Abstract
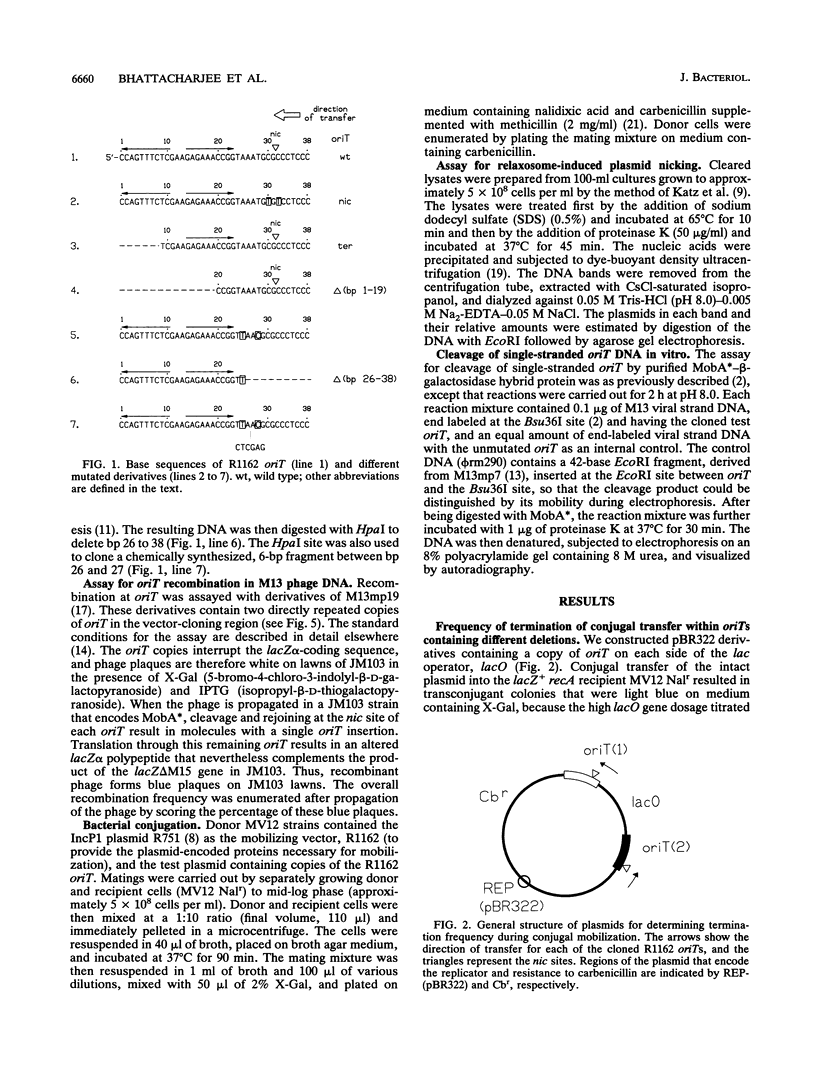
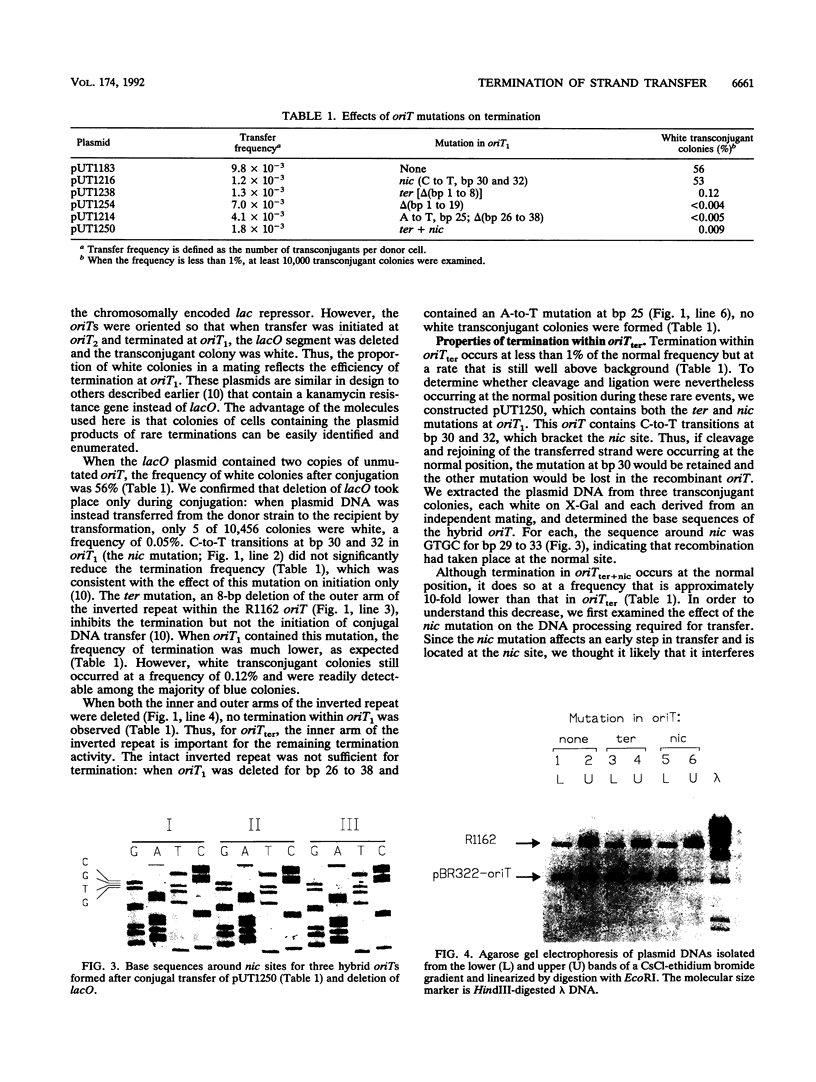
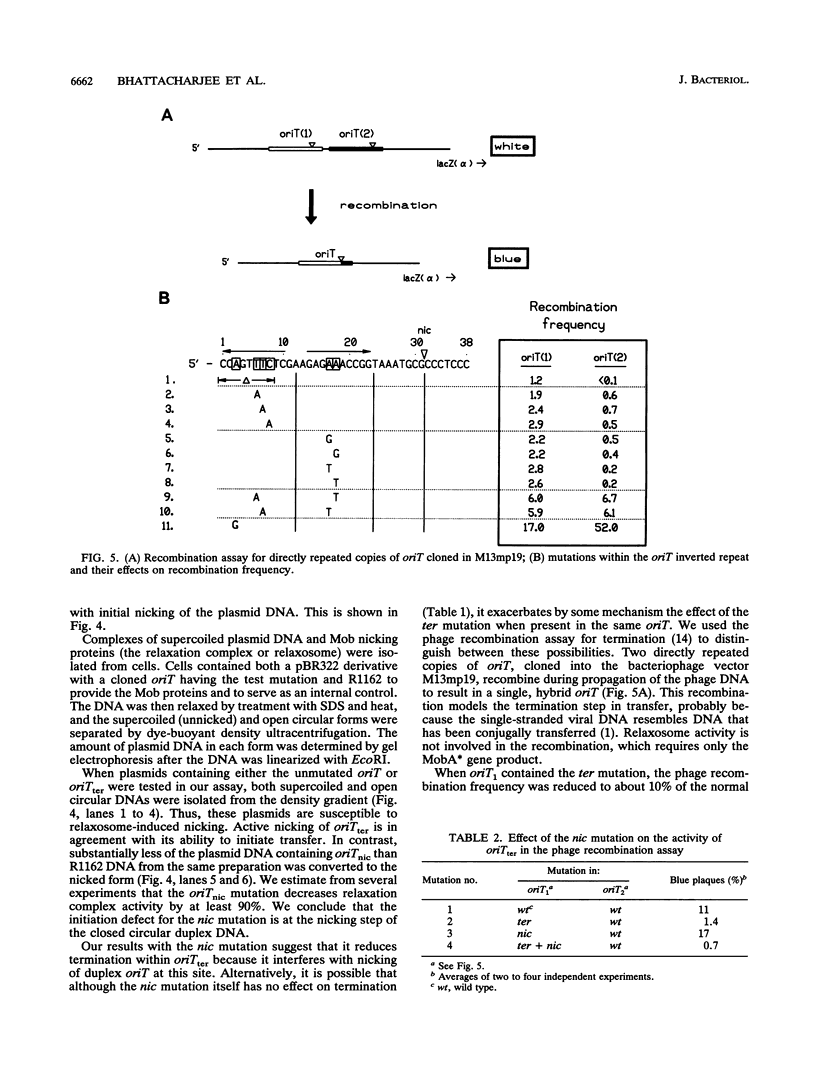
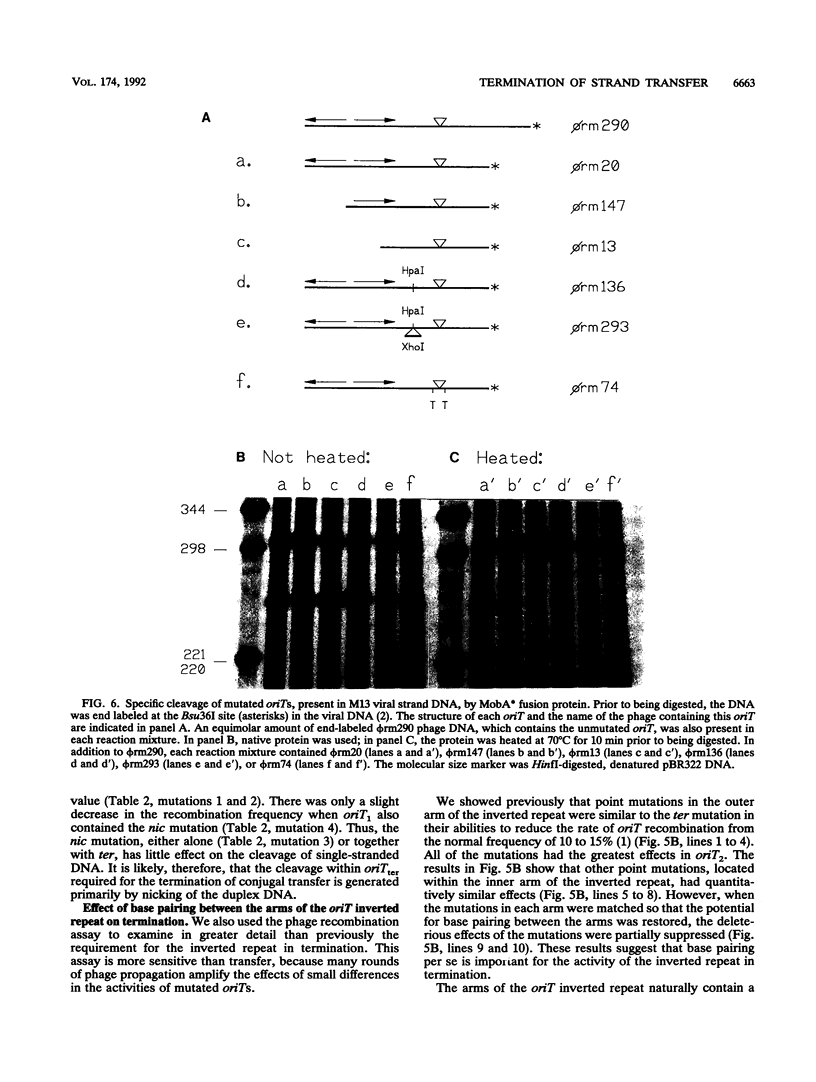
Conjugal transfer of the broad-host-range plasmid R1162 is initiated and terminated at the nic site within the 38-bp origin of transfer (oriT). Termination involves ligation of the transferred single strand by the plasmid-encoded MobA protein. Several different assays were used to identify the oriT DNA required for termination. For plasmids containing two oriTs, with transfer initiated at one and terminated at the other, the inverted repeat within oriT is important for termination. Deletion of the outer arm reduces the termination frequency; those terminations that do occur probably depend upon nicking at this oriT prior to transfer. The locations of second-site suppressor mutations indicate that base pairing between the arms of the inverted repeat is important for termination. In vitro, the inverted repeat is not required for specific cleavage of single-stranded DNA at nic, but competition experiments indicate that oriTs with the inverted repeat are preferentially cleaved. We propose that the function of the oriT inverted repeat is to trap the plasmid-encoded MobA protein at the end of a round of strand transfer, thus ensuring that the protein is available for the ligation step.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlett M. M., Erickson M. J., Meyer R. J. Recombination between directly repeated origins of conjugative transfer cloned in M13 bacteriophage DNA models ligation of the transferred plasmid strand. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3579–3586. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee M. K., Meyer R. J. A segment of a plasmid gene required for conjugal transfer encodes a site-specific, single-strand DNA endonuclease and ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1129–1137. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch M. A., Meyer R. J. A 38 base-pair segment of DNA is required in cis for conjugative mobilization of broad host-range plasmid R1162. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Helinski D. R. The DNA-protein relaxation complex of the plasmid RK2: location of the site-specific nick in the region of the proposed origin of transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00273212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Datta N. Trimethoprim R factors in enterobacteria from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Meyer R. J. Unidirectional transfer of broad host-range plasmid R1162 during conjugative mobilization. Evidence for genetically distinct events at oriT. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupersztoch-Portnoy Y. M., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Strand and site specificity of the relaxation event for the relaxation complex of the antibiotic resistance plasmid R6K. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5484–5490. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hinds M., Brasch M. Properties of R1162, a broad-host-range, high-copy-number plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):552–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.552-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. Site-specific recombination at oriT of plasmid R1162 in the absence of conjugative transfer. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):799–806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.799-806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Timmis K. N. Location of two relaxation nick sites in R6K and single sites in pSC101 and RSF1010 close to origins of vegetative replication: implication for conjugal transfer of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):923–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.923-932.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzinger E., Lurz R., Otto S., Dobrinski B. In vitro cleavage of double- and single-stranded DNA by plasmid RSF1010-encoded mobilization proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stougaard P., Molin S. Vertical dye-buoyant density gradients for rapid analysis and preparation of plasmid DNA. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Crowther C. Mobilization of the non-conjugative IncQ plasmid RSF1010. Genet Res. 1981 Jun;37(3):311–316. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. M., Muesing M. A., Polisky B. Temperature-sensitive copy number mutants of CoIE1 are located in an untranslated region of the plasmid genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3570–3574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]