Abstract
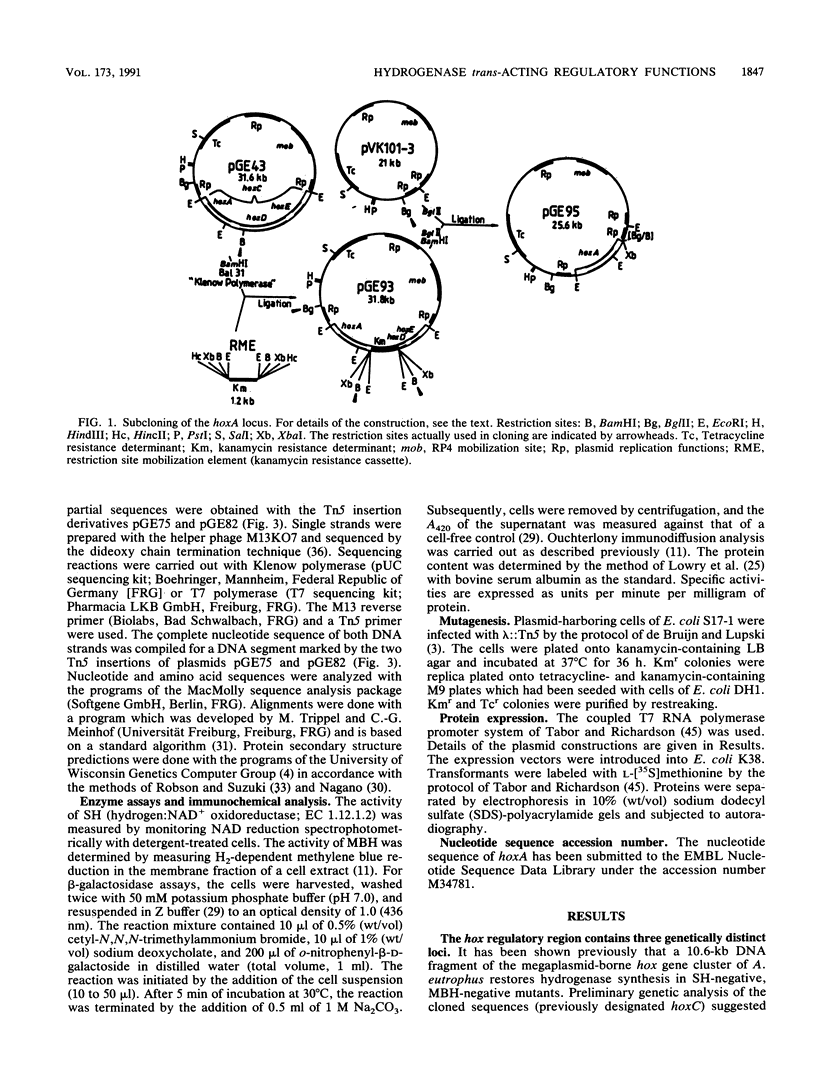
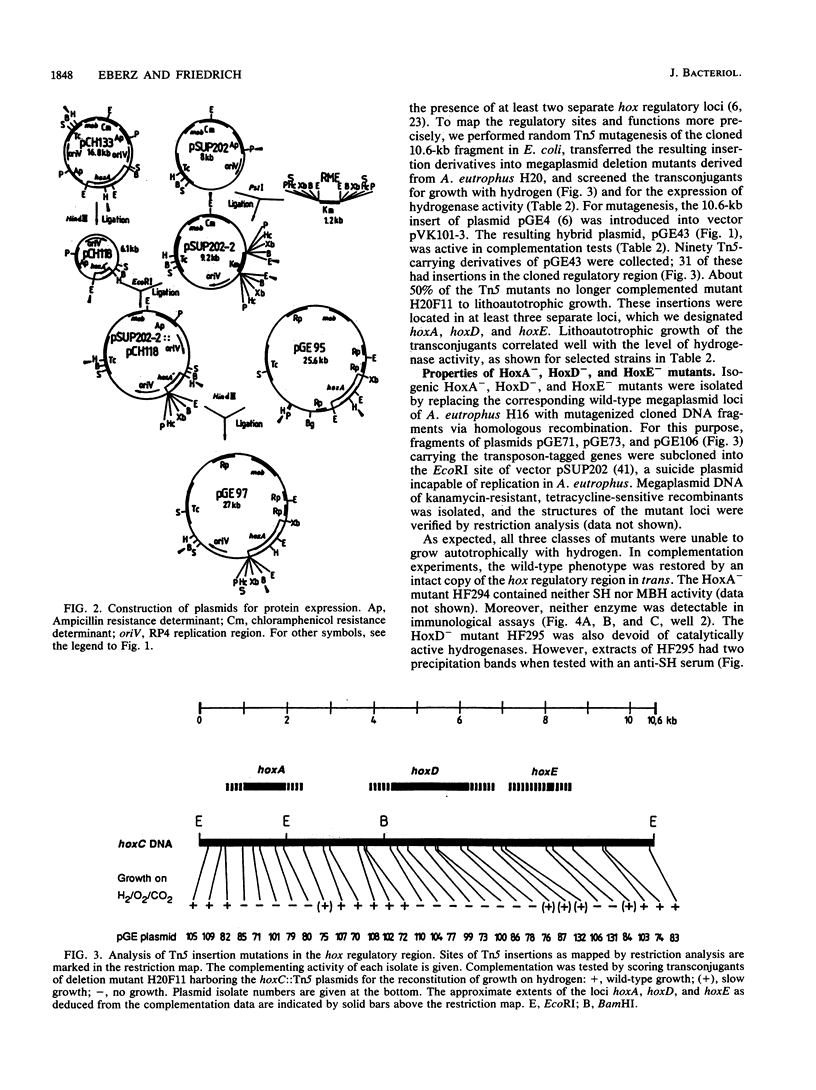
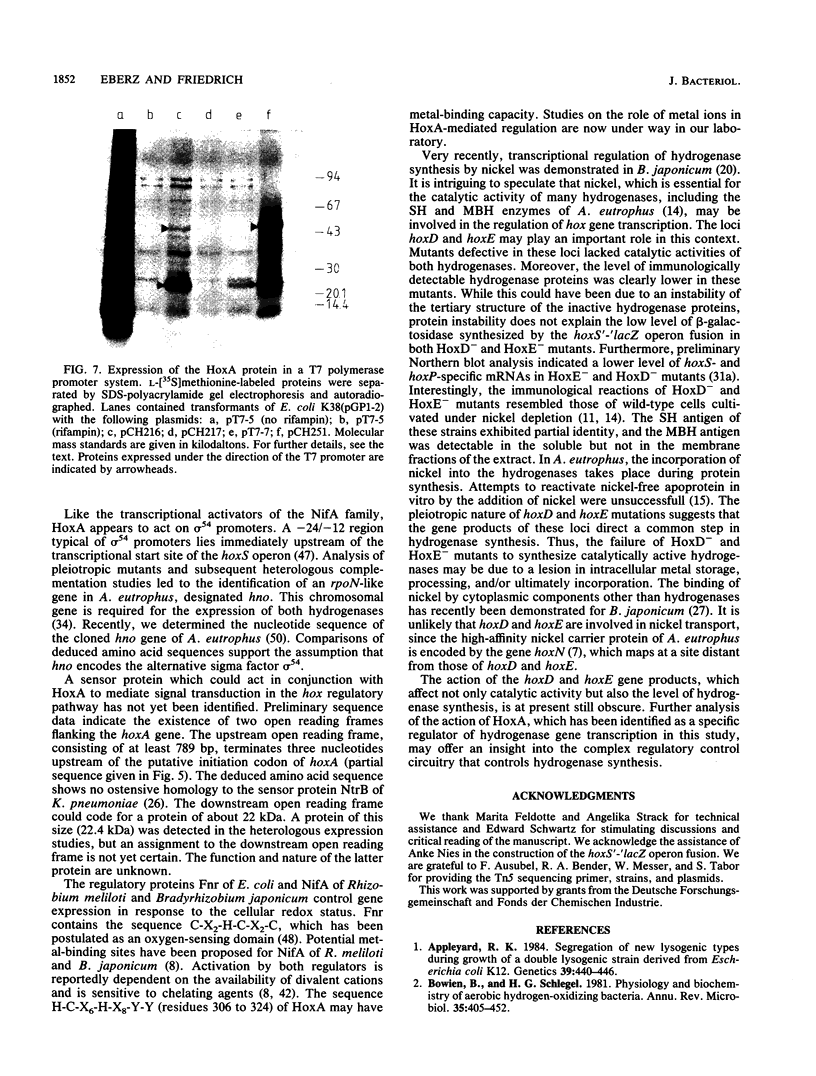
Random Tn5 mutagenesis of the regulatory region of megaplasmid pHG1 of Alcaligenes eutrophus led to the identification of three distinct loci designated hoxA, hoxD, and hoxE. Sequencing of the hoxA locus revealed an open reading frame which could code for a polypeptide of 482 amino acids with a molecular mass of 53.5 kDa. A protein of comparable apparent molecular mass was detected in heterologous expression studies with a plasmid-borne copy of the hoxA gene. Amino acid alignments revealed striking homologies between HoxA and the transcriptional activators NifA and NtrC of Klebsiella pneumoniae and HydG of Escherichia coli. HoxA- mutants of A. eutrophus lacked both NAD-reducing soluble hydrogenase and membrane-bound hydrogenase. In HoxA- mutants, the synthesis of beta-galactosidase from a hoxS'-'lacZ operon fusion was drastically reduced, indicating that HoxA is essential for the transcription of hydrogenase genes. Mutants defective in hoxD and hoxE also lacked the catalytic activities of the two hydrogenases; however, in contrast to HoxA- mutants, they contained immunologically detectable NAD-reducing soluble hydrogenase and membrane-bound hydrogenase proteins, although at a reduced level. The low hydrogenase content in the HoxD- and HoxE- mutants correlated with a decrease in beta-galactosidase synthesized under the direction of a hoxS'-'lacZ operon fusion. Thus, hoxD and hoxE apparently intervene both in the regulation of hydrogenase synthesis and in subsequent steps leading to the formation of catalytically active enzymes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberz G., Hogrefe C., Kortlüke C., Kamienski A., Friedrich B. Molecular cloning of structural and regulatory hydrogenase (hox) genes of Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):636–641. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.636-641.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Heine E., Finck A., Friedrich C. G. Nickel requirement for active hydrogenase formation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1144-1149.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Hogrefe C., Schlegel H. G. Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.198-205.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G. Depression of hydrogenase during limitation of electron donors and derepression of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during carbon limitation of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.203-210.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G., Friedrich B. Regulation of hydrogenase formation is temperature sensitive and plasmid coded in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.176-181.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G., Schneider K., Friedrich B. Nickel in the catalytically active hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):42–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.42-48.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogrefe C., Römermann D., Friedrich B. Alcaligenes eutrophus hydrogenase genes (Hox). J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.43-48.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Maier R. J. Transcriptional regulation of hydrogenase synthesis by nickel in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18729–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klintworth R., Husemann M., Salnikow J., Bowien B. Chromosomal and plasmid locations for phosphoribulokinase genes in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):954–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.954-956.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFarlane S. A., Merrick M. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrogen regulation gene ntrB and the glnA-ntrBC intergenic region of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7591–7606. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Pihl T. D., Stults L., Sray W. Nickel accumulation and storage in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1905–1911. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1905-1911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano K. Triplet information in helix prediction applied to the analysis of super-secondary structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):251–274. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Suzuki E. Conformational properties of amino acid residues in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):327–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Shearman C. A., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum is autoregulatory and in the presence of plant exudate induces the nodA,B,C genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3369–3373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römermann D., Warrelmann J., Bender R. A., Friedrich B. An rpoN-like gene of Alcaligenes eutrophus and Pseudomonas facilis controls expression of diverse metabolic pathways, including hydrogen oxidation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1093-1099.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Schlegel H. G. The membrane-bound hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus: II. Localization and immunological comparison with other hydrogenase systems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00422224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Schlegel H. G. Purification and properties of soluble hydrogenase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):66–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Roberts R. E., Guest J. R. FNR-dependent repression of the ndh gene of Escherichia coli and metal ion requirement for FNR-regulated gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Reijnders W. N., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Initial cloning and sequencing of hydHG, an operon homologous to ntrBC and regulating the labile hydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4448–4456. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4448-4456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Betcke A., Warnecke U., Böcker C., Zaborosch C., Friedrich B. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of the genes for the subunits of NAD-reducing hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2920–2929. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2920-2929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Guest J. R. Isolation and characterization of the Fnr protein, the transcriptional regulator of anaerobic electron transport in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




