Abstract
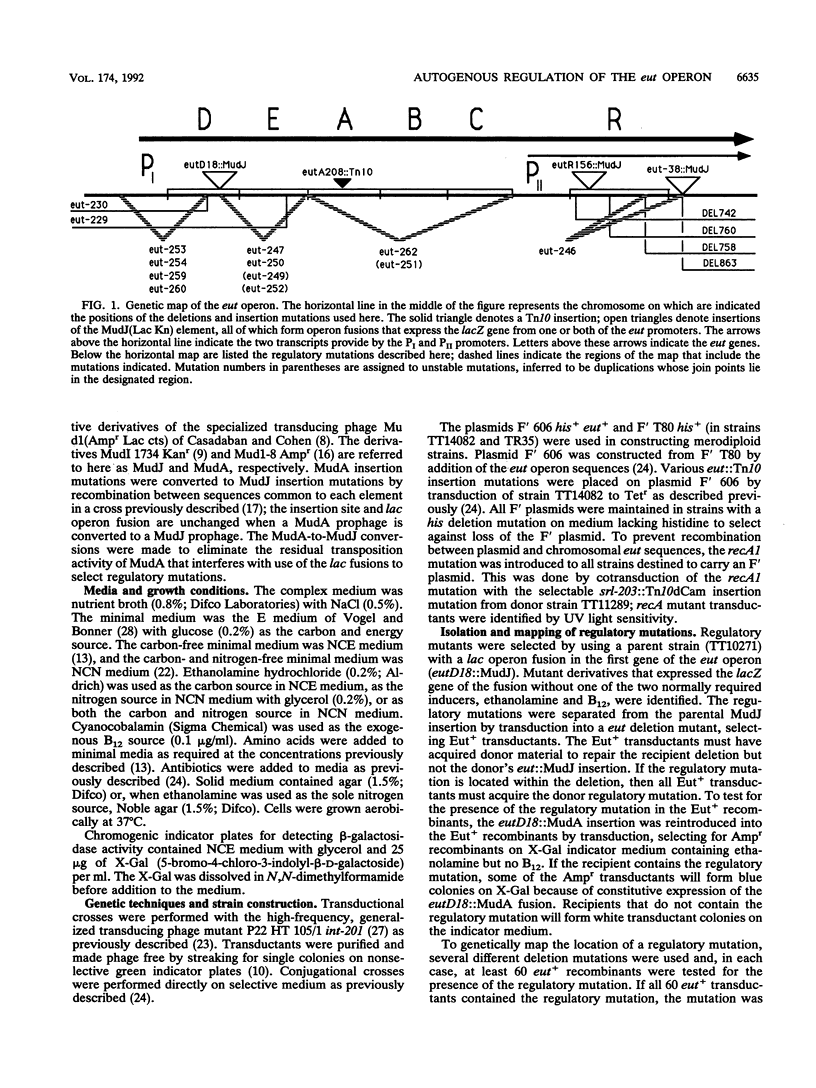
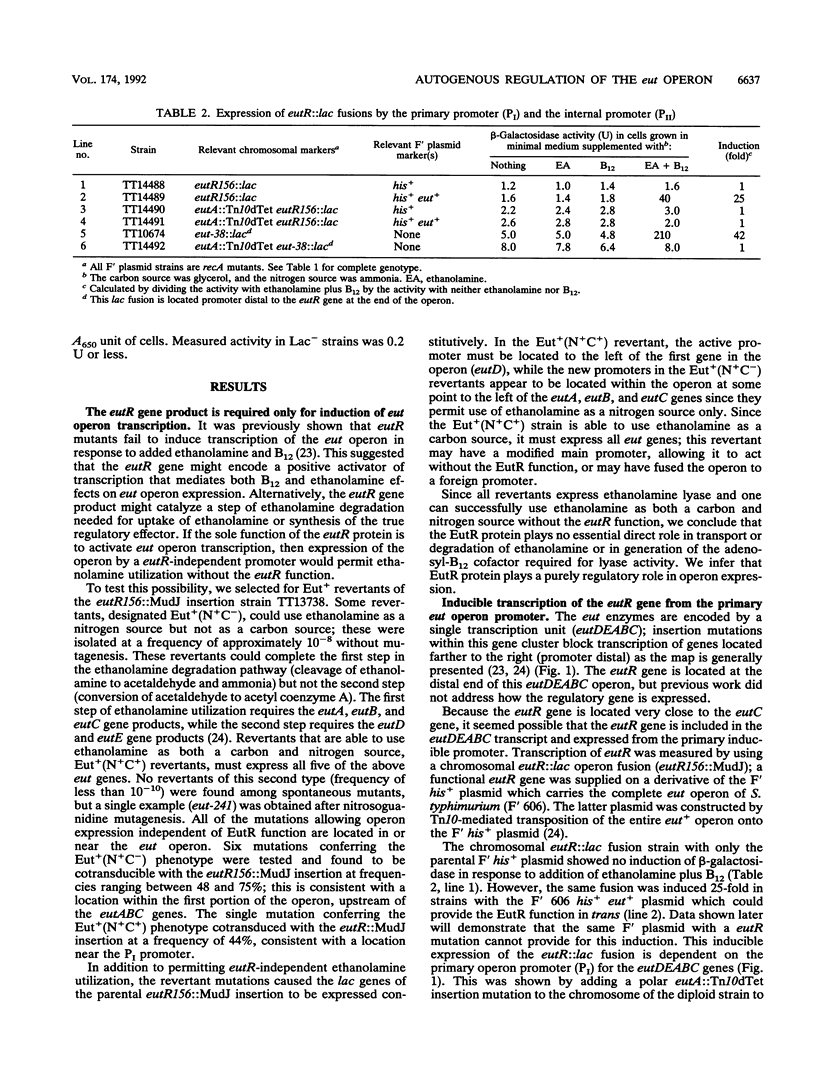
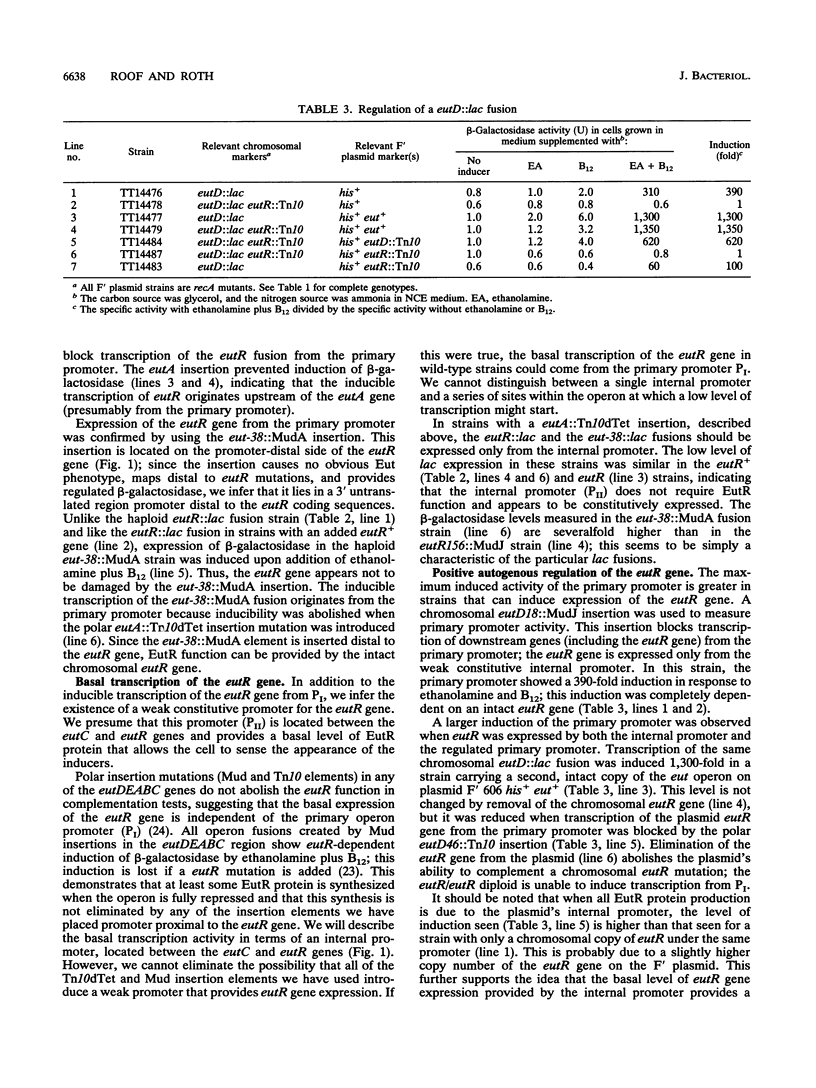
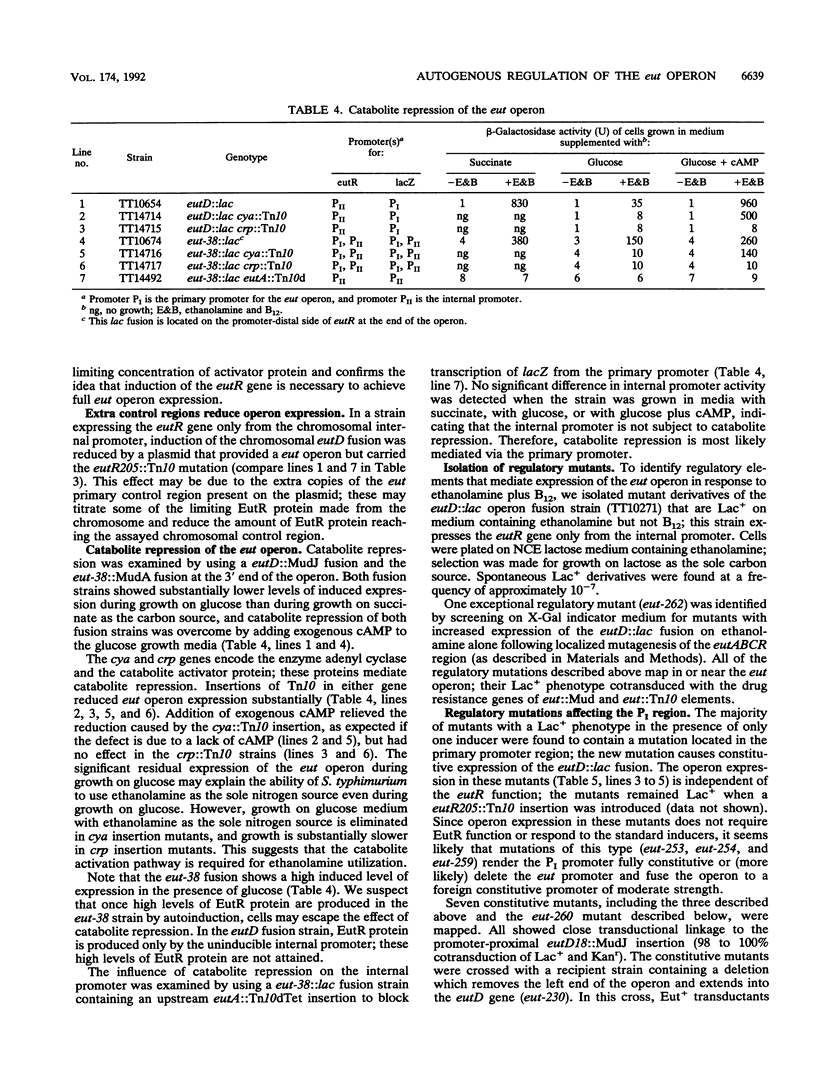
The genes required for use of ethanolamine as a carbon and nitrogen source are encoded by a single operon (eut) whose expression is induced by the simultaneous presence of both ethanolamine and cobalamin (vitamin B12). The action of B12 as an inducer of this operon reflects the fact that this cofactor is required by the degradative enzyme ethanolamine lyase (eutBC). The eutR gene encodes a protein that activates transcription of the eut operon in response to the simultaneous presence of B12 and ethanolamine. The eutR gene is expressed by a weak constitutive promoter activity (PII) and by the main regulated promoter (PI). Because it is encoded within the operon that it activates, the EutR protein controls its own production. Initial induction of the eut operon by ethanolamine plus B12 causes an increase in expression of the eutR gene; this increase acts as part of a positive feedback loop that is required for maximal operon expression. Because of this mode of regulation, constitutive regulatory mutations, described here, include mutations that generate new internal promoters and thereby increase the basal level of eutR gene expression. In mutants with an increased level of activator protein, each inducer (B12 or ethanolamine), presented singly, is sufficient for partial operon induction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem chromosomal duplications in Salmonella typhimurium: fusion of histidine genes to novel promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 15;119(1):147–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson D. I., Roth J. R. Mutations affecting regulation of cobinamide biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6726–6733. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6726-6733.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson D. I., Roth J. R. Redox regulation of the genes for cobinamide biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6734–6739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6734-6739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, kadner R. J. Genetic analysis of components involved in vitamin B12 uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.796-805.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. M., Scarlett F. A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Control of formation and stability of partially purified ethanolamine ammonia-lyase in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):133–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. M., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Formation of coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase and its concerted induction in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):751–757. doi: 10.1042/bj1760751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbeer C. The clostridial fermentations of choline and ethanolamine. II. Requirement for a cobamide coenzyme by an ethanolamine deaminase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4675–4681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Botstein D., Watanabe T., Ogata Y. Specialized transduction of tetracycline resistance by phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. II. Properties of a high-frequency-transducing lysate. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):883–898. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90442-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. W., Chang J. T. Evidence for the B12-dependent enzyme ethanolamine deaminase in Salmonella. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):150–151. doi: 10.1038/254150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Roth J. R. Characterization of Tn10d-Cam: a transposition-defective Tn10 specifying chloramphenicol resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):332–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00339599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Roth J. R. Regulation of cobalamin biosynthetic operons in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2251–2258. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2251-2258.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Roth J. R. Conditionally transposition-defective derivative of Mu d1(Amp Lac). J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):130–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.130-137.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Roth J. R. Transitory cis complementation: a method for providing transposition functions to defective transposons. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):9–12. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeter R. M., Olivera B. M., Roth J. R. Salmonella typhimurium synthesizes cobalamin (vitamin B12) de novo under anaerobic growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):206–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.206-213.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W., Turner J. M. A model for the common control of enzymes of ethanolamine catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):849–860. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W., Turner J. M. Interrelationships between the enzymes of ethanolamine metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Feb;130(2):299–308. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzkin B., Roth J. Cluster of genes controlling proline degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):744–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.744-754.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Roth J. R. Ethanolamine utilization in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3855–3863. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3855-3863.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Roth J. R. Functions required for vitamin B12-dependent ethanolamine utilization in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3316–3323. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3316-3323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett F. A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Ethanolamine catabolism mediated by coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jul;95(1):173–176. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sennett C., Rosenberg L. E., Mellman I. S. Transmembrane transport of cobalamin in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:1053–1086. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala V., Schneider E., Ames G. F. Tandem chromosomal duplications: role of REP sequences in the recombination event at the join-point. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):939–946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



