Abstract
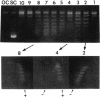
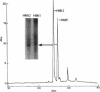
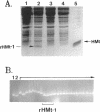
HMt, a histone-related protein, has been isolated and characterized from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum delta H. HMt preparations contain two polypeptides designated HMt1 and HMt2, encoded by the hmtA and hmtB genes, respectively, that have been cloned, sequenced, and expressed in Escherichia coli. HMt1 and HMt2 are predicted to contain 68 and 67 amino acid residues, respectively, and have calculated molecular masses of 7,275 and 7,141 Da, respectively. Aligning the amino acid sequences of HMt1 and HMt2 with the sequences of HMf1 and HMf2, the subunit polypeptides of HMf, a histone-related protein from the hyperthermophile Methanothermus fervidus, revealed that 40 amino acid residues (approximately 60%) are conserved in all four polypeptides. In pairwise comparisons, these four polypeptides are 66 to 84% identical. The sequences and locations of the TATA box promoter elements and ribosome binding sites are very similar upstream of the hmtA and hmtB genes in M. thermoautotrophicum and upstream of the hmfA and hmfB genes in M. fervidus. HMt binding compacted linear pUC19 DNA molecules in vitro and therefore increased their electrophoretic mobilities through agarose gels. At protein/DNA mass ratios of < 0.2:1, HMt binding caused an increase in the overall negative superhelicity of relaxed, circular DNA molecules, but at HMt/DNA mass ratios of > 0.2:1, positive supercoils were introduced into these molecules. HMt and HMf are indistinguishable in terms of their abilities to compact and constrain DNA molecules in positive toroidal supercoils in vitro. Histone-related proteins with these properties are therefore not limited to reverse gyrase-containing hyperthermophilic species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokranz M., Bäumner G., Allmansberger R., Ankel-Fuchs D., Klein A. Cloning and characterization of the methyl coenzyme M reductase genes from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):568–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.568-577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Holy A. Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Daniels C. J., Reeve J. N. Gene structure, organization, and expression in archaebacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(4):287–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Nucleosomes: regulators of transcription. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):395–400. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90299-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner W., Frey G., Thomm M. Control regions of an archaeal gene. A TATA box and an initiator element promote cell-free transcription of the tRNA(Val) gene of Methanococcus vannielii. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90492-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. T., Sandman K., Reeve J. N., Griffith J. D. HMf, a histone-related protein from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanothermus fervidus, binds preferentially to DNA containing phased tracts of adenines. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7864–7867. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7864-7867.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave D. R., Sandman K. M., Reeve J. N. DNA binding by the archaeal histone HMf results in positive supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10397–10401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Beckler G. S., Cram D. S., Hamilton P. T., Brown J. W., Krzycki J. A., Kolodziej A. F., Alex L., Orme-Johnson W. H., Walsh C. T. A hydrogenase-linked gene in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum strain delta H encodes a polyferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3031–3035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman K., Krzycki J. A., Dobrinski B., Lurz R., Reeve J. N. HMf, a DNA-binding protein isolated from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanothermus fervidus, is most closely related to histones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5788–5791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):387–389. doi: 10.1038/343387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Nucleosome positioning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 28;1130(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Sandman K., Frey G., Koller G., Reeve J. N. Transcription in vivo and in vitro of the histone-encoding gene hmfB from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanothermus fervidus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3508–3513. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3508-3513.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil C. F., Cram D. S., Sherf B. A., Reeve J. N. Structure and comparative analysis of the genes encoding component C of methyl coenzyme M reductase in the extremely thermophilic archaebacterium Methanothermus fervidus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4718–4726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4718-4726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]