Abstract
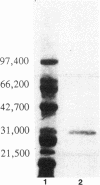
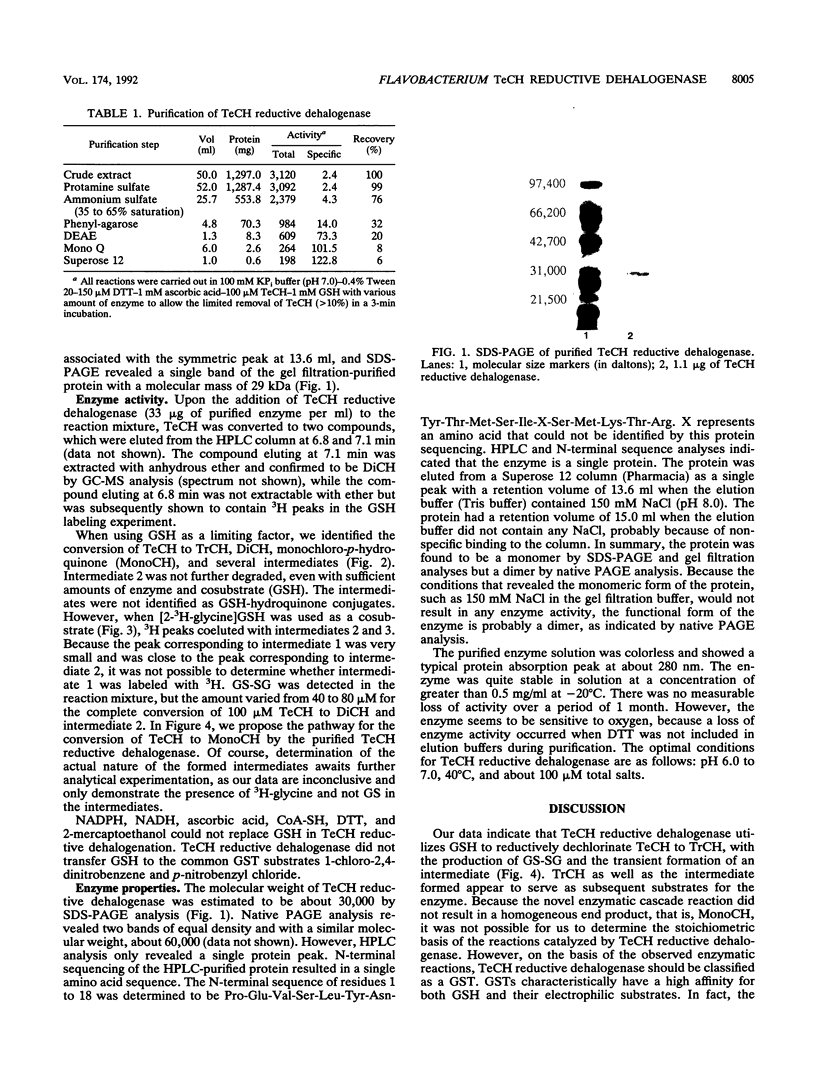
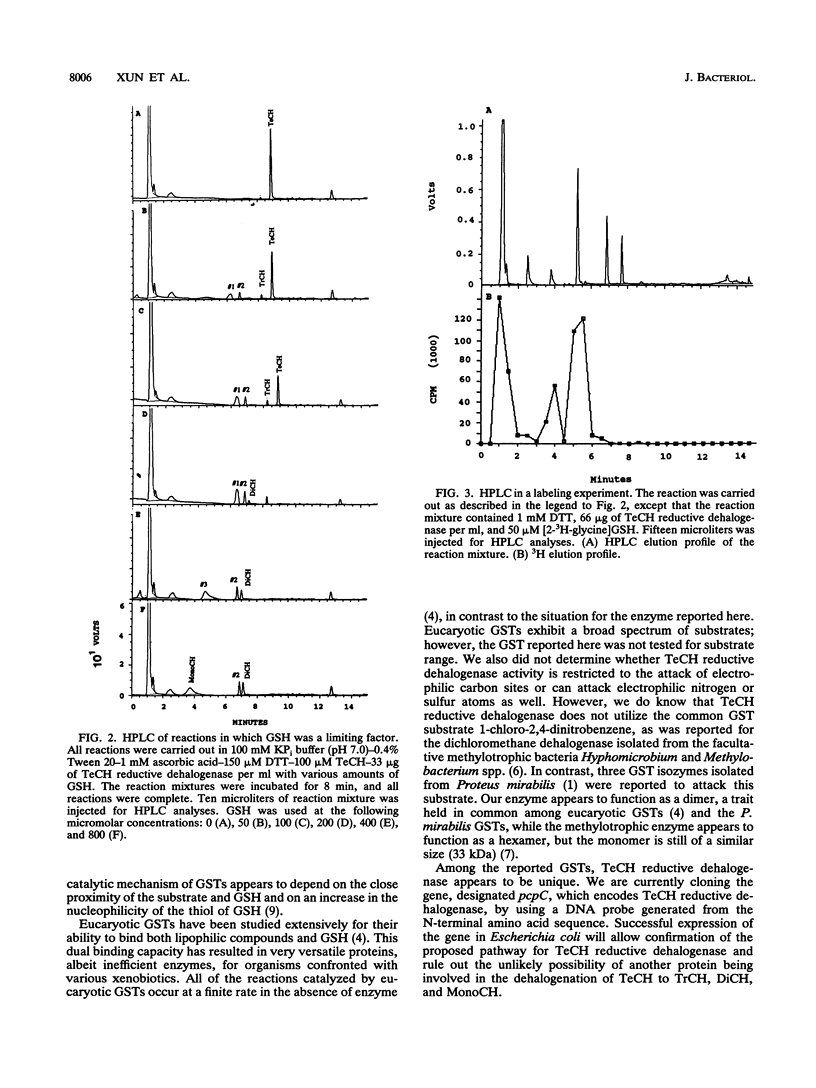
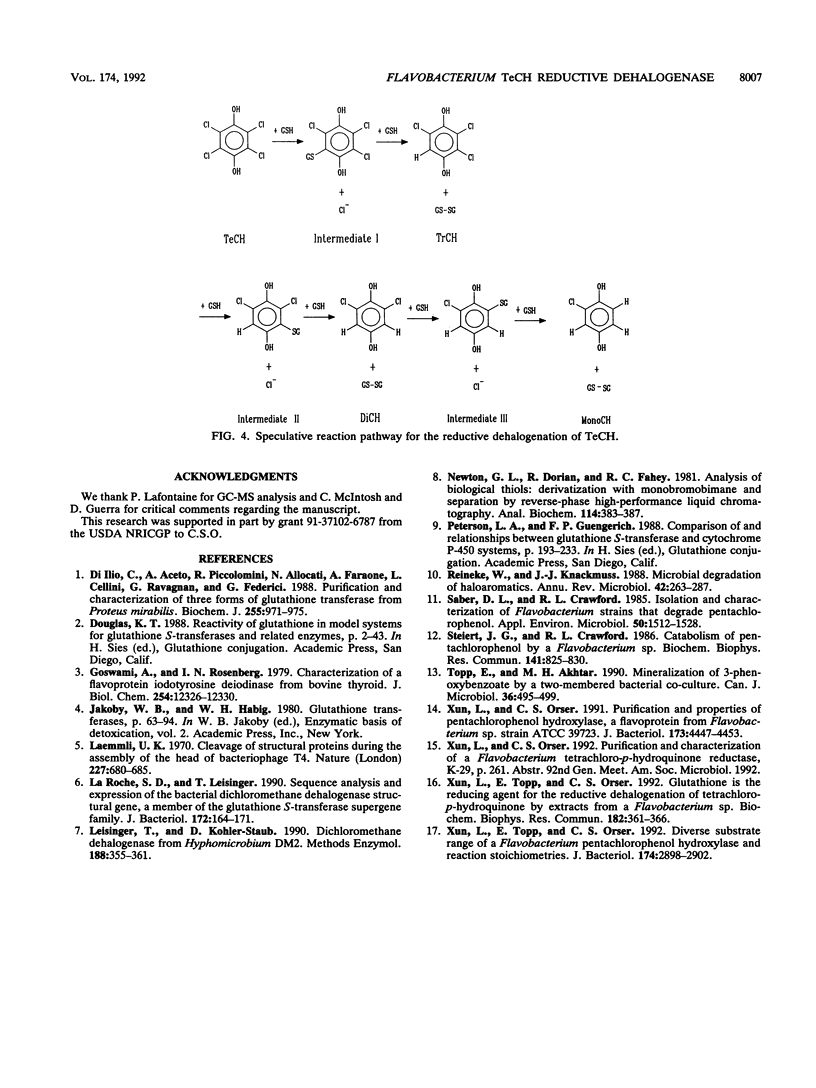
Tetrachloro-p-hydroquinone (TeCH) is the first intermediate in pentachlorophenol (PCP) degradation by Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723. We previously purified a PCP hydroxylase that oxidized PCP to TeCH. Subsequently, we identified the reductive dehalogenation of TeCH to 2,3,6-trichloro-p-hydroquinone and then to 2,6-dichloro-p-hydroquinone in a cell extract with the reduced form of glutathione as the reducing agent under anaerobic conditions. Here we report the purification of a TeCH reductive dehalogenase that reductively dehalogenated TeCH to trichlorohydroquinone and then to dichlorohydroquinone. The enzyme was purified by protamine sulfate treatment, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and phenyl-agarose, anion-exchange, and gel filtration column chromatographies. As determined by gel filtration and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analyses, the protein has a molecular weight of about 30,000; nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis suggests that the native enzyme exists as a dimer. The enzyme used glutathione but not NADPH, NADH, dithiothreitol, or ascorbic acid as the reducing agent. The optimal pH was close to neutral.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Di Ilio C., Aceto A., Piccolomini R., Allocati N., Faraone A., Cellini L., Ravagnan G., Federici G. Purification and characterization of three forms of glutathione transferase from Proteus mirabilis. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):971–975. doi: 10.1042/bj2550971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami A., Rosenberg I. N. Characterization of a flavoprotein iodotyrosine deiodinase from bovine thyroid. Flavin nucleotide binding and oxidation-reduction properties. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12326–12330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Roche S. D., Leisinger T. Sequence analysis and expression of the bacterial dichloromethane dehalogenase structural gene, a member of the glutathione S-transferase supergene family. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.164-171.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton G. L., Dorian R., Fahey R. C. Analysis of biological thiols: derivatization with monobromobimane and separation by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Microbial degradation of haloaromatics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber D. L., Crawford R. L. Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1512-1518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Crawford R. L. Catabolism of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Purification and properties of pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, a flavoprotein from Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4447–4453. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4447-4453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Topp E., Orser C. S. Diverse substrate range of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol hydroxylase and reaction stoichiometries. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2898–2902. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2898-2902.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Topp E., Orser C. S. Glutathione is the reducing agent for the reductive dehalogenation of tetrachloro-p-hydroquinone by extracts from a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 15;182(1):361–366. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]