Abstract
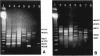
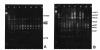
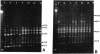
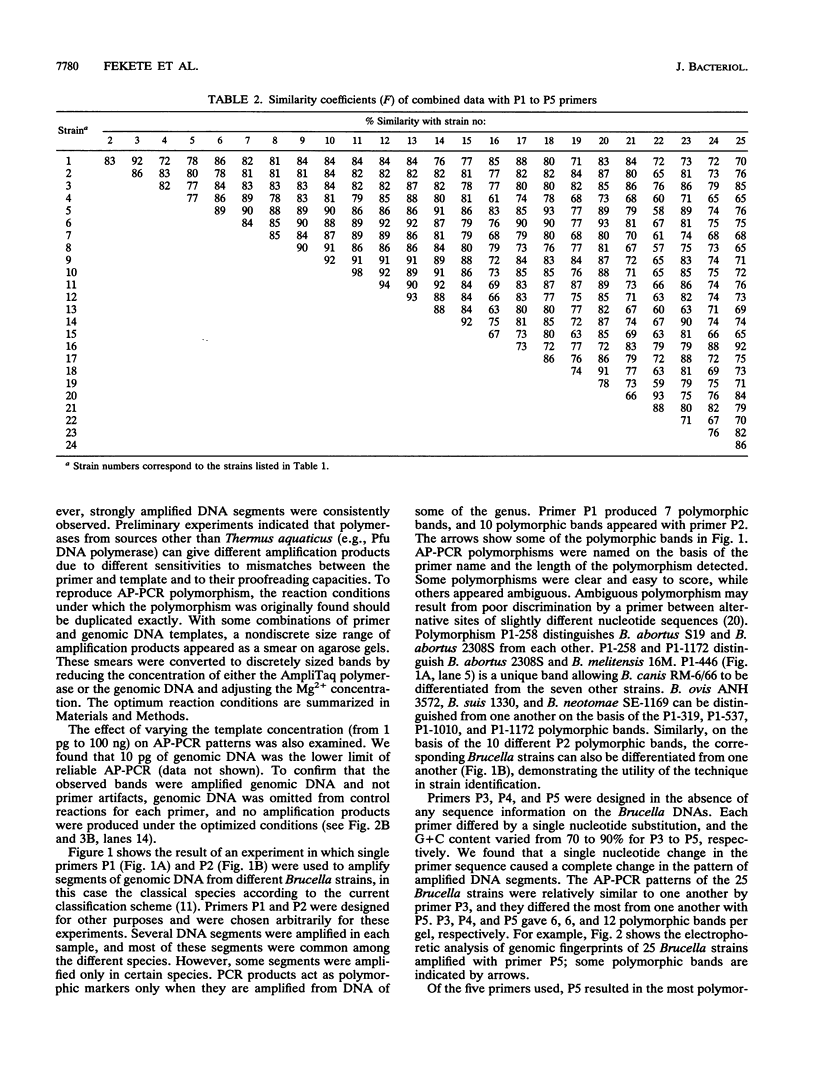
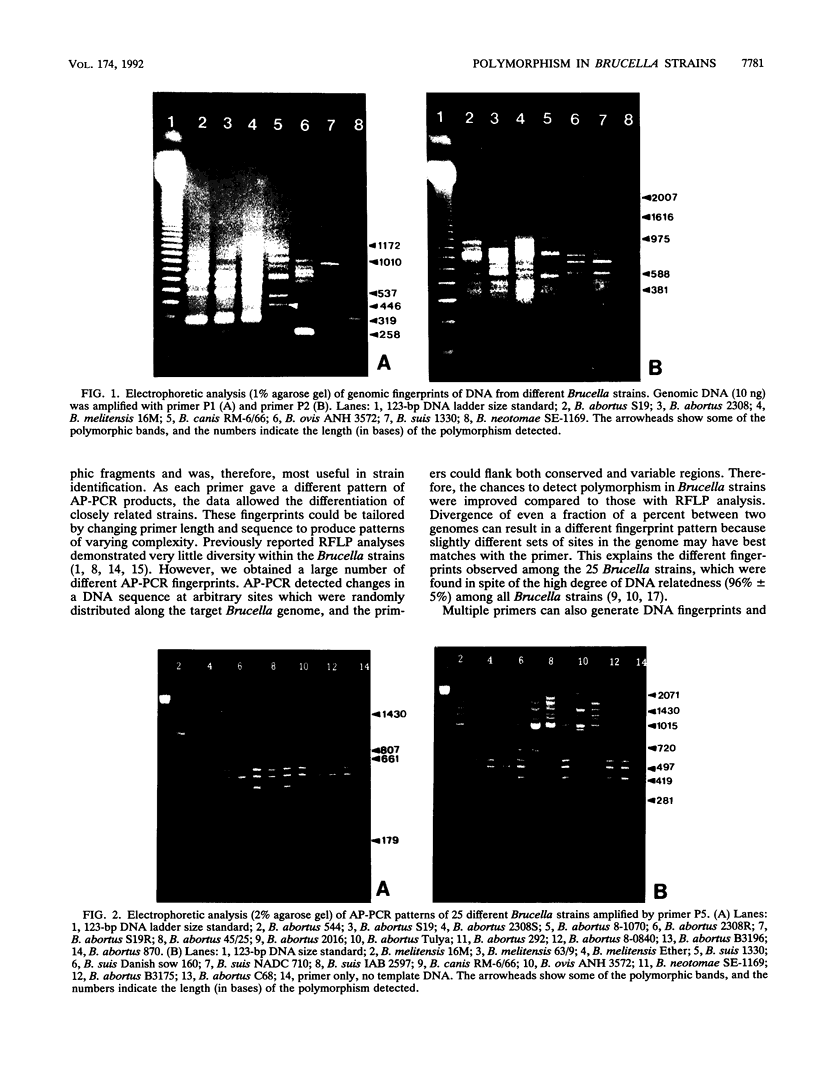
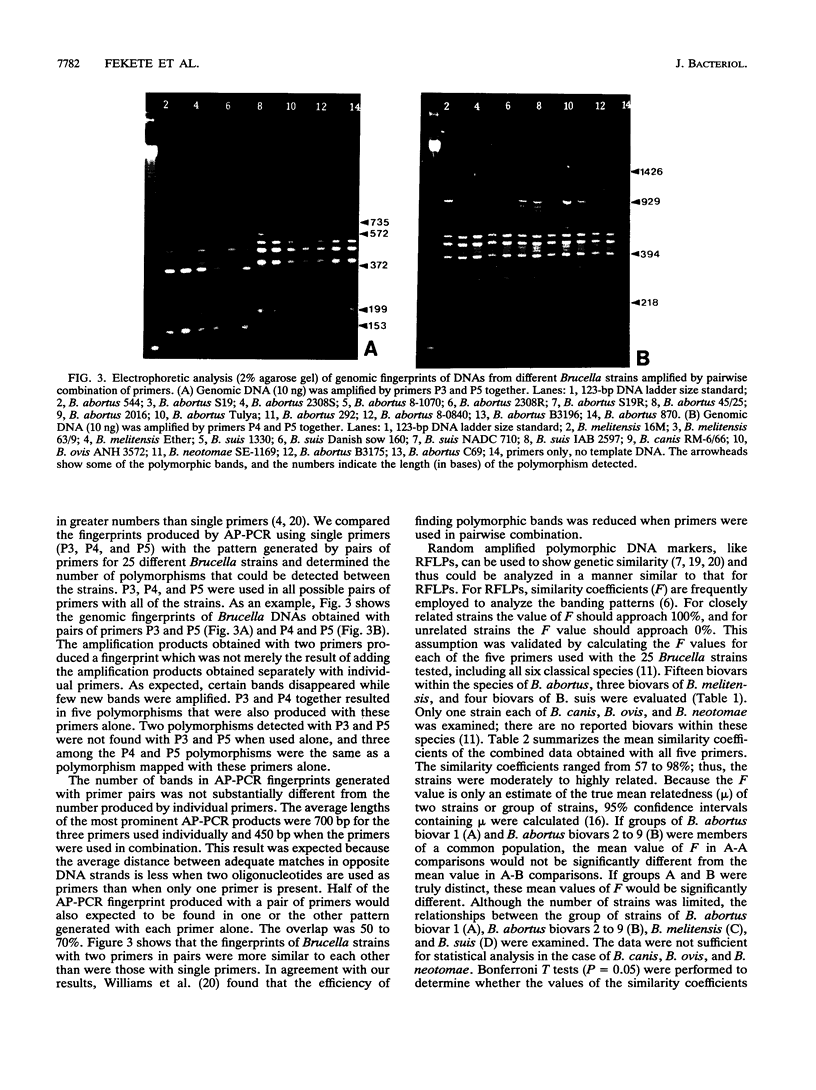
DNA heterogeneity among members of the genus Brucella was demonstrated with the arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction (AP-PCR). Simple, reproducible genomic fingerprints from DNA of 25 different Brucella strains were generated with five arbitrarily chosen primers, alone and in pairs, with the PCR. Reaction conditions were optimized for each primer. Several DNA segments were amplified in each sample with all of the primers. PCR products that are not shared among all strains act as polymorphic markers. Polymorphism was apparent for each primer. The Brucella strains can be distinguished according to the banding patterns of their amplified DNA on agarose gels, and the differences can be diagnostic of specific strains. To determine genetic relatedness among the Brucella strains, similarity coefficients were calculated. Statistical analysis of the similarity coefficients revealed the degrees of relatedness among strains of the genus Brucella.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allardet-Servent A., Bourg G., Ramuz M., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G. DNA polymorphism in strains of the genus Brucella. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4603–4607. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4603-4607.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. J., Bills M. M., Egerton J. R., Mattick J. S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding the structural subunit of Bacteroides nodosus fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):748–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.748-754.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Bassam B. J., Gresshoff P. M. DNA amplification fingerprinting using very short arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jun;9(6):553–557. doi: 10.1038/nbt0691-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin P. H., Annis S. L. Rapid identification of genetic variation and pathotype of Leptosphaeria maculans by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2482–2486. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2482-2486.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Zehr E. S. Polymorphism in Brucella spp. due to highly repeated DNA. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6637–6640. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6637-6640.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer B. H., McCullough N. B. Homologies of deoxyribonucleic acids from Brucella ovis, canine abortion organisms, and other Brucella species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1783–1790. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1783-1790.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer B. H., McCullough N. B. Polynucleotide homologies of Brucella deoxyribonucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.444-448.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A. The use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in taxonomy of Brucella. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):231–237. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzny D. M., Ficht T. A., Templeton J. W., Adams L. G. DNA homology of Brucella abortus strains 19 and 2308. Am J Vet Res. 1989 May;50(5):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara M. J., Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Brucella ovis and other Brucella species. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Aug;10(5):425–429. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]