Abstract
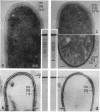
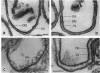
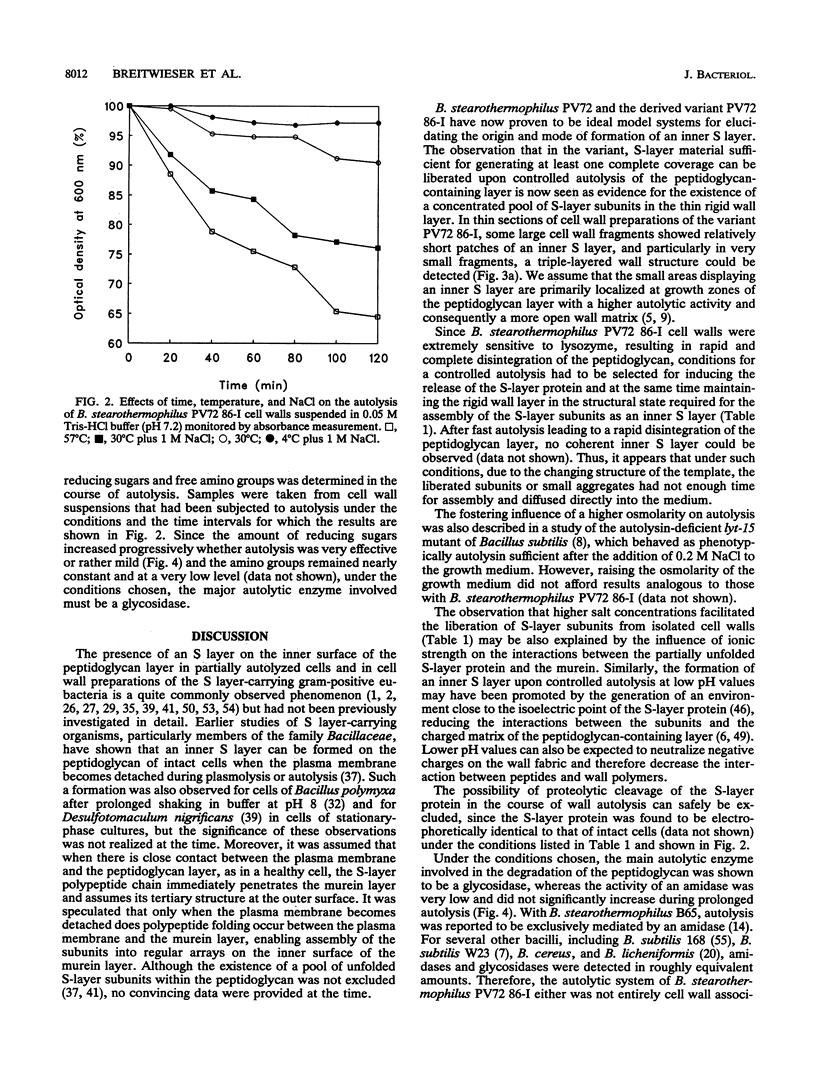
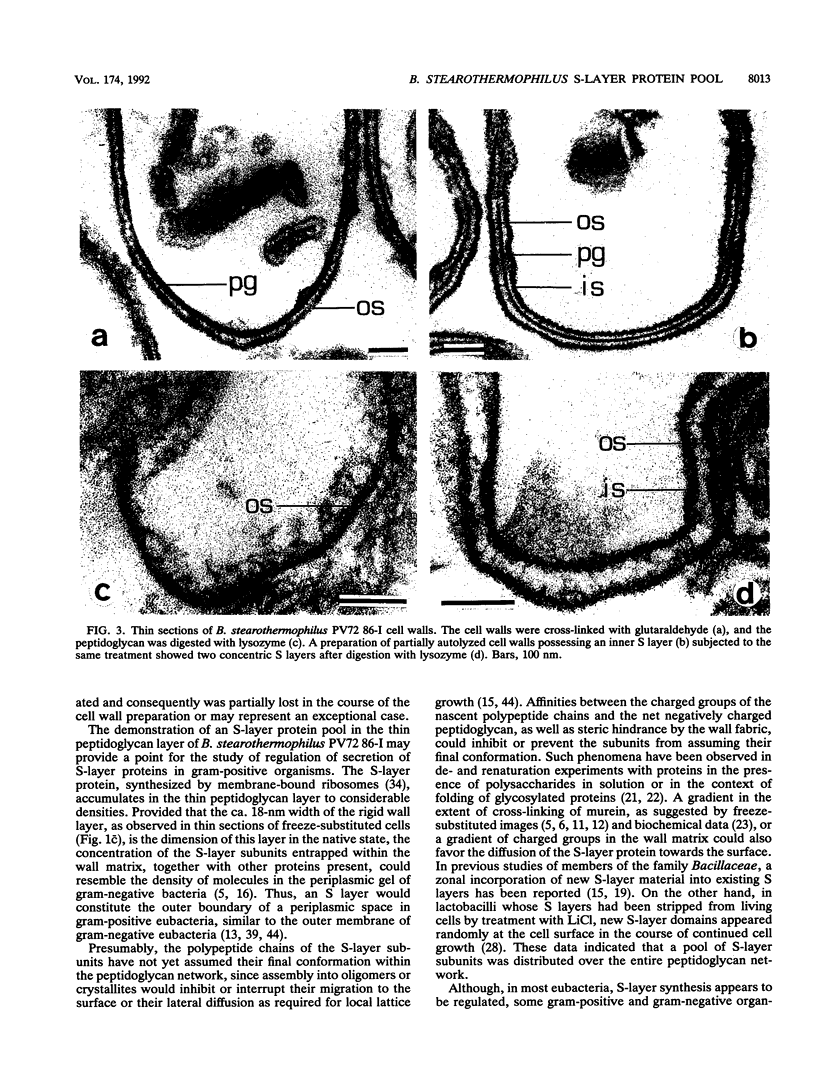
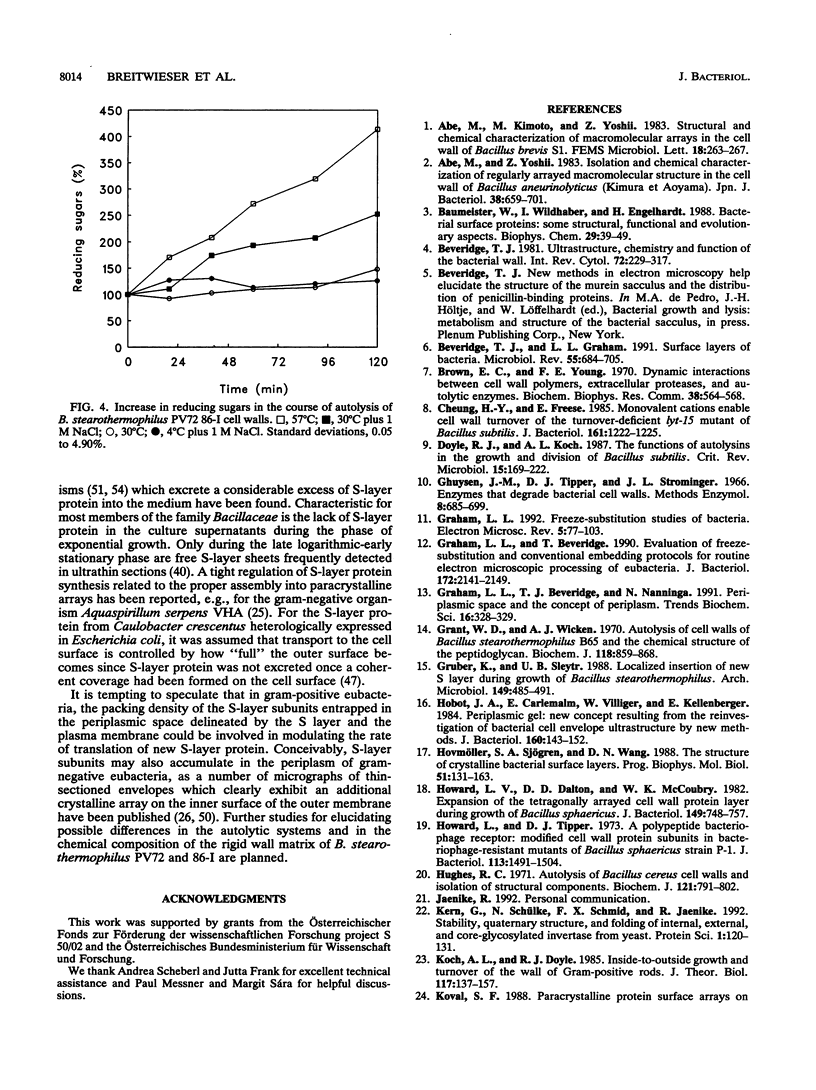
Intact cells of Bacillus stearothermophilus PV72 revealed, after conventional thin-sectioning procedures, the typical cell wall profile of S-layer-carrying gram-positive eubacteria consisting of a ca. 10-nm-thick peptidoglycan-containing layer and a ca. 10-nm-thick S layer. Cell wall preparations obtained by breaking the cells and removing the cytoplasmic membrane by treatment with Triton X-100 revealed a triple-layer structure, with an additional S layer on the inner surface of the peptidoglycan. This profile is characteristic for cell wall preparations of many S-layer-carrying gram-positive eubacteria. Among several variants of strain PV72 obtained upon single colony isolation, we investigated the variant PV72 86-I, which does not exhibit an inner S layer on isolated cell walls but instead possesses a profile identical to that observed for intact cells. In the course of a controlled mild autolysis of isolated cell walls, S-layer subunits were released from the peptidoglycan of the variant and assembled into an additional S layer on the inner surface of the walls, leading to a three-layer cell wall profile as observed for cell wall preparations of the parent strain. In comparison to conventionally processed bacteria, freeze-substituted cells of strain PV72 and the variant strain revealed in thin sections a ca. 18-nm-wide electron-dense peptidoglycan-containing layer closely associated with the S layer. The demonstration of a pool of S-layer subunits in such a thin peptidoglycan layer in an amount at least sufficient for generating one coherent lattice on the cell surface indicated that the subunits must have occupied much of the free space in the wall fabric of both the parent strain and the variant. It can even be speculated that the rate of synthesis and translation of the S-layer protein is influenced by the packing density of the S-layer subunits in the periplasm of the cell wall delineated by the outer S layer and the cytoplasmic membrane. Our data indicate that the matrix of the rigid wall layer inhibits the assembly of the S-layer subunits which are in transit to the outside.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumeister W., Wildhaber I., Engelhardt H. Bacterial surface proteins. Some structural, functional and evolutionary aspects. Biophys Chem. 1988 Feb;29(1-2):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)87023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Graham L. L. Surface layers of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Dec;55(4):684–705. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.4.684-705.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. Ultrastructure, chemistry, and function of the bacterial wall. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;72:229–317. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Young F. E. Dynamic interactions between cell wall polymers, extracellular proteases and autolytic enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):564–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. Y., Freese E. Monovalent cations enable cell wall turnover of the turnover-deficient lyt-15 mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1222–1225. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1222-1225.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Koch A. L. The functions of autolysins in the growth and division of Bacillus subtilis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(2):169–222. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaubert A. M., Sleytr U. B. Analysis of regular arrays of subunits on bacterial surfaces: evidence for a dynamic process of assembly. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jan;50(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J. Evaluation of freeze-substitution and conventional embedding protocols for routine electron microscopic processing of eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2141–2149. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2141-2149.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J., Nanninga N. Periplasmic space and the concept of the periplasm. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Sep;16(9):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90135-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L. Freeze-substitution studies of bacteria. Electron Microsc Rev. 1992;5(1):77–103. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(92)90006-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. D., Wicken A. J. Autolysis of cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus B65 and the chemical structure of the peptidoglycan. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):859–868. doi: 10.1042/bj1180859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber K., Sleytr U. B. Localized insertion of new S-layer during growth of Bacillus stearothermophilus strains. Arch Microbiol. 1988;149(6):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00446749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmöller S., Sjögren A., Wang D. N. The structure of crystalline bacterial surface layers. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):131–163. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Dalton D. D., McCoubrey W. K., Jr Expansion of the tetragonally arrayed cell wall protein layer during growth of Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):748–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.748-757.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L., Tipper D. J. A polypeptide bacteriophage receptor: modified cell wall protein subunits in bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Bacillus sphaericus strain P-1. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1491–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1491-1504.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. Autolysis of Bacillus cereus cell walls and isolation of structural components. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):791–802. doi: 10.1042/bj1210791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern G., Schülke N., Schmid F. X., Jaenicke R. Stability, quaternary structure, and folding of internal, external, and core-glycosylated invertase from yeast. Protein Sci. 1992 Jan;1(1):120–131. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L., Doyle R. J. Inside-to-outside growth and turnover of the wall of gram-positive rods. J Theor Biol. 1985 Nov 7;117(1):137–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., Rousseau M., van Heijenoort J. Structure of the cell wall of Bacillus species C.I.P. 76-111. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):153–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer F., Lurz R., Schoberth S. Electron microscopic investigation of the hydrogen-oxidizing acetate-forming anaerobic bacterium Acetobacterium woodii. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Nov 18;115(2):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00406376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner P., Sleytr U. B. Crystalline bacterial cell-surface layers. Adv Microb Physiol. 1992;33:213–275. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Murray R. G. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1949–1965. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1949-1965.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Glauert A. M. Ultrastructure of the cell walls of two closely related clostridia that possess different regular arrays of surface subunits. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):869–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.869-882.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B. Regular arrays of macromolecules on bacterial cell walls: structure, chemistry, assembly, and function. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;53:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Sára M., Küpcü Z., Messner P. Structural and chemical characterization of S-layers of selected strains of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Desulfotomaculum nigrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1986 Oct;146(1):19–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00690152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U., Adam H., Klaushofer H. Die Feinstruktur der Zellwand und Cytoplasmamembran von Clostridium nigrificans, dargestellt mit Hilfe der Gefrierätz- und Ultradünnschnittechnik. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;66(1):40–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Agabian N. Cell surface patterning and morphogenesis: biogenesis of a periodic surface array during Caulobacter development. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):41–49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld E. M., Beveridge T. J., Doyle R. J. Discontinuity of charge on cell wall poles of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Sep;31(9):875–877. doi: 10.1139/m85-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sára M., Sleytr U. B. Charge distribution on the S layer of Bacillus stearothermophilus NRS 1536/3c and importance of charged groups for morphogenesis and function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2804–2809. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2804-2809.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Oliver R. C., Glauert A. M. Synthesis and turnover of the regularly arranged surface protein of Acinetobacter sp. relative to the other components of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):440–450. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.440-450.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Morphological alterations of cell wall concomitant with protein release in a protein-producing bacterium, Bacillus brevis 47. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):322–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.322-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Autolytic enzyme associated with cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3462–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]