Abstract
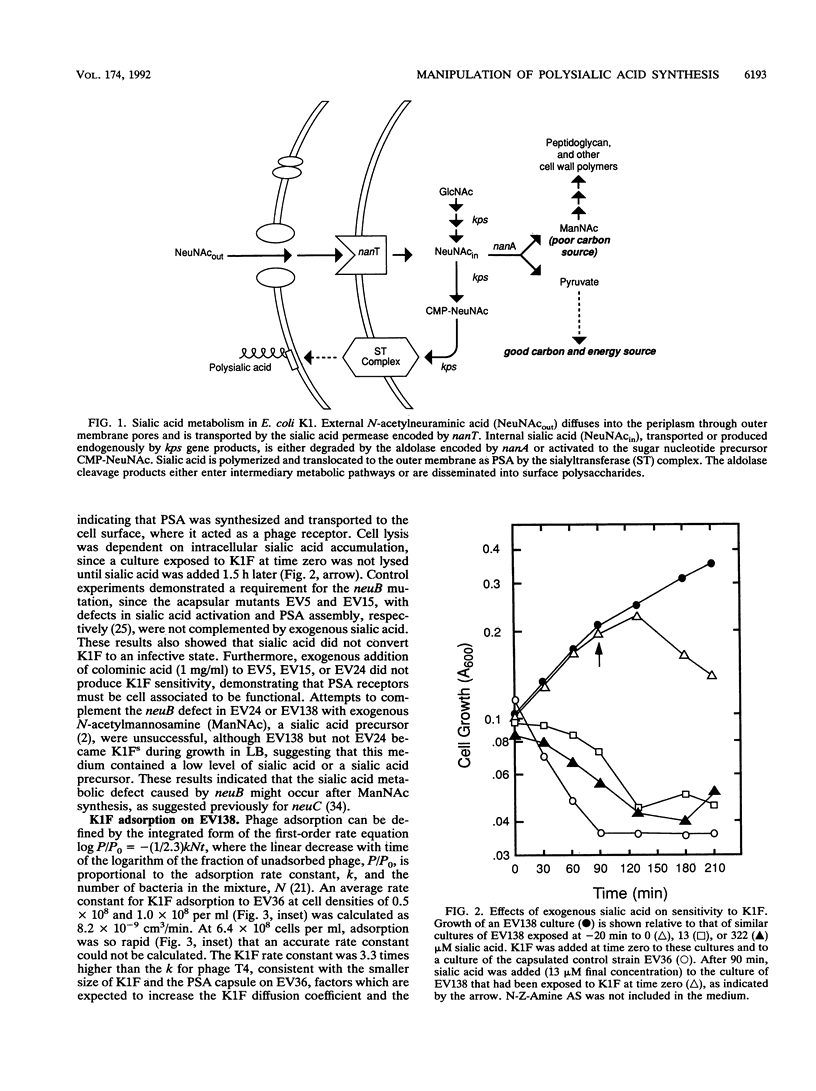
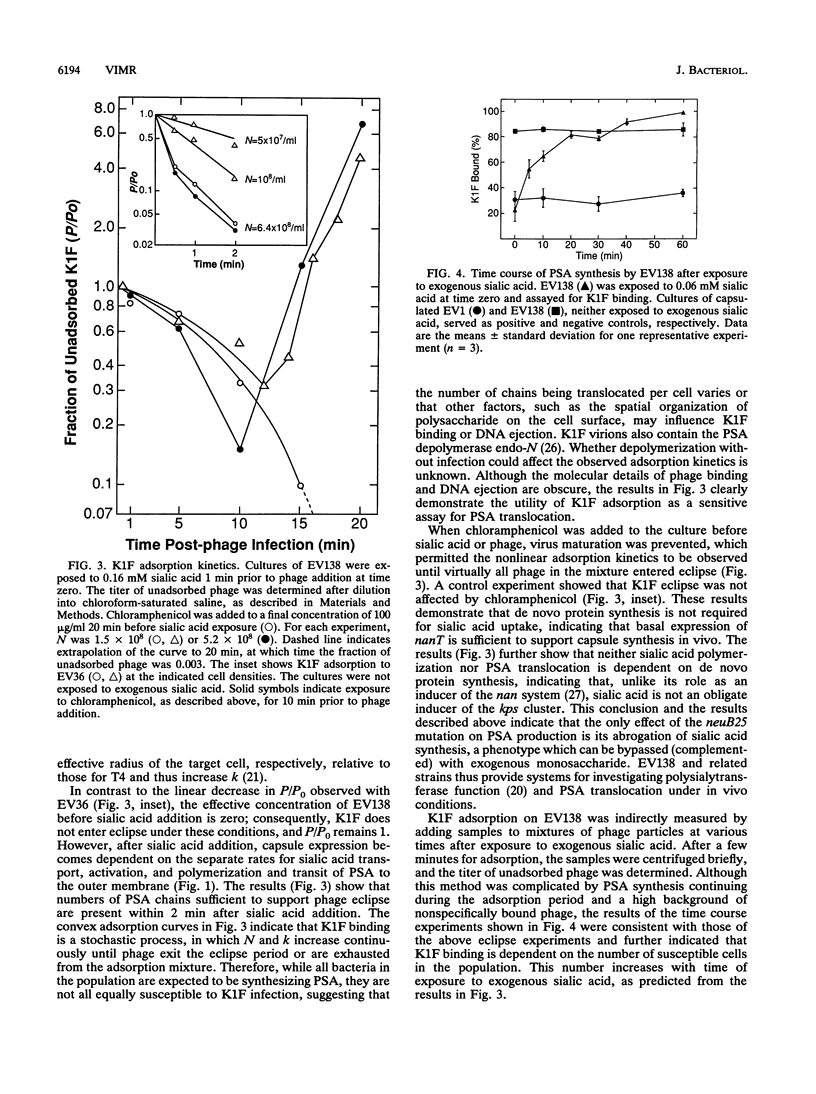
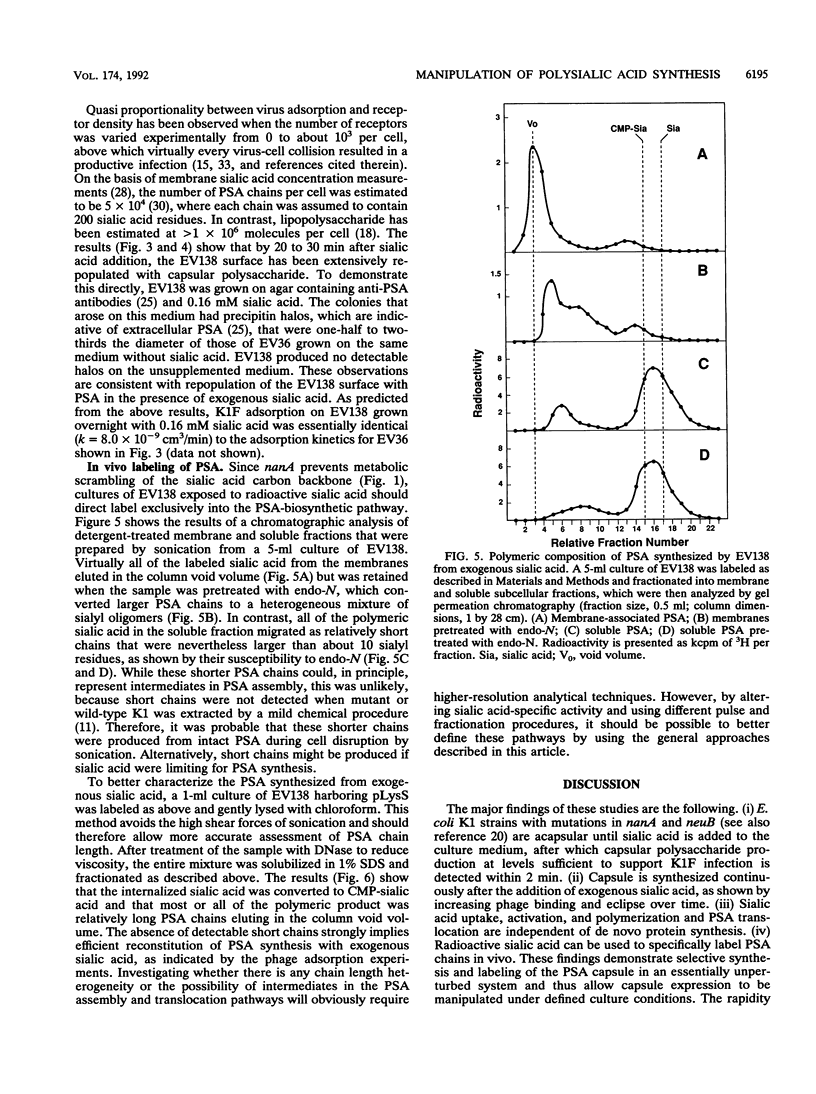
The enzymes required for polysialic acid capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K1 are encoded by region 2 neu genes of the multigenic kps cluster. To facilitate analysis of capsule synthesis and translocation, an E. coli K1 strain with mutations in nanA and neuB, affecting sialic acid degradation and synthesis, respectively, was constructed by transduction. The acapsular phenotype of the mutant was corrected in vivo by exogenous addition of sialic acid. By blocking sialic acid degradation, the nanA mutation allows intracellular metabolite accumulation, while the neuB mutation prevents dilution by the endogenous sialic acid pool and allows capsule synthesis to be controlled experimentally by the exogenous addition of sialic acid to the growth medium. Complementation was detected by bacteriophage K1F adsorption or infectivity assays. Polysialic acid translocation was observed within 2 min after addition of sialic acid to the growth medium, demonstrating the rapidity in vivo of sialic acid transport, activation, and polymerization and translocation of polysaccharide to the cell surface. Phage adsorption was not inhibited by chloramphenicol, demonstrating that de novo protein synthesis was not required for polysialic acid synthesis or translocation at 37 degrees C. Exogenous radiolabeled sialic acid was incorporated exclusively into capsular polysaccharide. The polymeric nature of the labeled capsular material was confirmed by gel permeation chromatography and susceptibility of sialyl polymers to K1F endo-N-acylneuraminidase. The ability to experimentally manipulate capsule expression provides new approaches for investigating polysialic acid synthesis and membrane translocation mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D., DODYK F., ROSEMAN S. Enzymatic synthesis of colominic acid. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1177–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKLOW R. S., WARREN L. Biosynthesis of sialic acids by Neisseria meningitidis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3520–3526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Jann K. Bacterial polysaccharide capsule synthesis, export and evolution of structural diversity. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1819–1823. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S., Hodge R., Hardy K. R., Jann K. B., Timmis K. N. Analysis of the K1 capsule biosynthesis genes of Escherichia coli: definition of three functional regions for capsule production. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):242–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00330449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Fraser B. A., Nishimura O., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y. Lipid on capsular polysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8915–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Golecki J. R., Jann K. Further electron microscopic studies on the expression of Escherichia coli group II capsules. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3469–3472. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3469-3472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Gilbert A. S., Moreno C. Sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli: esterification between adjacent residues. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Aug 1;94(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Lin W., Egan W., Hoff G. E., Robbins J. B. Form variation in Escherichia coli K1: determined by O-acetylation of the capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):669–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen S., Häyrinen J., Finne J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the capsular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli K1 and other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2646–2653. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2646-2653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohr T. E., Troy F. A. Structure and biosynthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2332–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergen S. M., Vimr E. R. Mechanism of polysialic acid chain elongation in Escherichia coli K1. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergen S. M., Wrona T. J., Vimr E. R. Functional analysis of the sialyltransferase complexes in Escherichia coli K1 and K92. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1099–1108. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1099-1108.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Silver R. P., Abeijon C., Chang K., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Finn C. W., Lindner W., Kotsatos M. Purification, properties, and genetic location of Escherichia coli cytidine 5'-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17556–17562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Aaronson W., Silver R. P. Genetic analysis of chromosomal mutations in the polysialic acid gene cluster of Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1106–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1106-1117.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R. Map position and genomic organization of the kps cluster for polysialic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1335–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1335-1338.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., McCoy R. D., Vollger H. F., Wilkison N. C., Troy F. A. Use of prokaryotic-derived probes to identify poly(sialic acid) in neonatal neuronal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Identification of an inducible catabolic system for sialic acids (nan) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):845–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.845-853.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Regulation of sialic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: role of N-acylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.854-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgerber C., Troy F. A. Biosynthesis of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. The endogenous acceptor of polysialic acid is a membrane protein of 20 kDa. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1578–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Vimr E. R., Costerton J. W., Troy F. A. Membrane proteins correlated with expression of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):743–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.743-749.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Vimr E. R., Costerton J. W., Troy F. A. Protein synthesis is required for in vivo activation of polysialic acid capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):321–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.321-328.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata G., Crowley J. M., Vann W. F. Sequence and expression of the Escherichia coli K1 neuC gene product. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):315–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.315-319.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


