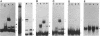Abstract
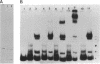
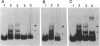
In a previous study, we showed that in bacteroids, transcription of the inducible nod genes does not occur and expression of nodD is decreased by 65% (H. R. M. Schlaman, B. Horvath, E. Vijgenboom, R.J.H. Okker, and B. J. J. Lugtenberg, J. Bacteriol. 173:4277-4287, 1991). In the present study, we show, using gel retardation, that in crude extracts of bacteroids of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar (bv.) viciae, NodD protein does not bind to the nodF, nodM, and nodO box and that it binds only weakly to the nodA box. Binding of NodD from bacteroids to nod box DNA could be restored by mild proteinase K treatment, indicating that NodD is present in bacteroids in an altered form or complex which prevents its binding to nod box DNA. In addition, a novel nodA box DNA-protein complex was found which is specific for the nodA promoter region. This novel complex was formed neither with material from cultured bacterial cells nor with an extract from uninfected roots, and it did not contain NodD but another protein. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the protein present in the novel retardation complex acts as a transcriptional repressor causing the decreased nodD expression in bacteroids. Such a repressor also explains the lack of nodABCIJ transcription despite the weak NodD binding to the nodA box.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett M. J., Long S. R. DNA sequence and translational product of a new nodulation-regulatory locus: syrM has sequence similarity to NodD proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3695–3700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3695-3700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Egelhoff T. T., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Specific binding of proteins from Rhizobium meliloti cell-free extracts containing NodD to DNA sequences upstream of inducible nodulation genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):282–293. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. DNA footprint analysis of the transcriptional activator proteins NodD1 and NodD3 on inducible nod gene promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5492–5502. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5492-5502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F., Burn J. E., Johnston A. W. Evidence that DNA involved in the expression of nodulation (nod) genes in Rhizobium binds to the product of the regulatory gene nodD. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9677–9690. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. D., Rossen L., Robertson J. G., Wells B., Downie J. A. Nodulation inhibition by Rhizobium leguminosarum multicopy nodABC genes and analysis of early stages of plant infection. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.552-558.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondorosi E., Gyuris J., Schmidt J., John M., Duda E., Hoffmann B., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Positive and negative control of nod gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti is required for optimal nodulation. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1331–1340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondorosi E., Pierre M., Cren M., Haumann U., Buiré M., Hoffmann B., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Identification of NolR, a negative transacting factor controlling the nod regulon in Rhizobium meliloti. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 20;222(4):885–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90583-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Horvath B., Vijgenboom E., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Suppression of nodulation gene expression in bacteroids of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4277–4287. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4277-4287.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Spaink H. P., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Subcellular localization of the nodD gene product in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4686–4693. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4686-4693.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Watson J. M. DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2891–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. B., Signer E. R. Temporal and spatial regulation of the symbiotic genes of Rhizobium meliloti in planta revealed by transposon Tn5-gusA. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):344–356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Okker R. J., Wijffelman C. A., Tak T., Goosen-de Roo L., Pees E., van Brussel A. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Symbiotic properties of rhizobia containing a flavonoid-independent hybrid nodD product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4045–4053. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4045-4053.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Sheeley D. M., van Brussel A. A., Glushka J., York W. S., Tak T., Geiger O., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N., Lugtenberg B. J. A novel highly unsaturated fatty acid moiety of lipo-oligosaccharide signals determines host specificity of Rhizobium. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):125–130. doi: 10.1038/354125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Wijffelman C. A., Spaink H. P., van Brussel A. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Induction of the nodA promoter of Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI by plant flavanones and flavones. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):198–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.198-204.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Wijfjes A. H., Spaink H. P., Ruiz-Sainz J. E., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. nodO, a new nod gene of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae sym plasmid pRL1JI, encodes a secreted protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6764–6770. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6764-6770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]