Abstract
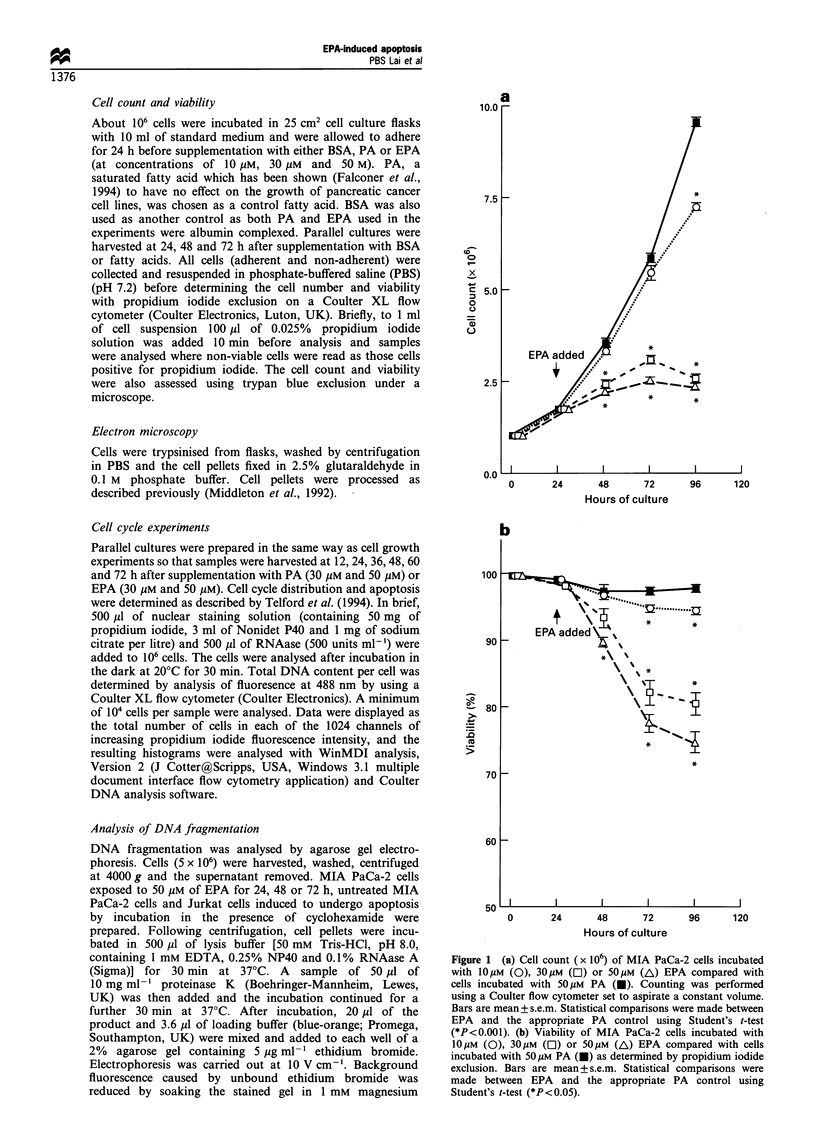
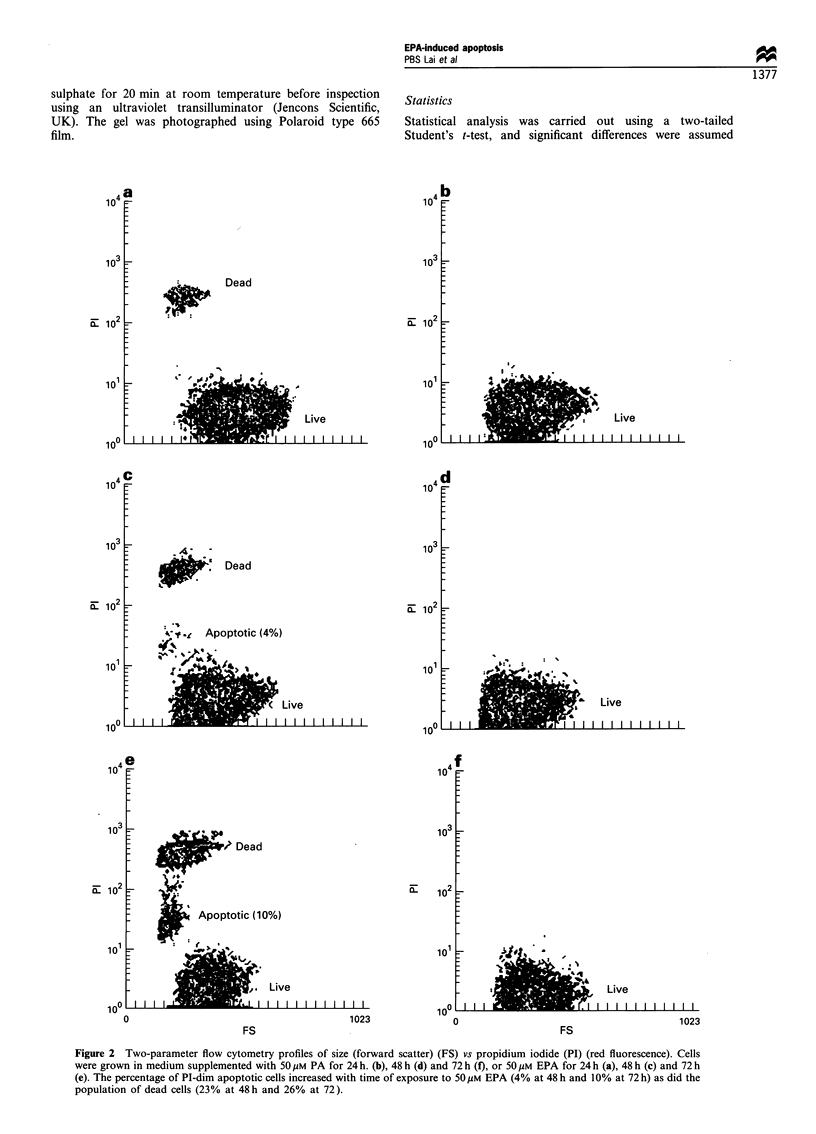
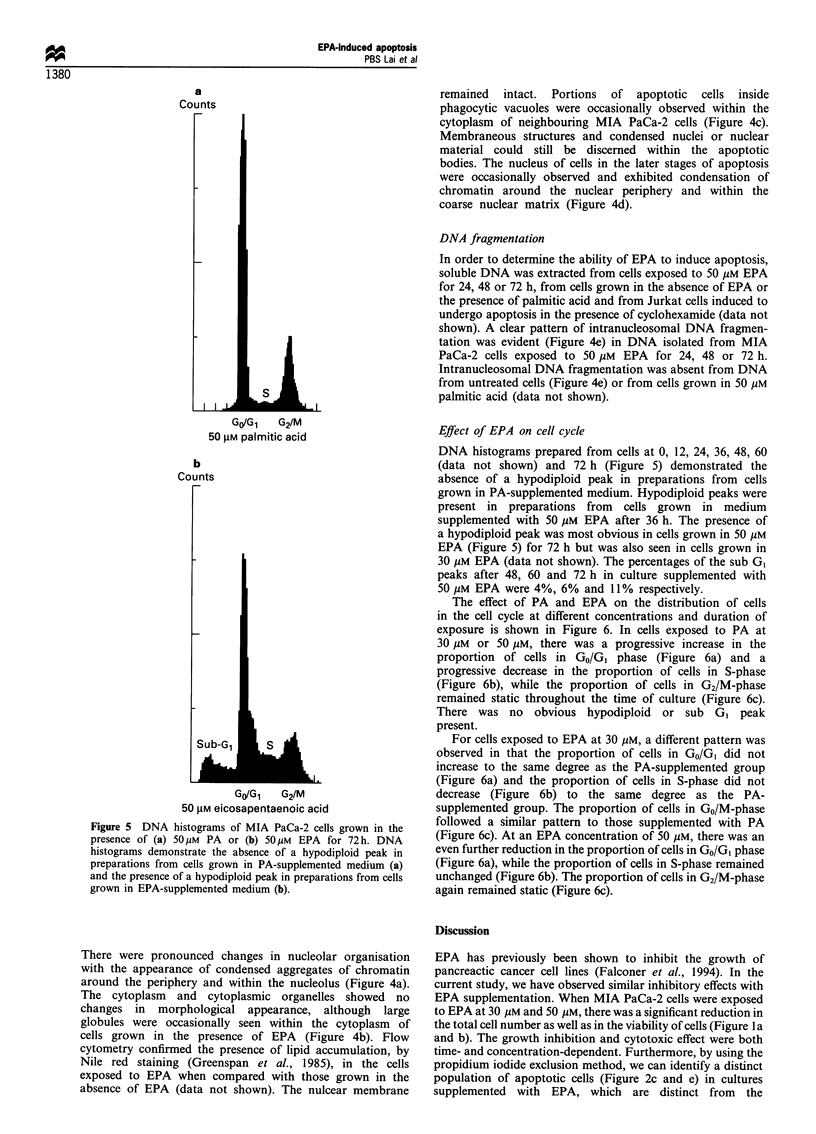
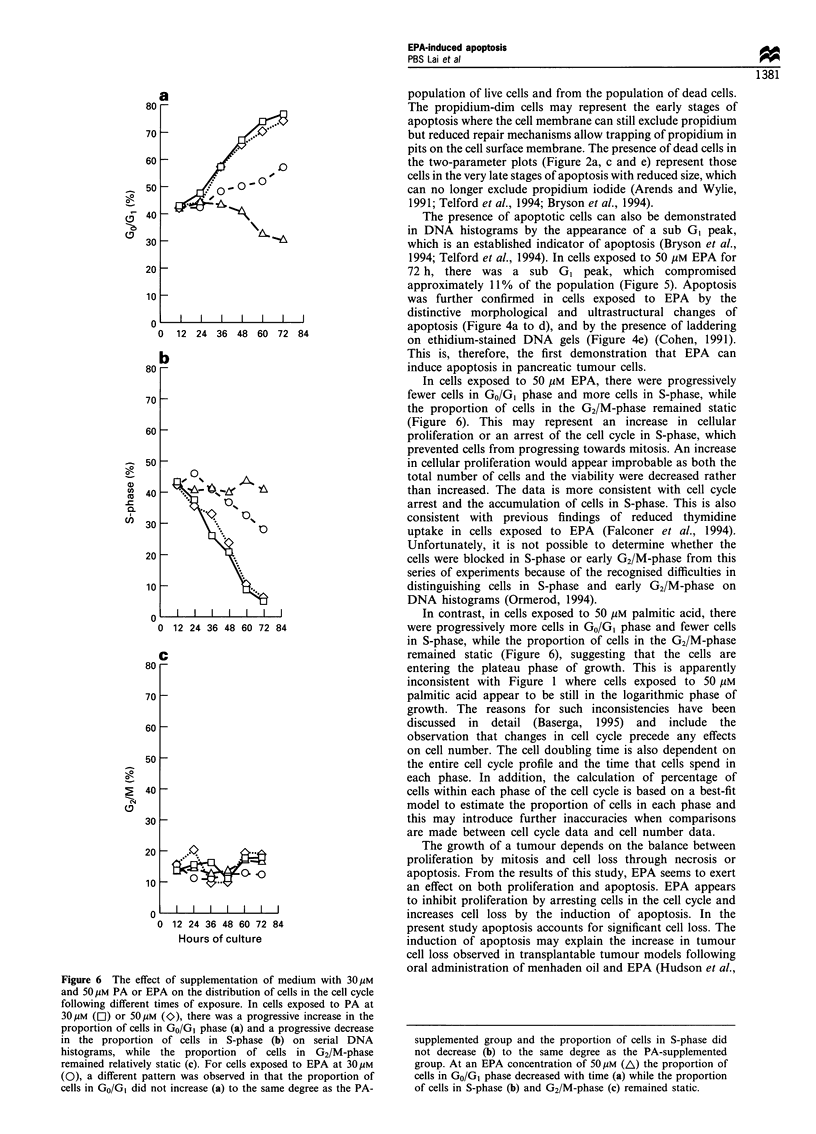
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has been shown to have an inhibitory effect on the growth of several pancreatic cancer cell lines in vitro. This study investigates the mechanism of growth inhibition and cytotoxicity of EPA on the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2. Cells were analysed for cell count, viability, cell cycle distribution and ultrastructural changes. There was a time- and dose-dependent decrease in cell count and viability in cultures of pancreatic cancer cells supplemented with EPA. Flow cytometric DNA analysis of MIA PaCa-2 cells incubated with EPA demonstrated the presence of sub G1 populations corresponding to the presence of apoptotic cells and the blockade of cell cycle progression in S-phase and G2/M-phase. The presence of apoptosis in EPA-supplemented cultures was further confirmed by DNA fragmentation and ultrastructural changes associated with apoptosis. Therefore, we conclude that EPA mediates its effect on the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2, at least in part, via cell cycle arrest and the induction of apoptosis.
Full text
PDF

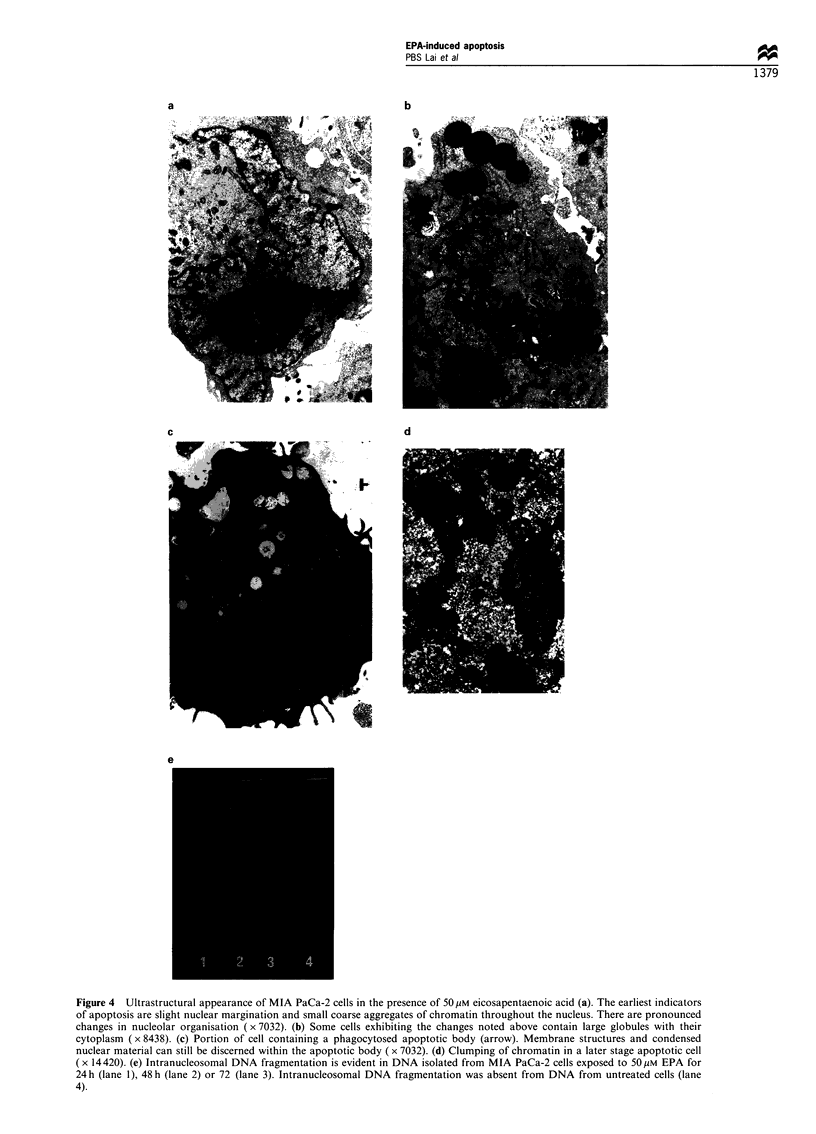


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-el-Ela S. H., Prasse K. W., Farrell R. L., Carroll R. W., Wade A. E., Bunce O. R. Effects of D,L-2-difluoromethylornithine and indomethacin on mammary tumor promotion in rats fed high n-3 and/or n-6 fat diets. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1434–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagwell C. B., Hudson J. L., Irvin G. L., 3rd Nonparametric flow cytometry analysis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Jan;27(1):293–296. doi: 10.1177/27.1.374589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay G. K., Hwang S., Imagawa W., Nandi S. Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids as signal transducers: amplification of signals from growth factor receptors by fatty acids in mammary epithelial cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1993 Jan;48(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(93)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer B. M., Kruth H. S., Vaughan M., Beaven M. A. Arrest of cultured cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle by indomethacin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jul;210(1):106–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S. A., Smith K. L., Tisdale M. J. Anticachectic and antitumor effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and its effect on protein turnover. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 15;51(22):6089–6093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. R., Subbaiah P. V. Differential effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on human skin fibroblasts. Lipids. 1994 Dec;29(12):825–829. doi: 10.1007/BF02536249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson G. J., Harmon B. V., Collins R. J. A flow cytometric study of cell death: failure of some models to correlate with morphological assessment. Immunol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;72(1):35–41. doi: 10.1038/icb.1994.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckman D. K., Hubbard N. E., Erickson K. L. Eicosanoids and linoleate-enhanced growth of mouse mammary tumor cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1991 Nov;44(3):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(91)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin M. E., Ells G., Das U. N., Horrobin D. F. Differential killing of human carcinoma cells supplemented with n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Nov;77(5):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder P. C., Bond J. A., Bevan S. J., Hunt S. V., Newsholme E. A. Effect of fatty acids on the proliferation of concanavalin A-stimulated rat lymph node lymphocytes. Int J Biochem. 1991;23(5-6):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Programmed cell death in the immune system. Adv Immunol. 1991;50:55–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarco D. M., Santoli D., Zurier R. B. Effects of fatty acids on proliferation and activation of human synovial compartment lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Nov;56(5):612–615. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer J. S., Ross J. A., Fearon K. C., Hawkins R. A., O'Riordain M. G., Carter D. C. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and other fatty acids on the growth in vitro of human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1994 May;69(5):826–832. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Hilf R. Failure of indomethacin to inhibit growth of the R3230AC mammary tumor in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Oct;75(4):751–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. M. In vivo effects of indomethacin on the growth of murine mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 1984 Jun;44(6):2416–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabor H., Abraham S. Effect of dietary menhaden oil on tumor cell loss and the accumulation of mass of a transplantable mammary adenocarcinoma in BALB/c mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jun;76(6):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan P., Mayer E. P., Fowler S. D. Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):965–973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., De Mello M. C., Horakova Z., Beaven M. A. Antiproliferative activity of anti-inflammatory drugs in two mammalian cell culture lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Baldwin J. H., Kiernan J. A. Control of growth of a tumor cell by linoleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3976–3978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson E. A., Beck S. A., Tisdale M. J. Kinetics of the inhibition of tumour growth in mice by eicosapentaenoic acid-reversal by linoleic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jun 9;45(11):2189–2194. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali R. A., Chao C. C., Basu A., Modak M. II. Effect of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids on mammary H-ras expression and PGE2 levels in DMBA-treated rats. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali R. A., Marsh J., Fuchs C. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on growth of a rat mammary tumor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Aug;73(2):457–461. doi: 10.1093/jnci/73.2.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman D., Douvdevani A., Schally A. V., Levy J., Sharoni Y. Direct growth inhibition of human endometrial cancer cells by the gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist SB-75: role of apoptosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Jan;170(1 Pt 1):96–102. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(94)70391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lystad E., Høstmark A. T., Kiserud C., Haugen A. Influence of fatty acids and bovine serum albumin on the growth of human hepatoma and immortalized human kidney epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1994 Sep;30A(9):568–573. doi: 10.1007/BF02631254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. G., Miller S., Ross J. A., Steel C. M., Guy K. Insertion of SMRV-H viral DNA at the c-myc gene locus of a BL cell line and presence in established cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1992 Sep 30;52(3):451–454. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoura T., Takata T., Sakaguchi M., Takada H., Yamamura M., Hioki K., Yamamoto M. Effect of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid on azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 1;48(17):4790–4794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer K. R., Kerr M., Knowles G., Cull A., Carter D. C., Leonard R. C. Chemotherapy prolongs survival in inoperable pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Surg. 1994 Jun;81(6):882–885. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800810629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. A., Sullivan-Tailyour G., Hulbert A. J. Membrane fatty acid changes during the cell cycle of CV-1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Nov;191(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90047-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D. P., Connolly J. M. Effects of fatty acids and inhibitors of eicosanoid synthesis on the growth of a human breast cancer cell line in culture. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7139–7144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinozzi F., Pagliacci M. C., Migliorati G., Moraca R., Grignani F., Riccardi C., Nicoletti I. The natural tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein produces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Jurkat T-leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 1994 Jun;18(6):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søyland E., Lea T., Sandstad B., Drevon A. Dietary supplementation with very long-chain n-3 fatty acids in man decreases expression of the interleukin-2 receptor (CD25) on mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes from patients with inflammatory skin diseases. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;24(4):236–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate G. A., Mandell B. F., Karmali R. A., Laposata M., Baker D. G., Schumacher H. R., Jr, Zurier R. B. Suppression of monosodium urate crystal-induced acute inflammation by diets enriched with gamma-linolenic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Dec;31(12):1543–1551. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford W. G., King L. E., Fraker P. J. Rapid quantitation of apoptosis in pure and heterogeneous cell populations using flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Jun 3;172(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M. J., Beck S. A. Inhibition of tumour-induced lipolysis in vitro and cachexia and tumour growth in vivo by eicosapentaenoic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 1;41(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M. J., Dhesi J. K. Inhibition of weight loss by omega-3 fatty acids in an experimental cachexia model. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):5022–5026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]