Abstract
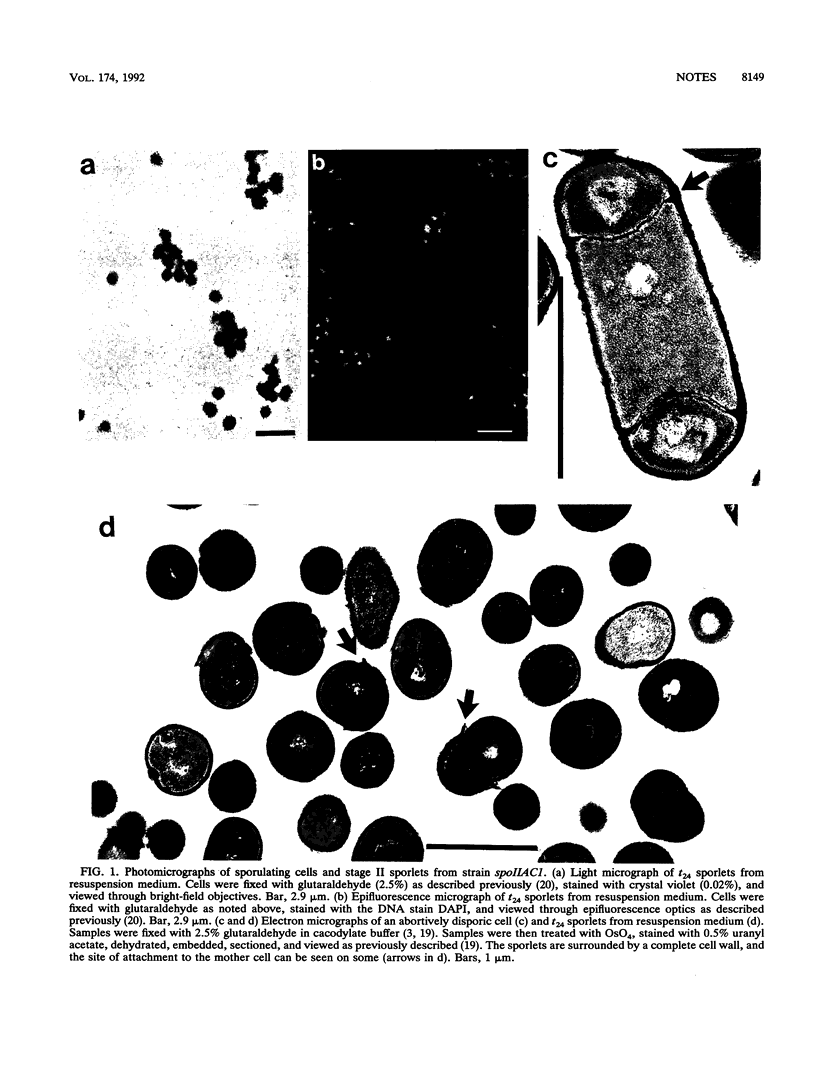
A number of abortively disporic spoII mutants of Bacillus subtilis released their forespore compartments (termed stage II sporlets) after mother cell lysis during sporulation in nutrient exhaustion or resuspension media. Stage II sporlets were viable and contained levels of ATP and a number of enzymes similar to those in cells 2 to 3 h after sporulation. However, stage II sporlets carried out essentially no macromolecular synthesis, a result suggesting that they were in a quiescent state. The nucleoid of these quiescent stage II sporlets was significantly condensed relative to that in the original vegetative cells, as was previously found to take place 1 to 2 h after initiation of sporulation (B. Setlow, N. Magill, P. Febbroriello, L. Nakhimousky, D. E. Koppel, and P. Setlow, J. Bacteriol. 173:6270-6278, 1991). Stage II sporlets may be a useful model system for analysis of forespore properties early in stage II of sporulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brehm S. P., Le Hegarat F., Hoch J. A. Developmental modulation of deoxyribonucleic acid-binding proteins of Bacillus subtilis during sporulation stages. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1443–1450. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1443-1450.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancer B. N. Requirement for peptidoglycan synthesis during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):786–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.786-797.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi S. C., MacAlister T. J., Setlow B., Setlow P. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of small, acid-soluble spore proteins in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5963–5967. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5963-5967.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldrick S., Setlow P. Expression of a Bacillus megaterium sporulation-specific gene during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1459–1462. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1459-1462.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illing N., Errington J. Genetic regulation of morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis: roles of sigma E and sigma F in prespore engulfment. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3159-3169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Holt S. C., Haldenwang W. G. Effects of antibiotics on synthesis and persistence of sigma E in sporulating Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4616–4623. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4616-4623.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitto G. B., Lewis R. G. Purification and properties of tuna supernatant and mitochondrial malate dehydrogenases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micka B., Groch N., Heinemann U., Marahiel M. A. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis gene encoding the DNA-binding protein HBsu. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3191–3198. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3191-3198.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow P. Dramatic increase in negative superhelicity of plasmid DNA in the forespore compartment of sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.7-14.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Lundgren D. G. Multiple septation in variants of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1426–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1426-1431.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salti V., Le Hégarat F., Hirschbein L. Isolation and characterization of small heat-stable acid-soluble DNA-binding proteins from Bacillus subtilis nucleoids. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):581–590. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Salas J. L., Santiago-Lara M. L., Setlow B., Sussman M. D., Setlow P. Properties of Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus subtilis mutants which lack the protease that degrades small, acid-soluble proteins during spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):807–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.807-814.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Hand A. R., Setlow P. Synthesis of a Bacillus subtilis small, acid-soluble spore protein in Escherichia coli causes cell DNA to assume some characteristics of spore DNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1642–1653. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1642-1653.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Magill N., Febbroriello P., Nakhimovsky L., Koppel D. E., Setlow P. Condensation of the forespore nucleoid early in sporulation of Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6270–6278. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6270-6278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Protease and peptidase activities in growing and sporulating cells and dormant spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):642–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.642-649.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P., Setlow B., Setlow P. Levels of small molecules and enzymes in the mother cell compartment and the forespore of sporulating Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1130-1138.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring T. G., Wold F. The purification and characterization of Escherichia coli enolase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6797–6802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis ans operon, which codes for L-asparaginase and L-aspartase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3831–3845. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3831-3845.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagar E. A., Stephens R. S. Developmental-form-specific DNA-binding proteins in Chlamydia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1678–1684. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1678-1684.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites W. M., Kay D., Dawes I. W., Wood D. A., Warren S. C., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Correlation of biochemical events with morphological changes in asporogenous mutants. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1180667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN ABORTIVELY DISPORIC VARIANT OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:242–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.242-254.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]