Abstract
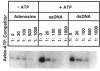
RecF protein is one of the important proteins involved in DNA recombination and repair. RecF protein has been shown to bind single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in the absence of ATP (T. J. Griffin IV and R. D. Kolodner, J. Bacteriol. 172:6291-6299, 1990; M. V. V. S. Madiraju and A. J. Clark, Nucleic Acids Res. 19:6295-6300, 1991). In the present study, using 8-azido-ATP, a photo-affinity analog of ATP, we show that RecF protein binds ATP and that the binding is specific in the presence of DNA. 8-Azido-ATP photo-cross-linking is stimulated in the presence of DNA (both ssDNA and double-stranded DNA [dsDNA]), suggesting that DNA enhances the affinity of RecF protein for ATP. These data suggest that RecF protein possesses independent ATP- and DNA-binding sites. Further, we find that stable RecF protein-dsDNA complexes are obtained in the presence of ATP or ATP-gamma-S [adenosine-5'-O-(3-thio-triphosphate)]. No other nucleoside triphosphates served as necessary cofactors for dsDNA binding, indicating that RecF is an ATP-dependent dsDNA-binding protein. Since a mutation in a putative phosphate-binding motif of RecF protein results in a recF mutant phenotype (S. J. Sandler, B. Chackerian, J. T. Li, and A. J. Clark, Nucleic Acids Res. 20:839-845, 1992), we suggest on the basis of our data that the interactions of RecF protein with ATP, with dsDNA, or with both are physiologically important for understanding RecF protein function in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caron P. R., Grossman L. Involvement of a cryptic ATPase activity of UvrB and its proteolysis product, UvrB* in DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10891–10902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Goff S. A., Webster T., Smith T., Goldberg A. L. Sequence of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. A heat-shock gene which encodes the ATP-dependent protease La. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11718–11728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. rec genes and homologous recombination proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):523–532. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90124-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J., Geahlen R., Haley B. Synthesis and use of azido photoaffinity analogs of adenine and guanine nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. Superfamily of UvrA-related NTP-binding proteins. Implications for rational classification of recombination/repair systems. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):583–591. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. J., 4th, Kolodner R. D. Purification and preliminary characterization of the Escherichia coli K-12 recF protein. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6291–6299. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6291-6299.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., McEntee K. Covalent modification of the recA protein from Escherichia coli with the photoaffinity label 8-azidoadenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):867–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C. Interaction of recA protein with a photoaffinity analogue of ATP, 8-azido-ATP: determination of nucleotide cofactor binding parameters and of the relationship between ATP binding and ATP hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):5872–5881. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madiraju M. V., Clark A. J. Effect of RecF protein on reactions catalyzed by RecA protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6295–6300. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madiraju M. V., Templin A., Clark A. J. Properties of a mutant recA-encoded protein reveal a possible role for Escherichia coli recF-encoded protein in genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6592–6596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Fry D. C. NMR studies of the mechanism of enzyme action. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;59:241–313. doi: 10.1002/9780470123058.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. H., Clark A. J. The dependence of postreplication repair on uvrB in a recF mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 24;155(3):279–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00272806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S. J., Chackerian B., Li J. T., Clark A. J. Sequence and complementation analysis of recF genes from Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Pseudomonas putida and Bacillus subtilis: evidence for an essential phosphate binding loop. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):839–845. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. W. Nature of the SOS-inducing signal in Escherichia coli. The involvement of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):79–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. Constitutive and UV-mediated activation of RecA protein: combined effects of recA441 and recF143 mutations and of addition of nucleosides and adenine. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5869–5875. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5869-5875.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., Lloyd R. G. Control of recA dependent activities in Escherichia coli: a possible role for the recF product. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):681–686. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms B., Wackernagel W. Regulatory role of recF in the SOS response of Escherichia coli: impaired induction of SOS genes by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in a recF mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1731–1736. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1731-1736.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms B., Wackernagel W. Suppression of the UV-sensitive phenotype of Escherichia coli recF mutants by recA(Srf) and recA(Tif) mutations requires recJ+. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3675–3681. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3675-3681.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R. Altered induction of the adaptive response to alkylation damage in Escherichia coli recF mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):99–103. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.99-103.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Hartke M. A. Suppression of Escherichia coli recF mutations by recA-linked srfA mutations. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):498–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.498-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Margossian L. J., Clark A. J. Two-component suppression of recF143 by recA441 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.702-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]