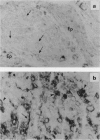
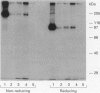
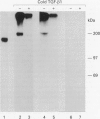
Abstract
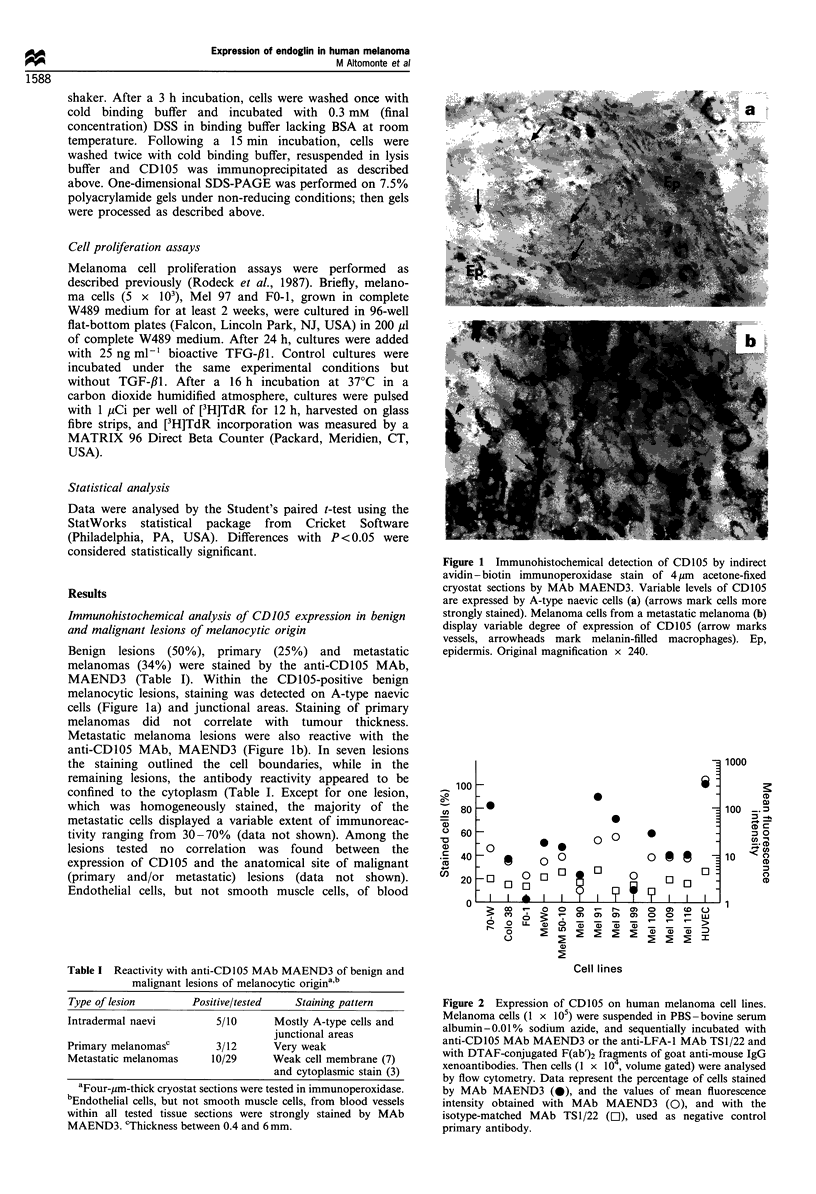
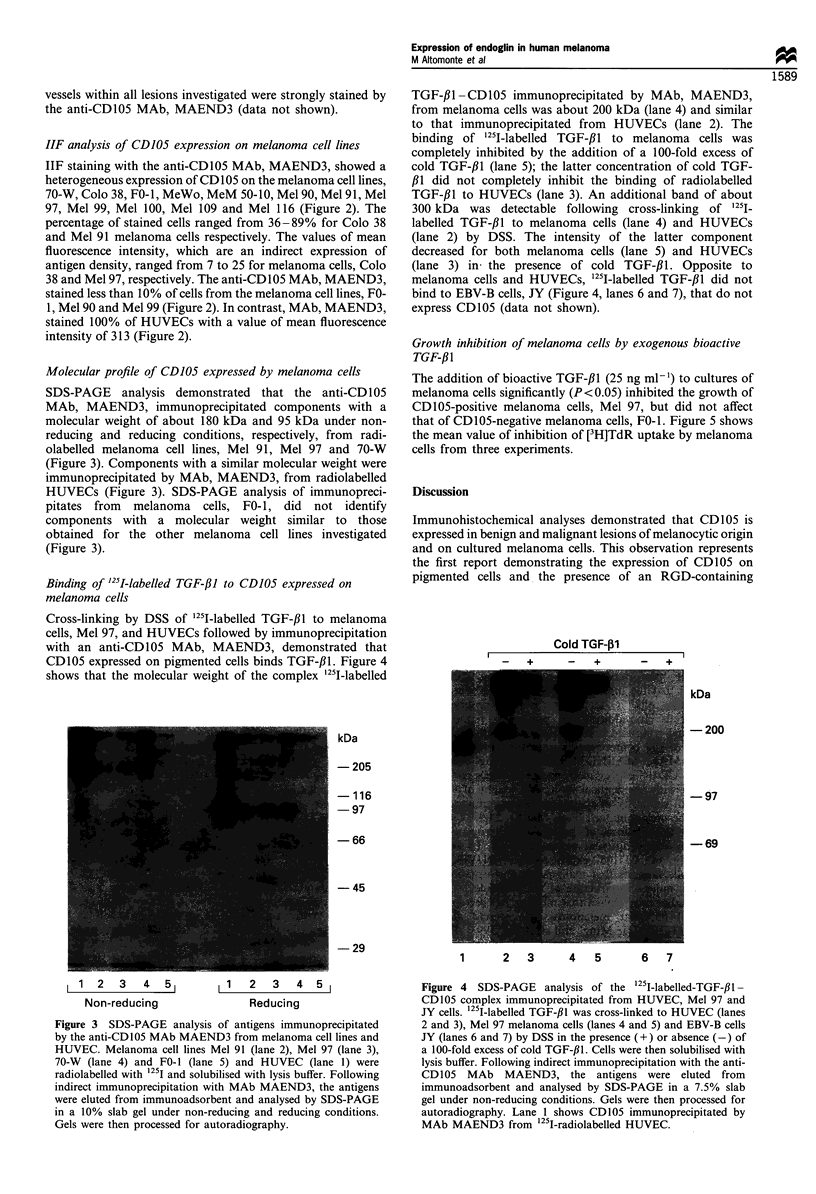
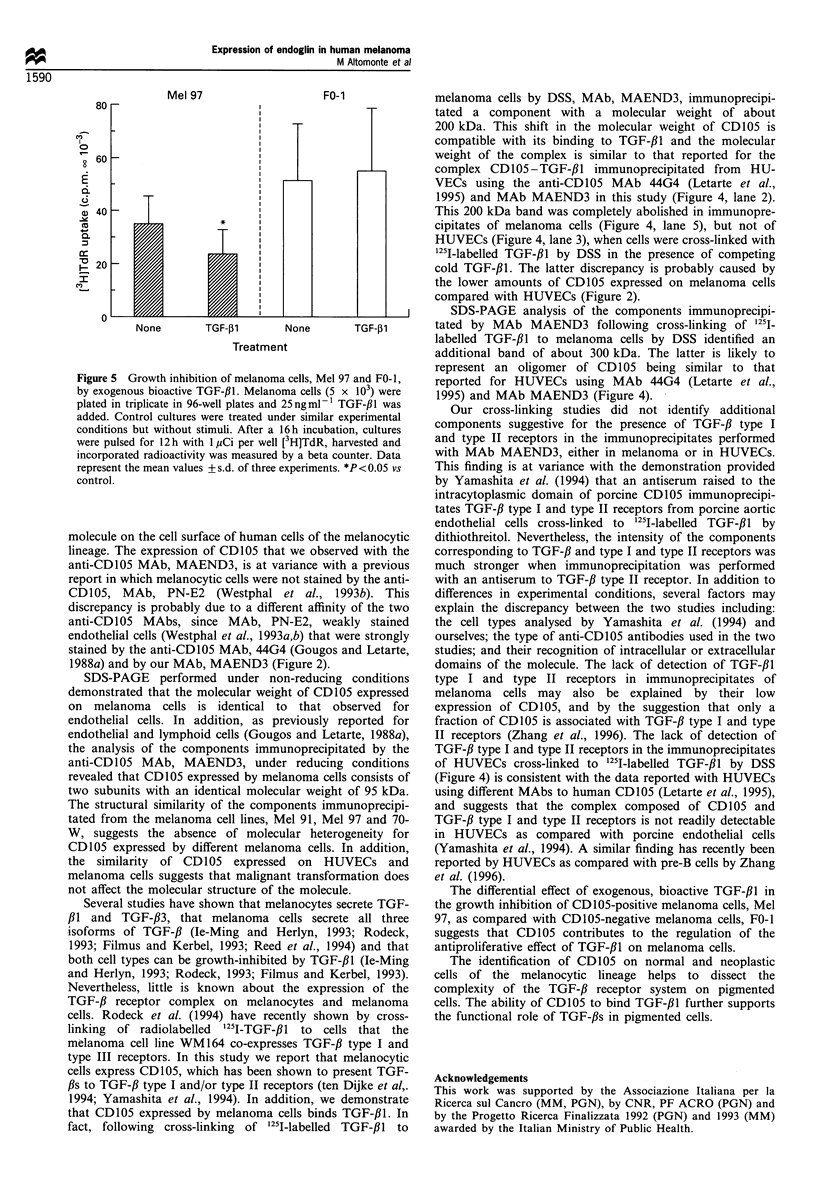
Human endoglin (CD105) is a member of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) receptor family that binds TGF-beta1 and -beta3, but not TGF-beta2, on human endothelial cells. Immunohistochemical analyses demonstrated that CD105 is expressed on normal and neoplastic cells of the melanocytic lineage. The anti-CD105 MAb, MAEND3, stained 50, 25 and 34% of intradermal naevi, primary and metastatic melanomas investigated, respectively, and nine out of 12 melanoma cell lines. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis revealed that CD105 expressed by melanoma cells consists of a homodimeric protein with an apparent molecular weight of 180 and 95 kDa under non-reducing and reducing conditions. Cross-linking of 125I-labelled TGF-beta1 to melanoma cells, Mel 97, by disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) demonstrated that CD105 expressed on pigmented cells binds TGF-beta1; the pattern of binding of TGF-beta1 to melanoma cells was found to be similar to that of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The addition of exogenous, bioactive TGF-beta1 significantly (P<0.05) inhibited the growth of CD105-positive melanoma cells, Mel 97, but did not affect that of CD105-negative melanoma cells, F0-1. These data, altogether, demonstrate that CD105 is expressed on pigmented cells and might play a functionally relevant role in the biology of human melanoma cells by regulating their sensitivity to TGF-betas.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altomonte M., Gloghini A., Bertola G., Gasparollo A., Carbone A., Ferrone S., Maio M. Differential expression of cell adhesion molecules CD54/CD11a and CD58/CD2 by human melanoma cells and functional role in their interaction with cytotoxic cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 15;53(14):3343–3348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow A. Tumor thickness, level of invasion and node dissection in stage I cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg. 1975 Nov;182(5):572–575. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197511000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühring H. J., Müller C. A., Letarte M., Gougos A., Saalmüller A., van Agthoven A. J., Busch F. W. Endoglin is expressed on a subpopulation of immature erythroid cells of normal human bone marrow. Leukemia. 1991 Oct;5(10):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Bellón T., Calés C., Vera S., Bernabeu C., Massagué J., Letarte M. Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth factor-beta receptor system in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19027–19030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. H., Jr, Ainsworth A. M., Bernardino E. A., Yang C. H., Mihm C. M., Jr, Reed R. J. The developmental biology of primary human malignant melanomas. Semin Oncol. 1975 Jun;2(2):83–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Kerbel R. S. Development of resistance mechanisms to the growth-inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor-beta during tumor progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 1993 Jan;5(1):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge A. Z., Butcher E. C. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding mouse endoglin, an endothelial cell TGF-beta ligand. Gene. 1994 Jan 28;138(1-2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90808-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougos A., Letarte M. Biochemical characterization of the 44G4 antigen from the HOON pre-B leukemic cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1934–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougos A., Letarte M. Identification of a human endothelial cell antigen with monoclonal antibody 44G4 produced against a pre-B leukemic cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1925–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougos A., St Jacques S., Greaves A., O'Connell P. J., d'Apice A. J., Bühring H. J., Bernabeu C., van Mourik J. A., Letarte M. Identification of distinct epitopes of endoglin, an RGD-containing glycoprotein of endothelial cells, leukemic cells, and syncytiotrophoblasts. Int Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(1):83–92. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Cheifetz S., Doody J., Andres J. L., Lane W. S., Massagué J. Structure and expression of the membrane proteoglycan betaglycan, a component of the TGF-beta receptor system. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio M., Pinto A., Carbone A., Zagonel V., Gloghini A., Marotta G., Cirillo D., Colombatti A., Ferrara F., Del Vecchio L. Differential expression of CD54/intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in myeloid leukemias and in lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Identification of receptors for type-beta transforming growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:174–195. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morén A., Ichijo H., Miyazono K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human and porcine transforming growth factor-beta type III receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):356–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush E. J., Letarte M. Identification of several cell surface proteins of non-T, non-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia by using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1276–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. A., McNutt N. S., Prieto V. G., Albino A. P. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 2 in malignant melanoma correlates with the depth of tumor invasion. Implications for tumor progression. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jul;145(1):97–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck U., Bossler A., Graeven U., Fox F. E., Nowell P. C., Knabbe C., Kari C. Transforming growth factor beta production and responsiveness in normal human melanocytes and melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 15;54(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck U. Growth factor independence and growth regulatory pathways in human melanoma development. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00665954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck U., Herlyn M., Menssen H. D., Furlanetto R. W., Koprowsk H. Metastatic but not primary melanoma cell lines grow in vitro independently of exogenous growth factors. Int J Cancer. 1987 Nov 15;40(5):687–690. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih I. M., Herlyn M. Role of growth factors and their receptors in the development and progression of melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Feb;100(2 Suppl):196S–203S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temponi M., Kageshita T., Perosa F., Ono R., Okada H., Ferrone S. Purification of murine IgG monoclonal antibodies by precipitation with caprylic acid: comparison with other methods of purification. Hybridoma. 1989 Feb;8(1):85–95. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. F., Lin H. Y., Ng-Eaton E., Downward J., Lodish H. F., Weinberg R. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the TGF-beta type III receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal J. R., Willems H. W., Schalkwijk C. J., Ruiter D. J., de Waal R. M. A new 180-kDa dermal endothelial cell activation antigen: in vitro and in situ characteristics. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jan;100(1):27–34. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12349946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Ichijo H., Grimsby S., Morén A., ten Dijke P., Miyazono K. Endoglin forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1995–2001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Shaw A. R., Mak A., Letarte M. Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor complex of human pre-B leukemic cells. J Immunol. 1996 Jan 15;156(2):564–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig S. E., Shevach E. M. Production and properties of monoclonal antibodies to guinea pig Ia antigens. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:66–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Franzén P., Yamashita H., Ichijo H., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Serine/threonine kinase receptors. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1994;5(1):55–72. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]