Abstract
Gene 10 of bacteriophage P1 encodes a regulatory function required for the activation of P1 late promoter sequences. In this report cis and trans regulatory functions involved in the transcriptional control of gene 10 are identified. Plasmid-borne fusions of gene 10 to the indicator gene lacZ were constructed to monitor expression from the gene 10 promoter. Production of gp10-LacZ fusion protein became measurable at about 15 min after prophage induction, whereas no expression was observed during lysogenic growth. The activity of an Escherichia coli-like promoter, Pr94, upstream of gene 10, was confirmed by mapping the initiation site of transcription in primer extension reactions. Two phage-encoded proteins cooperate in the trans regulation of transcription from Pr94: C1 repressor and Bof modulator. Both proteins are necessary for complete repression of gene 10 expression during lysogeny. Under conditions that did not ensure repression by C1 and Bof, the expression of gp10-LacZ fusion proteins from Pr94 interfered with transformation efficiency and cell viability. Results of in vitro DNA-binding studies confirmed that C1 binds specifically to an operator sequence, Op94, which overlaps the -35 region of Pr94. Although Bof alone does not bind to DNA, together with C1 it increases the efficiency of the repressor-operator interaction. These results are in line with the idea that gp10 plays the role of mediator between early and late gene transcription during lytic growth of bacteriophage P1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumstark B. R., Scott J. R. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. I. Isolation of the c1 protein and determination of the P1 DNA region to which it binds. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumstark B. R., Stovall S. R., Ashkar S. Interaction of the P1c1 repressor with P1 DNA: localization of repressor binding sites near the c1 gene. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):404–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Schuster H. The c4 repressors of bacteriophages P1 and P7 are antisense RNAs. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Velleman M., Schuster H. Three additional operators, Op21, Op68, and Op88, of bacteriophage P1. Evidence for control of the P1 dam methylase by Op68. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3611–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Sternberg N. Genetic analysis of the lytic replicon of bacteriophage P1. I. Isolation and partial characterization. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90443-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ari R., Jaffé-Brachet A., Touati-Schwartz D., Yarmolinsky M. B. A dnaB analog specified by bacteriophage P1. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):341–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreiseikelmann B., Velleman M., Schuster H. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. Isolation and characterization of the repressor protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1391–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliason J. L., Sternberg N. Characterization of the binding sites of c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. Evidence for multiple asymmetric sites. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidolin A., Zingg J. M., Lehnherr H., Arber W. Bacteriophage P1 tail-fibre and dar operons are expressed from homologous phage-specific late promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B. Structure and regulation of the lytic replicon of phage P1. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich J., Riedel H. D., Baumstark B. R., Kimura M., Schuster H. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1 operator-repressor interaction of wild-type and mutant repressor proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7681–7692. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel T., Velleman M., Schuster H. C1 repressor of phage P1 is inactivated by noncovalent binding of P1 Coi protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4183–4188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel T., Velleman M., Schuster H. The c1 repressor inactivator protein coi of bacteriophage P1. Cloning and expression of coi and its interference with c1 repressor function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17928–17934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
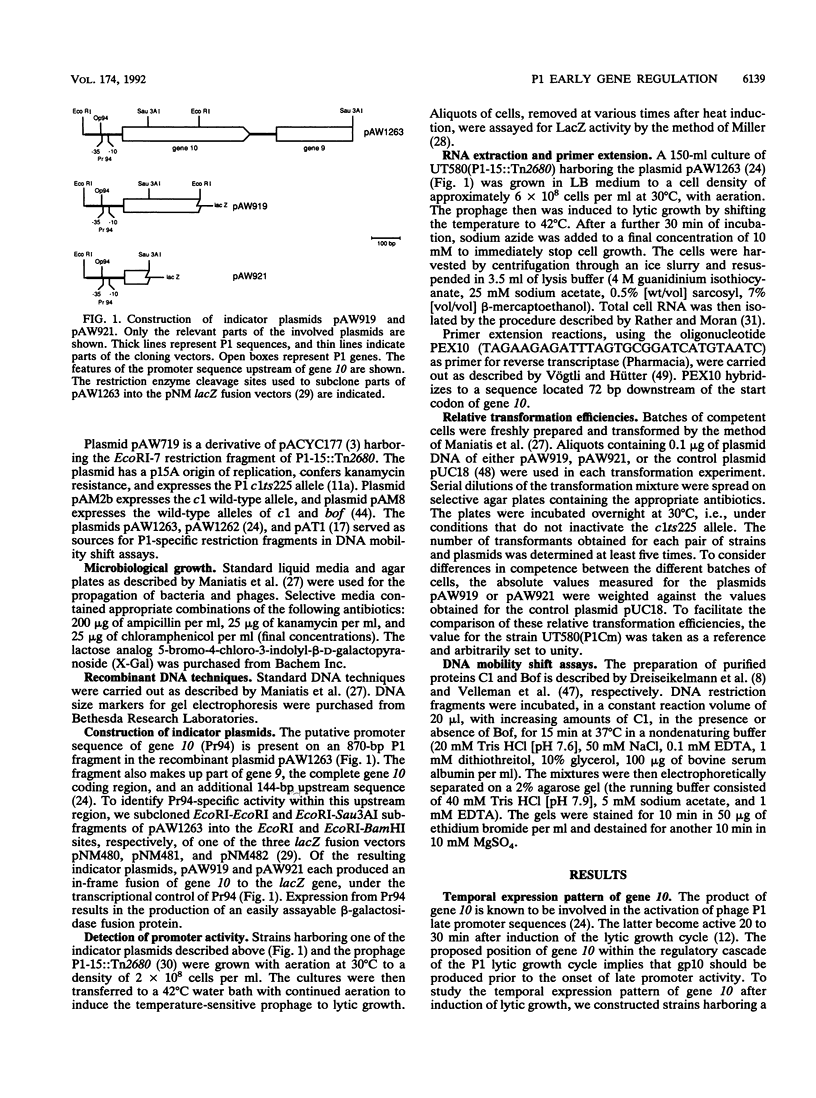
- Heinzel T., Velleman M., Schuster H. ban operon of bacteriophage P1. Mutational analysis of the c1 repressor-controlled operator. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig A., Riedel H. D., Dobrinski B., Lurz R., Schuster H. Organization of the immunity region immI of bacteriophage P1 and synthesis of the P1 antirepressor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):525–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90591-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig A., Severin I., Seefluth A. K., Schuster H. Regulation of the ban gene containing operon of prophage P1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Mar;206(3):368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00428873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner P., Arber W. Mutational analysis of a prokaryotic recombinational enhancer element with two functions. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):577–585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Streiff M. B., Bickle T. A., Arber W. Two DNA antirestriction systems of bacteriophage P1, darA, and darB: characterization of darA- phages. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90324-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONDO E., MITSUHASHI S. DRUG RESISTANCE OF ENTERIC BACTERIA. IV. ACTIVE TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE P1 CM PRODUCED BY THE COMBINATION OF R FACTOR WITH BACTERIOPHAGE P1. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1266–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1266-1276.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnherr H., Guidolin A., Arber W. Bacteriophage P1 gene 10 encodes a trans-activating factor required for late gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6438–6445. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6438-6445.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
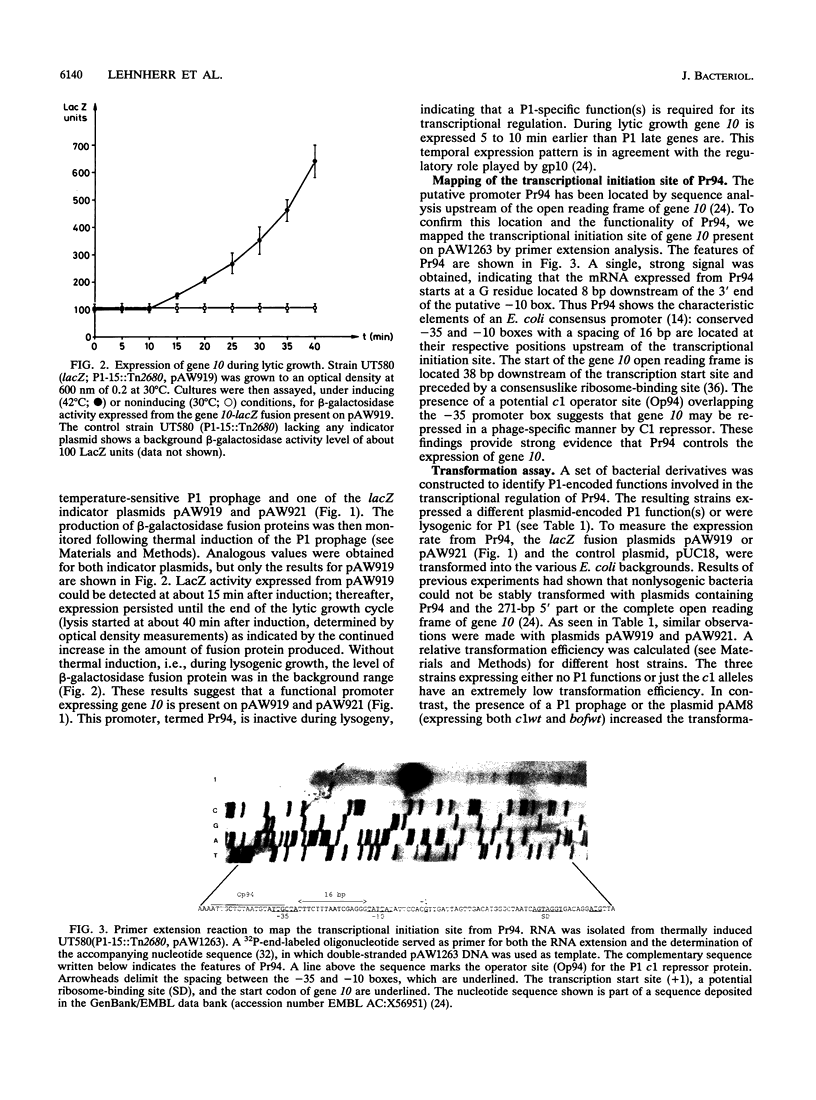
- Lurz R., Heisig A., Velleman M., Dobrinski B., Schuster H. The ban operon of bacteriophage P1. Localization of the promoter controlled by P1 repressor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16575–16579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P. Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollet B., Clerget M., Meyer J., Iida S. Organization of the Tn6-related kanamycin resistance transposon Tn2680 carrying two copies of IS26 and an IS903 variant, IS903. B. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.55-60.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Moran C. P., Jr Compartment-specific transcription in Bacillus subtilis: identification of the promoter for gdh. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5086–5092. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5086-5092.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer T. S., Hays J. B. Bacteriophage P1 Bof protein is an indirect positive effector of transcription of the phage bac-1 ban gene in some circumstances and a direct negative effector in other circumstances. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6469–6474. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6469-6474.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer T. S., Hays J. B. The bof gene of bacteriophage P1: DNA sequence and evidence for roles in regulation of phage c1 and ref genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3269–3277. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3269-3277.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R. Genetic studies on bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):564–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorupski K., Pierce J. C., Sauer B., Sternberg N. Bacteriophage P1 genes involved in the recognition and cleavage of the phage packaging site (pac). J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):977–989. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90256-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N. A characterization of bacteriophage P1 DNA fragments cloned in a lambda vector. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Cohen G. Genetic analysis of the lytic replicon of bacteriophage P1. II. Organization of replicon elements. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):111–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90444-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Coulby J. Cleavage of the bacteriophage P1 packaging site (pac) is regulated by adenine methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8070–8074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Coulby J. Recognition and cleavage of the bacteriophage P1 packaging site (pac). I. Differential processing of the cleaved ends in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):453–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati-Schwartz D. A new pleiotropic bacteriophage P1 mutation, bof, affecting c1 repression activity, the expression of plasmid incompatibility and the expression of certain constitutive prophage genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 13;174(2):189–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00268355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velleman M., Dreiseikelmann B., Schuster H. Multiple repressor binding sites in the genome of bacteriophage P1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velleman M., Heinzel T., Schuster H. The Bof protein of bacteriophage P1 exerts its modulating function by formation of a ternary complex with operator DNA and C1 repressor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12174–12181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velleman M., Heirich M., Günther A., Schuster H. A bacteriophage P1-encoded modulator protein affects the P1 c1 repression system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18511–18517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. T., Walker D. H., Jr Coliphage P1 morphogenesis: analysis of mutants by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1118–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1118-1139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. T., Walker D. H. Mutations in coliphage p1 affecting host cell lysis. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):519–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.519-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle B. E., Hays J. B. A phage P1 function that stimulates homologous recombination of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle B. E., Laufer C. S., Hays J. B. Sequence and deletion analysis of the recombination enhancement gene (ref) of bacteriophage P1: evidence for promoter-operator and attenuator-antiterminator control. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4881–4889. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4881-4889.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]