tumors in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1988;21(1):71–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00262744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]