Abstract
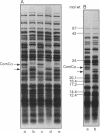
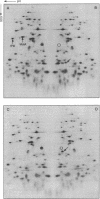
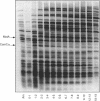
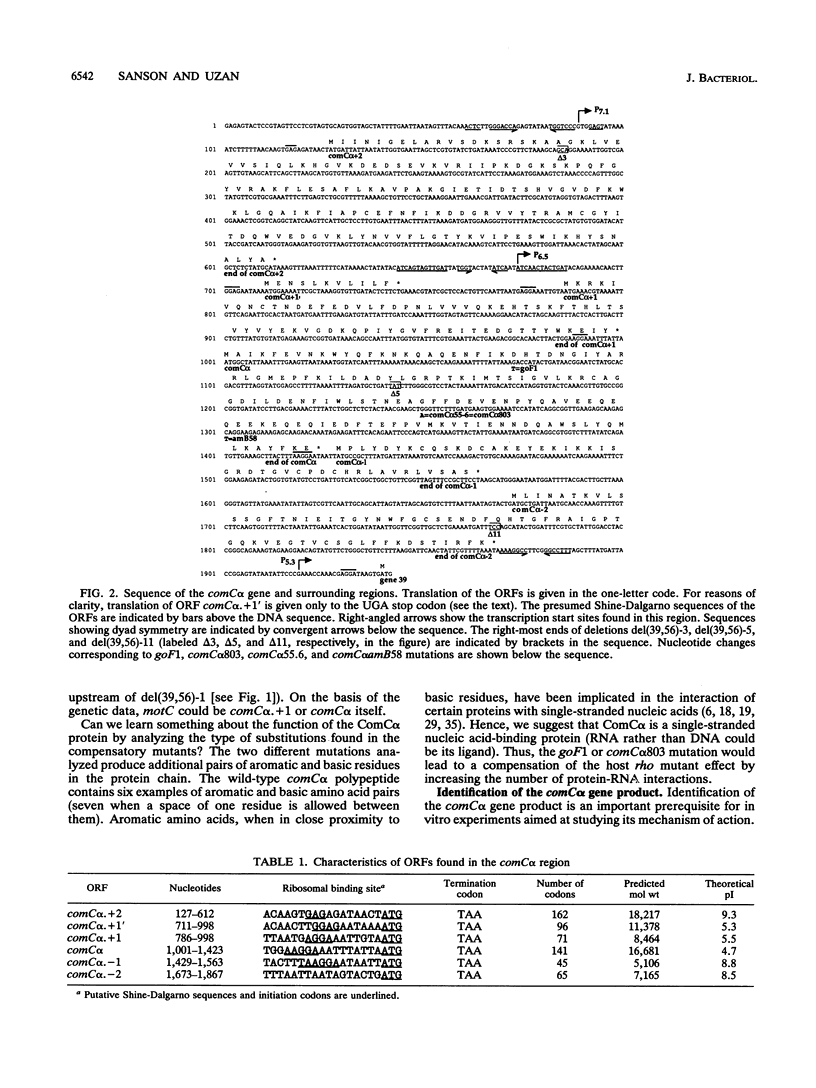
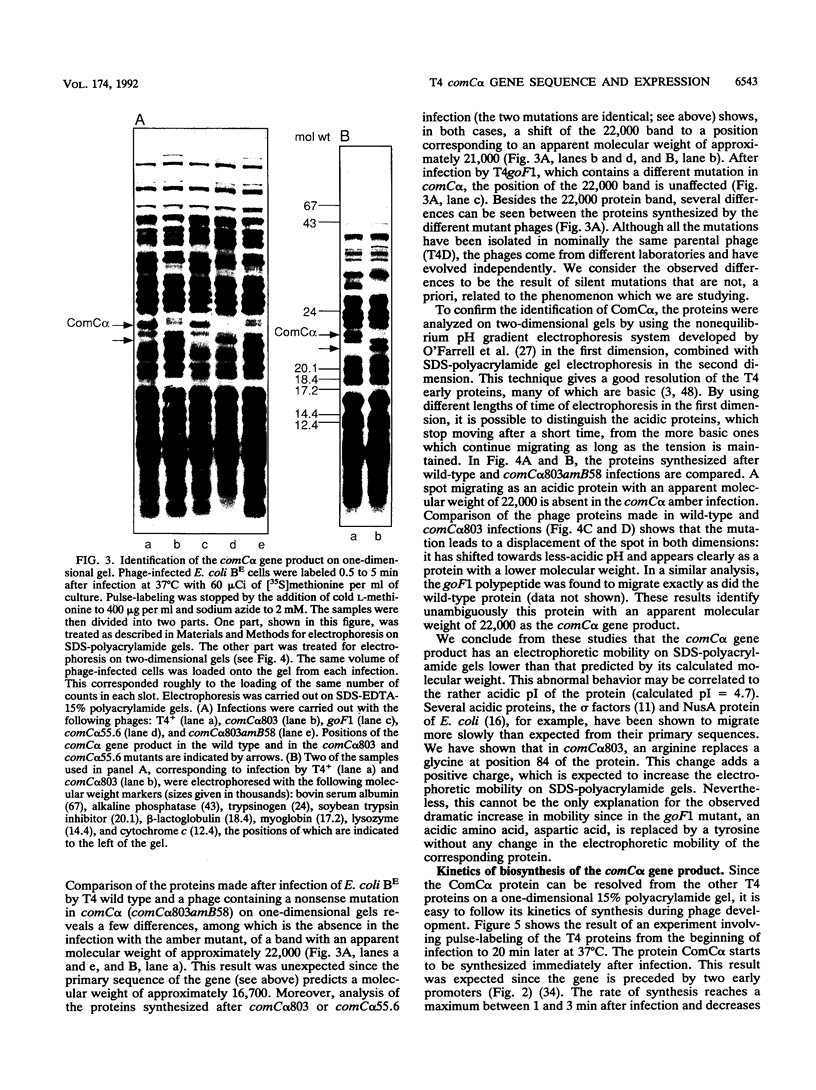
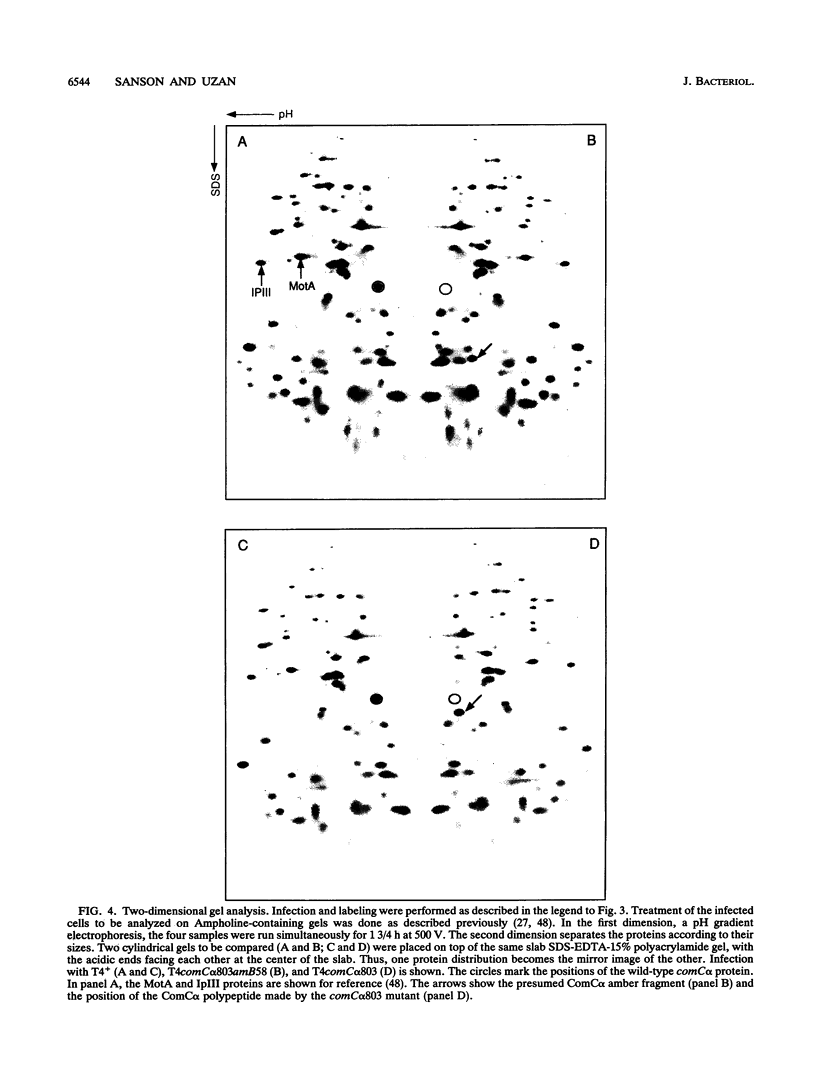
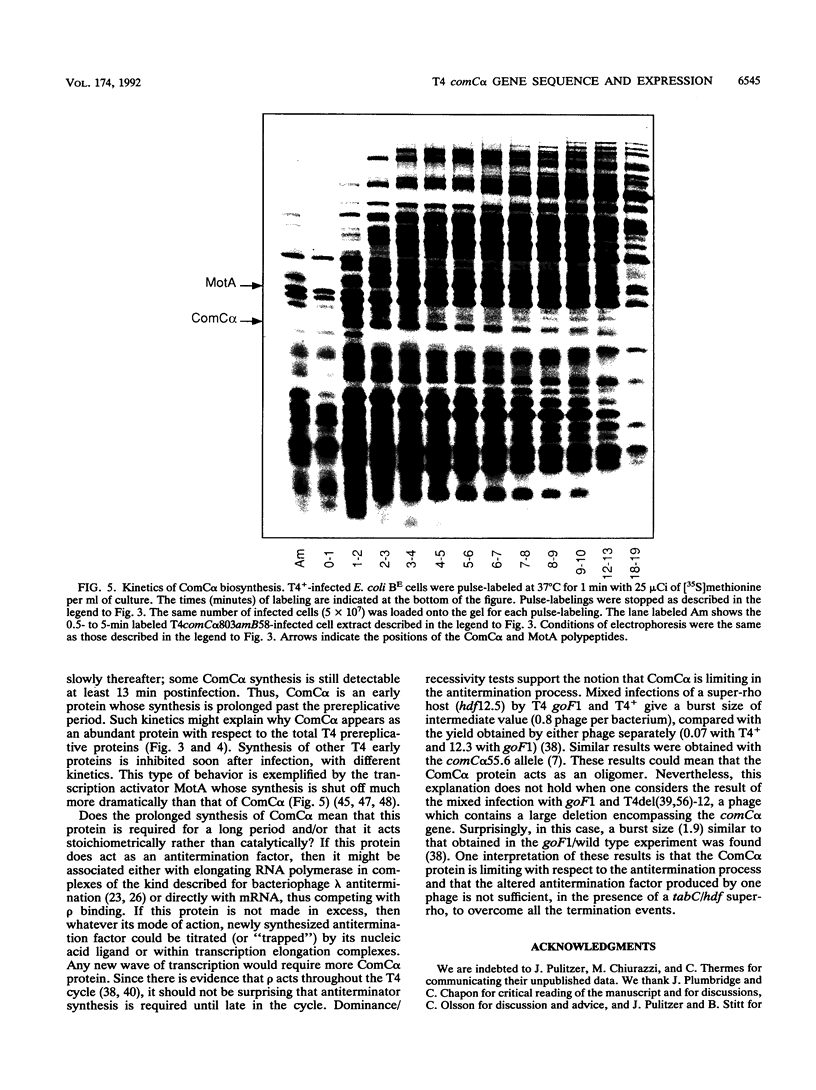
We have sequenced a 1,340-bp region of the bacteriophage T4 DNA spanning the comC alpha gene, a gene which has been implicated in transcription antitermination. We show that comC alpha, identified unambiguously by sequencing several missense and nonsense mutations within the gene, codes for an acidic polypeptide of 141 residues, with a predicted molecular weight of 16,680. We have identified its product on one- and two-dimensional gel systems and found that it migrates abnormally as a protein with a molecular weight of 22,000. One of the missense mutations (comC alpha 803) is a glycine-to-arginine change, and the resulting protein exhibits a substantially faster electrophoretic mobility. The ComC alpha protein appears immediately after infection. Its rate of synthesis is maximum around 2 to 3 min postinfection (at 37 degrees C) and then starts to decrease slowly. Some residual biosynthesis is still detectable during the late period of phage development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Baron C. Selenoprotein synthesis: an expansion of the genetic code. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardillo T. S., Landry E. F., Wiberg J. S. regA protein of bacteriophage T4D: identification, schedule of synthesis, and autogenous regulation. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):905–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.905-916.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso M., Coppo A., Manzi A., Pulitzer J. F. Host--virus interactions in the control of T4 prereplicative transcription. I. tabC (rho) mutants. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):959–977. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Gottesman M. E., Wardwell J., Trisler P., Gottesman S. lambda mutation in the Escherichia coli rho gene that inhibits the N protein activity of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessen P., Fondrat C., Valencien C., Mugnier C. BISANCE: a French service for access to biomolecular sequence databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Oct;6(4):355–356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild N., Gayle M., Sweeney R., Hollingsworth T., Modeer T., Gold L. Transcriptional activation of bacteriophage T4 middle promoters by the motA protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M. Altered expression of the bacteriophage T4 gene 41 (primase-helicase) in an Escherichia coli rho mutant. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14440–14446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M. Transcription from a bacteriophage T4 middle promoter using T4 motA protein and phage-modified RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18034–18044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homyk T., Jr, Weil J. Deletion analysis of two nonessential regions of the T4 genome. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):505–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M. Nucleotide sequence of a type II DNA topoisomerase gene. Bacteriophage T4 gene 39. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7751–7765. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ihara M., Maekawa T., Nakamura Y., Uchida H., Imamoto F. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned nusA gene and its flanking region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3333–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. L., Susman M. A mutant of E. coli that restricts growth of bacteriophage T4 at elevated temperatures. Genetics. 1980 Feb;94(2):301–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. C., Coleman J. E. Two-dimensional 1H NMR of gene 5 protein indicates that only two aromatic rings interact significantly with oligodeoxynucleotide bases. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2929–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricker M. C., Tindall K. R. Direct sequencing of bacteriophage T4 DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebig H. D., Rüger W. Bacteriophage T4 early promoter regions. Consensus sequences of promoters and ribosome-binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):517–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. W., Greenblatt J. Assembly of transcription elongation complexes containing the N protein of phage lambda and the Escherichia coli elongation factors NusA, NusB, NusG, and S10. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1504–1512. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nodwell J. R., Greenblatt J. The nut site of bacteriophage lambda is made of RNA and is bound by transcription antitermination factors on the surface of RNA polymerase. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2141–2151. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. Errors and alternatives in reading the universal genetic code. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):273–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.273-298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B. V., Chiu W. Sequence comparison of single-stranded DNA binding proteins and its structural implications. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):579–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulitzer J. F., Colombo M., Ciaramella M. New control elements of bacteriophage T4 pre-replicative transcription. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):249–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulitzer J. F., Coppo A., Caruso M. Host--virus interactions in the control of T4 prereplicative transcription. II. Interaction between tabC (rho) mutants and T4 mot mutants. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):979–997. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruckman J., Parma D., Tuerk C., Hall D. H., Gold L. Identification of a T4 gene required for bacteriophage mRNA processing. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):54–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoo Y., Ghosaini L. R., Keating K. M., Williams K. R., Sturtevant J. M., Konigsberg W. H. Site-specific mutagenesis of T4 gene 32: the role of tyrosine residues in protein-nucleic acid interactions. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7409–7417. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Snover D., Doermann A. H. Bacterial mutation affecting T4 phage DNA synthesis and tail production. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):451–455. doi: 10.1038/252451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L., Mosig G. Impaired expression of certain prereplicative bacteriophage T4 genes explains impaired T4 DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli rho (nusD) mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3872–3880. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3872-3880.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L., Revel H. R., Lielausis I., Wood W. B. Role of the host cell in bacteriophage T4 development. II. Characterization of host mutants that have pleiotropic effects on T4 growth. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):775–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.775-789.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. L., Ward D. F., Gottesman M. E. Effect of Escherichia coli nusG function on lambda N-mediated transcription antitermination. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1339–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1339-1344.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Coppo A., Manzi A., Martire G., Pulitzer J. F. Design of a system of conditional lethal mutations (tab/k/com) affecting protein-protein interactions in bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H. Genetic and physiological characterization of Escherichia coli K12 mutants (tabC) which induce the abortive infection of bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):256–265. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Yoshikawa H. Genetic study of a new early gene, comC-alpha, of bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Brody E., Favre R. Nucleotide sequence and control of transcription of the bacteriophage T4 motA regulatory gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1487–1496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Favre R., Brody E. A nuclease that cuts specifically in the ribosome binding site of some T4 mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8895–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Leautey J., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Brody E. Identification and biosynthesis of the bacteriophage T4 mot regulatory protein. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1207–1212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Favre R., de Franciscis V., Brody E. The T4 mot protein functions as part of a pre-replicative DNA-protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):633–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]