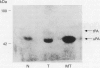
Abstract
The expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) was investigated in squamous cell carcinoma of the human larynx. For this purpose, tissue extracts from 25 matched samples of normal mucosa and neoplastic larynx were compared for the levels of uPA activity as evaluated by a chromogenic PA assay and sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) zymography. Also, uPA antigen was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 19 cases. The results demonstrate a significant increase in the levels of uPA activity and protein in tumour tissue extracts, more pronounced in tumours with lymph node metastases. Immunohistochemistry performed on 70 biopsies showed that uPA positivity is present both in neoplastic cells and in fibroblast-like cells and macrophages. However, depending on the histological grading and invasive capacity of the tumour, a pronounced intra- and intertumoral heterogeneity in uPA staining was observed. In situ hybridisation confirmed the presence of uPA mRNA in both tumour and stromal cells. The present study provides experimental evidence for a role of uPA in the invasive growth of human laryngeal carcinoma.
Full text
PDF

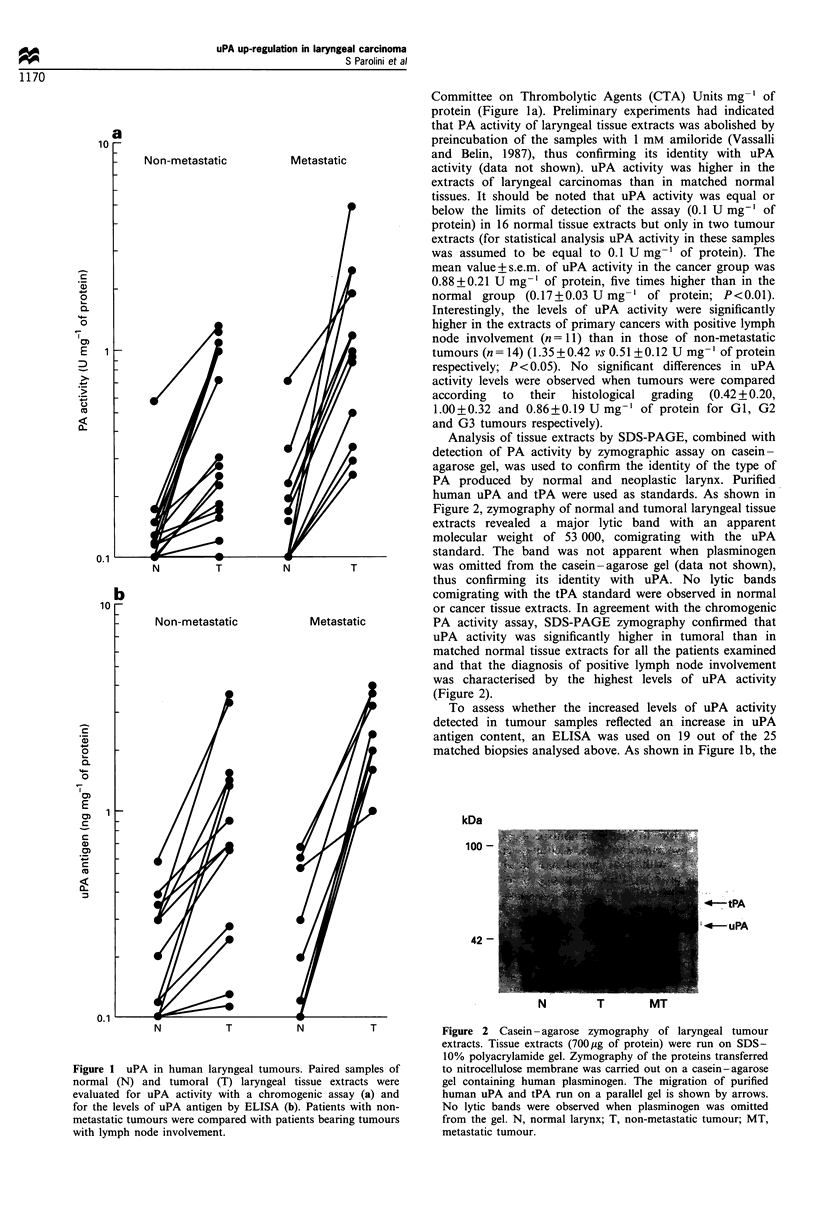




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonelli A. R., Nicolai P., Cappiello J., Peretti G., Molinari Tosatti M. P., Rosa D., Grigolato P. G., Favret M., Maroccolo D. Basement membrane components in normal, dysplastic, neoplastic laryngeal tissue and metastatic lymph nodes. Acta Otolaryngol. 1991;111(2):437–443. doi: 10.3109/00016489109137416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camiolo S. M., Markus G., Englander L. S., Siuta M. R., Hobika G. H., Kohga S. Plasminogen activator content and secretion in explants of neoplastic and benign human prostate tissues. Cancer Res. 1984 Jan;44(1):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camiolo S. M., Markus G., Evers J. L., Hobika G. H., DePasquale J. L., Beckley S., Grimaldi J. P. Plasminogen activator content of neoplastic and benign human prostate tissues; fibrin augmentation of an activator activity. Int J Cancer. 1981 Feb 15;27(2):191–198. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman G., Wang S. W., Nicolson G. L., el-Naggar A., Mazar A., Henkin J., Blasi F., Goepfert H., Boyd D. D. Regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression in squamous-cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Int J Cancer. 1993 Apr 22;54(1):73–80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombi M., Barlati S., Magdelenat H., Fiszer-Szafarz B. Relationship between multiple forms of plasminogen activator in human breast tumors and plasma and the presence of metastases in lymph nodes. Cancer Res. 1984 Jul;44(7):2971–2975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombi M., Moro L., Zoppi N., Barlati S. Quantitative evaluation of mRNAs by in situ hybridization and image analysis: principles and applications. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;12(7):629–636. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombi M., Moro L., Zoppi N., Ghinelli A., Barlati S. Altered fibronectin mRNA splicing in skin fibroblasts from Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients: in situ hybridization analysis. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Dec;15(12):1195–1206. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90091-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corasanti J. G., Celik C., Camiolo S. M., Mittelman A., Evers J. L., Barbasch A., Hobika G. H., Markus G. Plasminogen activator content of human colon tumors and normal mucosae: separation of enzymes and partial purification. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Aug;65(2):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R. Increased protease levels in transformed cells: a casein overlay assay for the detection of plasminogen activator production. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Christensen I. J., Rosenquist C., Brünner N., Mouridsen H. T., Danø K., Blichert-Toft M. High levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor PAI-1 in cytosolic extracts of breast carcinomas are associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2513–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasui Y., Marutsuka K., Suzumiya J., Kitada S., Osada Y., Sumiyoshi A. The content of urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen as a prognostic factor in urinary bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 1992 Apr 1;50(6):871–873. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasui Y., Suzumiya J., Marutsuka K., Sumiyoshi A., Hashida S., Ishikawa E. Comparative study of plasminogen activators in cancers and normal mucosae of human urinary bladder. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):1067–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Law L. W., Corti A., Appella E., Blasi F. Modulation of metastatic potential by cell surface urokinase of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1270–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohga S., Harvey S. R., Weaver R. M., Markus G. Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1787–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Pyke C., Lund L. R., Andreasen P. A., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 in Lewis lung carcinoma. Histochemistry. 1990;93(6):559–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00272198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Takita H., Camiolo S. M., Corasanti J. G., Evers J. L., Hobika G. H. Content and characterization of plasminogen activators in human lung tumors and normal lung tissue. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):841–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):161–195. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro L., Colombi M., Crespi S., Di Lernia R., Barlati S. Study of fibronectin expression in tumour cells by dot-blot and in situ hybridization: quantitative evaluation by image analysis. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1990 Aug;14(8):701–715. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(90)91189-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro L., Colombi M., Molinari Tosatti M. P., Barlati S. Study of fibronectin and mRNA in human laryngeal and ectocervical carcinomas by in situ hybridization and image analysis. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jul 9;51(5):692–697. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman T., Stephens R. W., Salonen E. M., Timmusk T., Vaheri A. Induction of morphological differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells is accompanied by induction of tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Jul;23(3):274–281. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino N., Aoki K., Tokura Y., Sakaguchi S., Takada Y., Takada A. The urokinase type of plasminogen activator in cancer of digestive tracts. Thromb Res. 1988 May 15;50(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. II. Mammalian fibroblast cultures transformed by DNA and RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):112–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Maier J. A., Ragnotti G. The mitogenic signaling pathway but not the plasminogen activator-inducing pathway of basic fibroblast growth factor is mediated through protein kinase C in fetal bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1877–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Belin D., Huarte J., Hirschel-Scholz S., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D. Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI115406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Busso N., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4043–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Jänicke F., Graeff H. Tumour-associated fibrinolysis: the prognostic relevance of plasminogen activators uPA and tPA in human breast cancer. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Dec;1(6):695–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Jänicke F., Moniwa N., Chucholowski N., Pache L., Graeff H. Tumor-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator: biological and clinical significance. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Jul;373(7):611–622. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim P. S., Stephens R. W., Fayle D. R., Doe W. F. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps: quantitative expression of active and proenzyme. Int J Cancer. 1988 Oct 15;42(4):483–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver L., Larsson L. I., Kielberg V., Nielsen L. S., Andresen P. B., Kristensen P., Danø K. Immunocytochemical localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in Lewis lung carcinoma. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):753–757. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura M., Kobayashi H., Kanayama N., Terao T. Clinical significance of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) in invasive cervical cancer of the uterus. Gynecol Oncol. 1992 Sep;46(3):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(92)90227-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiyoshi K., Baba S., Sakaguchi S., Urano T., Takada Y., Takada A. Increase in levels of plasminogen activator and type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in human breast cancer: possible roles in tumor progression and metastasis. Thromb Res. 1991 Jul 1;63(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiyoshi K., Serizawa K., Urano T., Takada Y., Takada A., Baba S. Plasminogen activator system in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1992 Feb 1;50(3):345–348. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney C. W., Satyaswaroop P. G., Mortel R. Plasminogen activator activity in human endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1985 Sep;22(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(85)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. L., Becker M. L., Hoal E. G., Dowdle E. B. Molecular species of plasminogen activators secreted by normal and neoplastic human cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Griffioen G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activators and tumor development in the human colon: activity levels in normal mucosa, adenomatous polyps, and adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4654–4657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]