Abstract
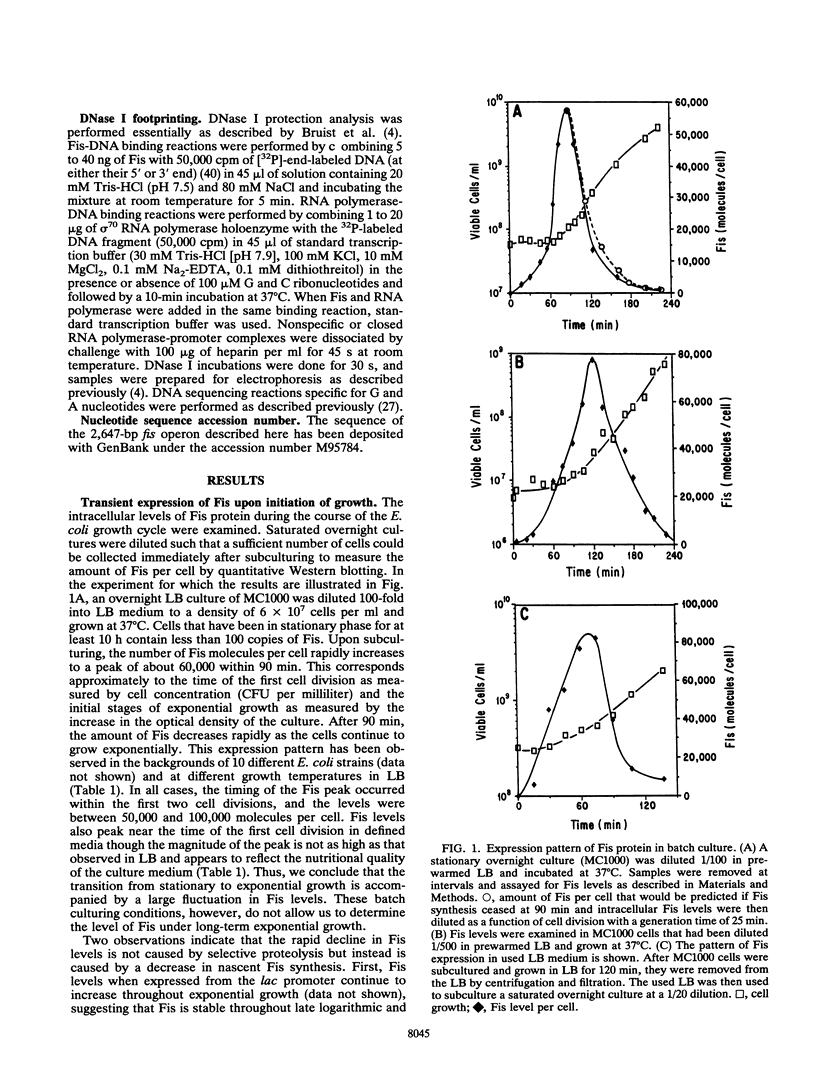
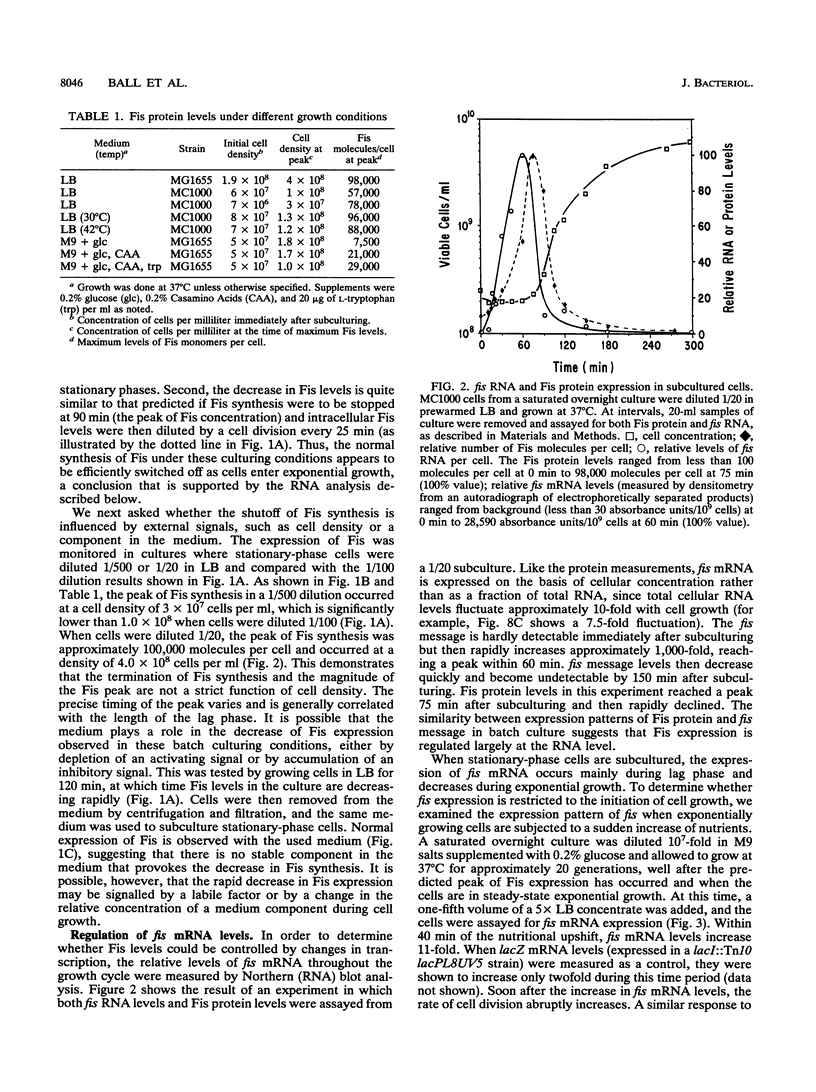
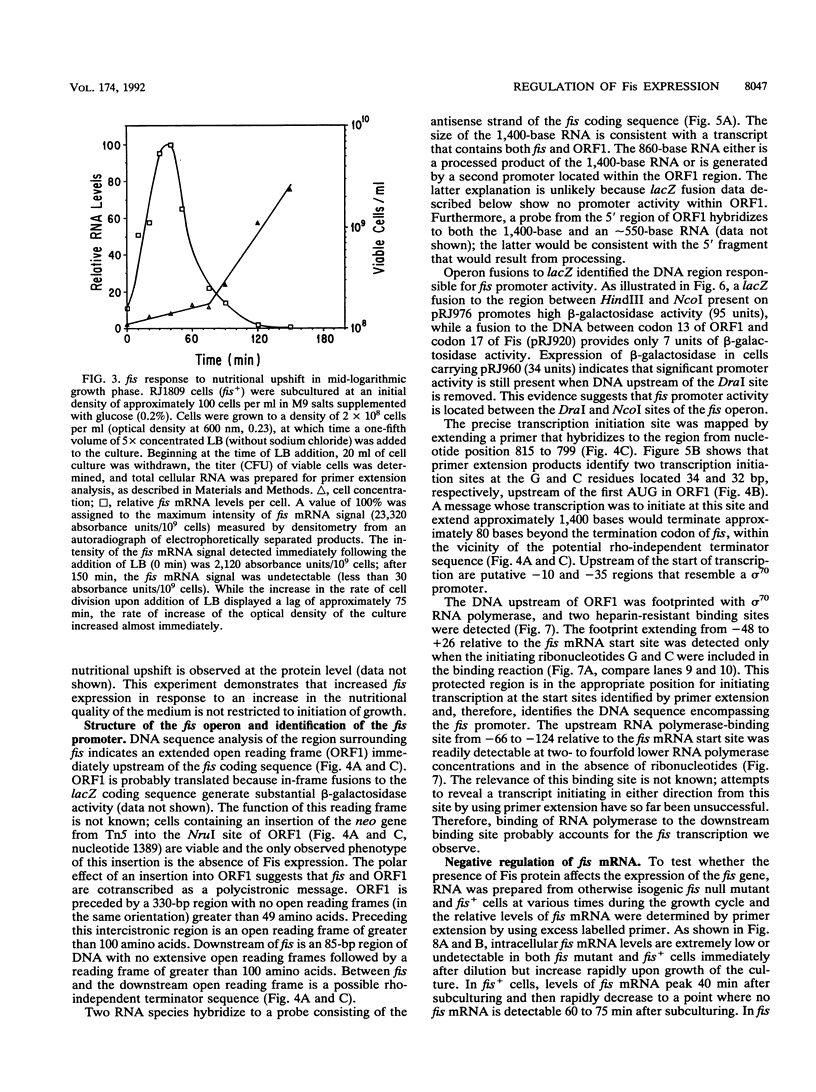
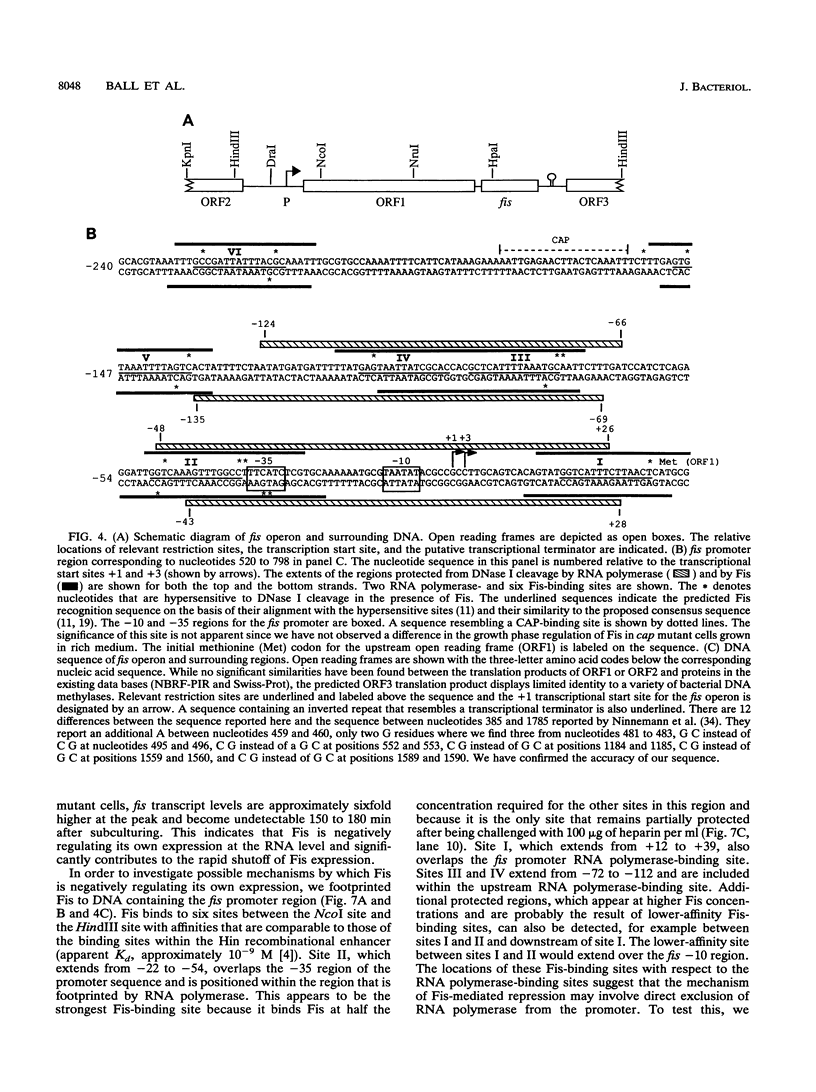
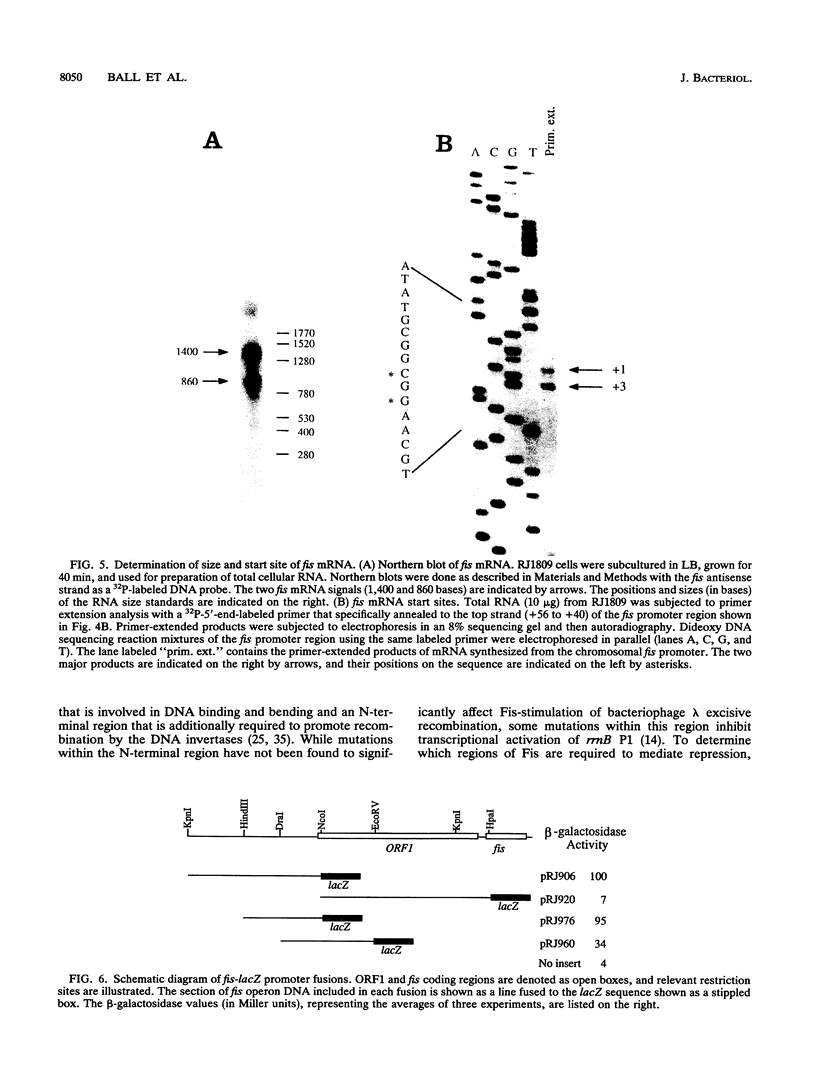
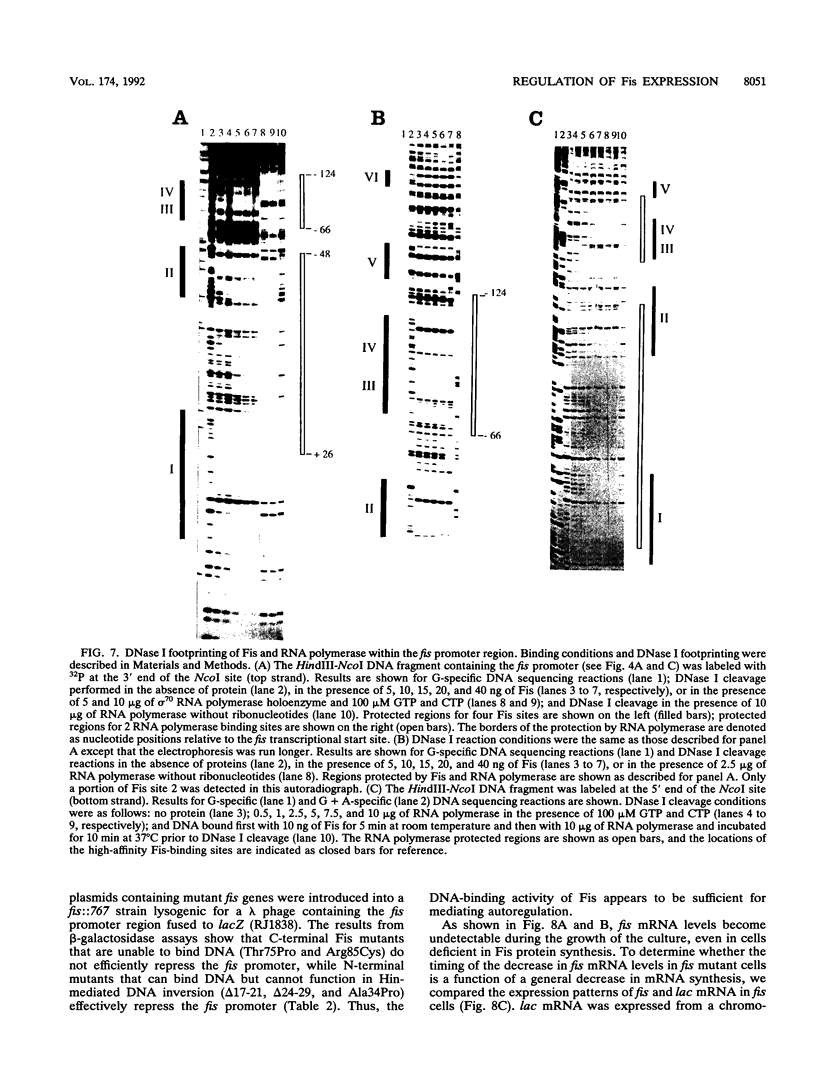
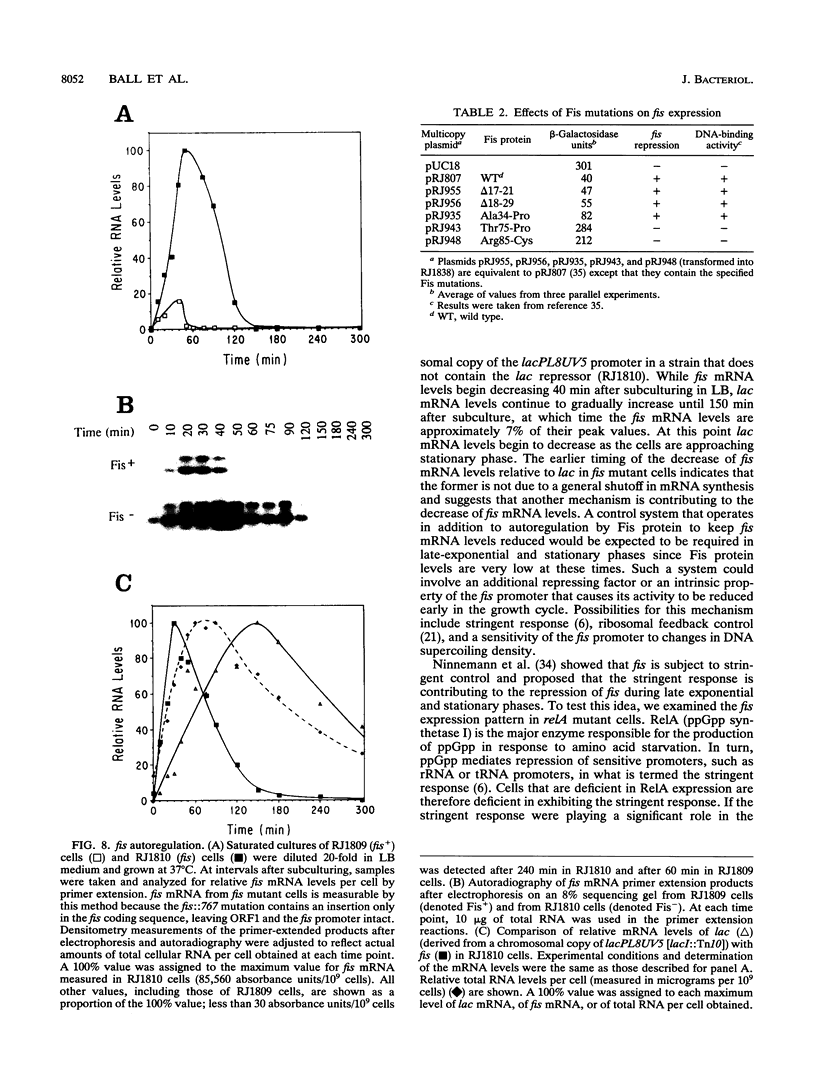
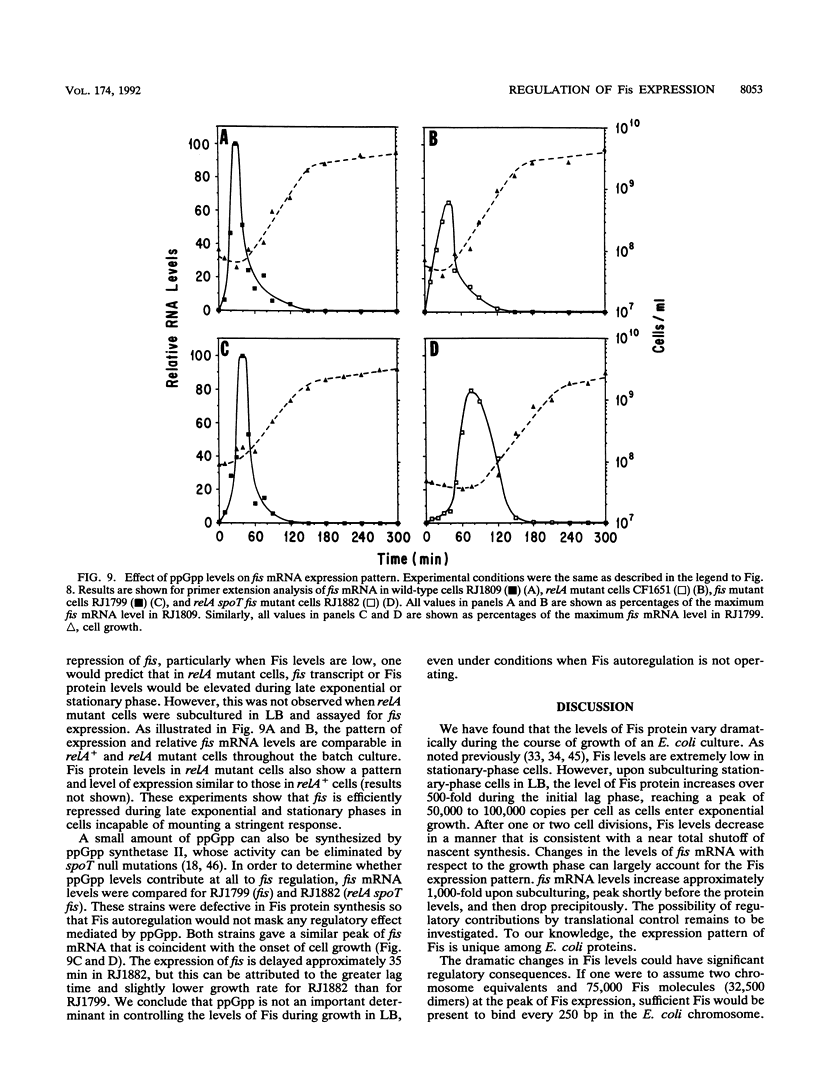
Fis is a small basic DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli that was identified because of its role in site-specific DNA recombination reactions. Recent evidence indicates that Fis also participates in essential cell processes such as rRNA and tRNA transcription and chromosomal DNA replication. In this report, we show that Fis levels vary dramatically during the course of cell growth and in response to changing environmental conditions. When stationary-phase cells are subcultured into a rich medium, Fis levels increase from less than 100 to over 50,000 copies per cell prior to the first cell division. As cells enter exponential growth, nascent synthesis is largely shut off, and intracellular Fis levels decrease as a function of cell division. Fis synthesis also transiently increases when exponentially growing cells are shifted to a richer medium. The magnitude of the peak of Fis synthesis appears to reflect the extent of the nutritional upshift. fis mRNA levels closely resemble the protein expression pattern, suggesting that regulation occurs largely at the transcriptional level. Two RNA polymerase-binding sites and at least six high-affinity Fis-binding sites are present in the fis promoter region. We show that expression of the fis operon is negatively regulated by Fis in vivo and that purified Fis can prevent stable complex formation by RNA polymerase at the fis promoter in vitro. However, autoregulation only partially accounts for the expression pattern of Fis. We suggest that the fluctuations in Fis levels may serve as an early signal of a nutritional upshift and may be important in the physiological roles Fis plays in the cell.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball C. A., Johnson R. C. Efficient excision of phage lambda from the Escherichia coli chromosome requires the Fis protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4027–4031. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4027-4031.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball C. A., Johnson R. C. Multiple effects of Fis on integration and the control of lysogeny in phage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4032–4038. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4032-4038.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Glasgow A. C., Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Fis binding to the recombinational enhancer of the Hin DNA inversion system. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):762–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case C. C., Roels S. M., González J. E., Simons E. L., Simons R. W. Analysis of the promoters and transcripts involved in IS10 anti-sense RNA control. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Olsson C. L., Hershey J. W., Grunberg-Manago M., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Requirement for initiation factor IF2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., Ross W., Wild J., Gourse R. L. Involvement of Fis protein in replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):398–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.398-407.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel S. E., Johnson R. C. The Fis protein: it's not just for DNA inversion anymore. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3257–3265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Egan J. B., Roth A., Messer W. The FIS protein binds and bends the origin of chromosomal DNA replication, oriC, of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4167–4172. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., Bickle T. A. Purification and DNA-binding properties of FIS and Cin, two proteins required for the bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination system, cin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Traut R., Gold L. Extension inhibition analysis of translation initiation complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez V. J., Bremer H. Escherichia coli ppGpp synthetase II activity requires spoT. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5991–5999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner P., Arber W. Mutational analysis of a prokaryotic recombinational enhancer element with two functions. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):577–585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ball C. A., Pfeffer D., Simon M. I. Isolation of the gene encoding the Hin recombinational enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I. Host protein requirements for in vitro site-specific DNA inversion. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90878-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Kahmann R. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli host factor required for inversion of the G segment in bacteriophage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15673–15678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Ninnemann O., Fuss H., Kahmann R. The N-terminal part of the E.coli DNA binding protein FIS is essential for stimulating site-specific DNA inversion but is not required for specific DNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5915–5922. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Schreiber G., Aizenman E., Cashel M., Glaser G. Characterization of the relA1 mutation and a comparison of relA1 with new relA null alleles in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21146–21152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Vanet A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. The role of FIS in trans activation of stable RNA operons of E. coli. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):727–734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Verbeek H., Vijgenboom E., van Drunen C., Vanet A., Bosch L. FIS-dependent trans activation of stable RNA operons of Escherichia coli under various growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):921–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.921-929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninnemann O., Koch C., Kahmann R. The E.coli fis promoter is subject to stringent control and autoregulation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1075–1083. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuna R., Finkel S. E., Johnson R. C. Identification of two functional regions in Fis: the N-terminus is required to promote Hin-mediated DNA inversion but not lambda excision. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1593–1603. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B. More than just "histone-like" proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90438-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Koch C., Kahmann R., Landy A. Cellular factors couple recombination with growth phase: characterization of a new component in the lambda site-specific recombination pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Kalman M., Ikehara K., Zemel S., Glaser G., Cashel M. Residual guanosine 3',5'-bispyrophosphate synthetic activity of relA null mutants can be eliminated by spoT null mutations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5980–5990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan H. S., Finkel S. E., Feng J. A., Kaczor-Grzeskowiak M., Johnson R. C., Dickerson R. E. The molecular structure of wild-type and a mutant Fis protein: relationship between mutational changes and recombinational enhancer function or DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]