Abstract
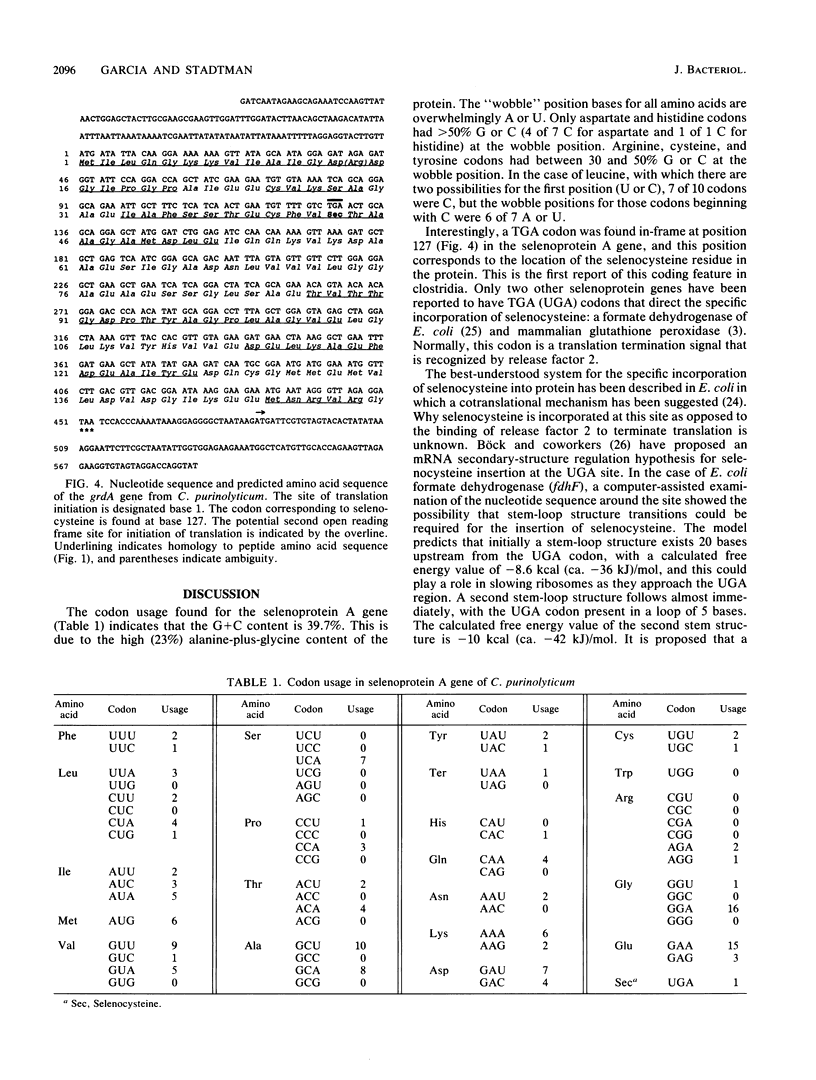
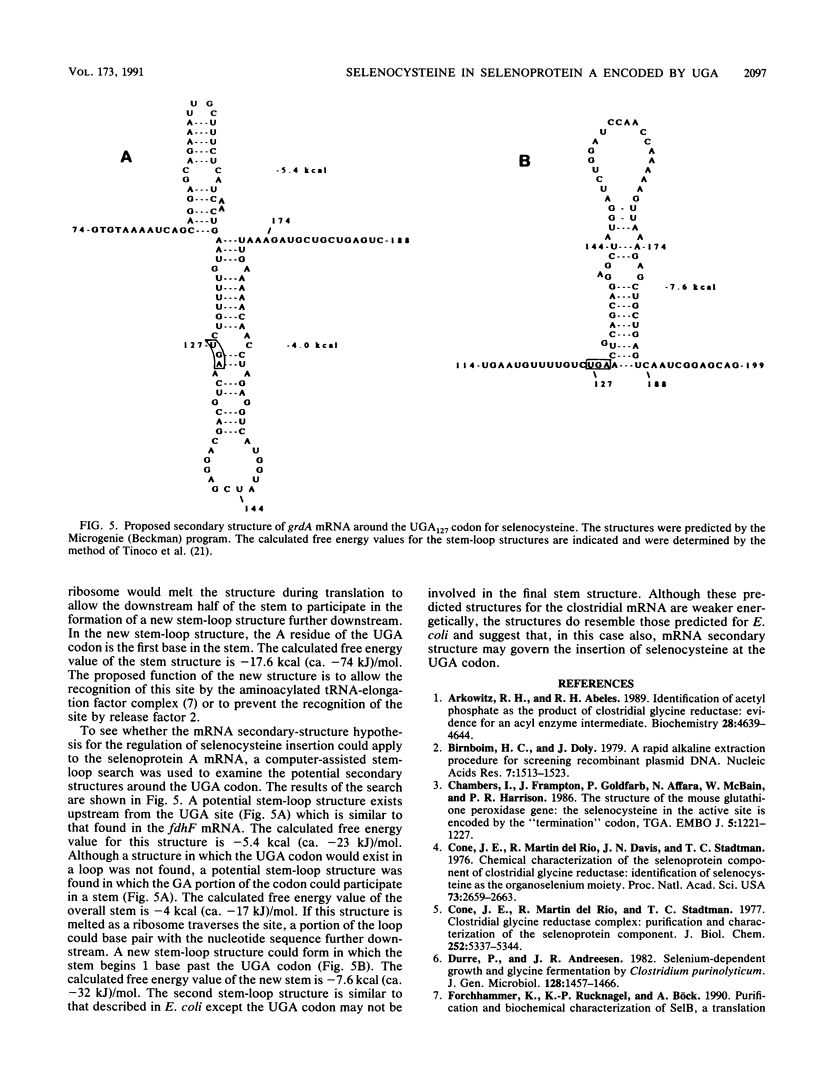
The gene encoding the selenoprotein A component of glycine reductase was isolated from Clostridium purinolyticum. The nucleotide sequence of this gene (grdA) was determined. The opal termination codon (TGA) was found in-frame at the position corresponding to the location of the selenocysteine residue in the gene product. A comparison of the nucleotide sequences and secondary mRNA structures corresponding to the selenoprotein A gene and the fdhF gene of Escherichia coli formate dehydrogenase shows that there is a similar potential for regulation of the specific insertion of selenocysteine at the UGA codon.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. E., Del Río R. M., Davis J. N., Stadtman T. C. Chemical characterization of the selenoprotein component of clostridial glycine reductase: identification of selenocysteine as the organoselenium moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. E., del Río R. M., Stadtman T. C. Clostridial glycine reductase complex. Purification and characterization of the selenoprotein component. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5337–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürre P., Andreesen J. R. Selenium-dependent growth and glycine fermentation by Clostridium purinolyticum. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jul;128(7):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-7-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. J., Subramani S., Scheffler I. E. Use of the DNA polymerase chain reaction for homology probing: isolation of partial cDNA or genomic clones encoding the iron-sulfur protein of succinate dehydrogenase from several species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1934–1938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., ELLIOTT P., TIEMANN L. Studies on the enzymic reduction of amino acids. III. Phosphate esterification coupled with glycine reduction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):961–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent glycine reductase: differences in physicochemical properties and biological activities of selenoprotein A components isolated from Clostridium sticklandii and Clostridium purinolyticum. Biofactors. 1988 Dec;1(4):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Stadtman T. C. Selenoprotein A of the clostridial glycine reductase complex: purification and amino acid sequence of the selenocysteine-containing peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):368–371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Glycine reduction to acetate and ammonia: identification of ferredoxin and another low molecular weight acidic protein as components of the reductase system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Selenium biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:111–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Specific occurrence of selenium in enzymes and amino acid tRNAs. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):375–379. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2445614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunde R. A. Molecular biology of selenoproteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 1990;10:451–474. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent clostridial glycine reductase. Purification and characterization of the two membrane-associated protein components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. C., Stadtman T. C. Purification of protein components of the clostridial glycine reductase system and characterization of protein A as a selenoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):366–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. R., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Clostridium acidiurici ("Clostridium acidi-urici") gene for 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase shows extensive amino acid homology with the trifunctional enzyme C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3255–3261. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3255-3261.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Cotranslational insertion of selenocysteine into formate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli directed by a UGA codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3156–3160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Stadtman T. C., Böck A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the selenocysteine-containing polypeptide of formate dehydrogenase (formate-hydrogen-lyase-linked) from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


