Abstract
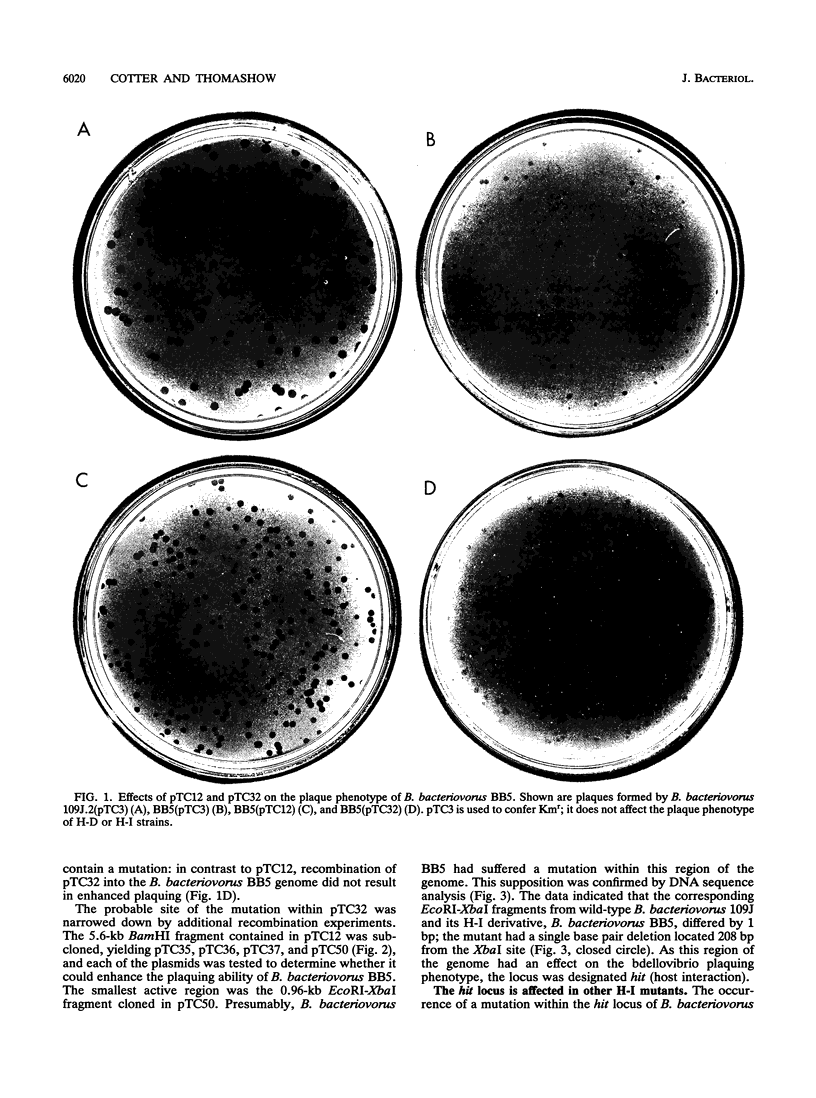
Bdellovibrios invade and grow within the periplasmic space of suitable gram-negative bacteria. Wild-type bdellovibrios are obligately dependent on host cells for growth, but spontaneous host-independent (H-I) mutants that grow axenically on standard rich culture media can be isolated. Such mutants generally retain the ability to grow intraperiplasmically, although the plaques that they produce on lawns of host cells are smaller and more turbid than those produced by wild-type bdellovibrios. Here, we identify the first genetic locus associated with the H-I phenotype: hit (host interaction). We show that three individual H-I mutants suffered mutations at the hit locus and that recombination of wild-type hit sequences into the genomes of the H-I mutants greatly enhanced their plaquing ability. DNA sequence analysis localized the hit mutation in each of the H-I mutants to a 135-bp region of the genome. Mutations at hit may not fully account for the H-I phenotype, however, as recombination of wild-type hit sequences into the genomes of the H-I mutants had little effect on the axenic-growth phenotype of the mutants. Possible explanations for this result and potential roles for the hit locus are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. W., Thomashow M. F. A conjugation procedure for Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and its use to identify DNA sequences that enhance the plaque-forming ability of a spontaneous host-independent mutant. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6011–6017. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6011-6017.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich D. L., Denny C. F., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Facultatively parasitic strain of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):989–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.989-996.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D. Growth of host dependent Bdellovibrio in host cell free system. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Feb;116(2):185–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00406035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. T., Kessel M., Shilo M. Growth cycle of predacious Bdellovibrios in a host-free extract system and some properties of the host extract. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):270–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.270-282.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E. A growth initiation factor for host-independent derivatives of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):243–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.243-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C. Nonidentity of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strains 109D and 109J. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):432–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.432-433.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Shilo M. Early host damage in the infection cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):149–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.149-160.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Isolation and characterization of host-independent Bdellovibrios. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):769–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.769-785.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M., Bruff B. Lysis of Gram-negative bacteria by host-independent ectoparasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus isolates. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):317–328. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Cotter T. W. Bdellovibrio host dependence: the search for signal molecules and genes that regulate the intraperiplasmic growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5767–5771. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5767-5771.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Seijffers J. Symbiosis-independent and symbiosis-incompetent mutants of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1191–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1191-1197.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]