Abstract
The genome of Myxococcus xanthus, which is 9,454 kbp, is one of the largest bacterial genomes. The organization of the DNA and the distribution of genes encoding social and developmental behaviors were examined by using pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Intact genomic DNA was digested with AseI into 16 restriction fragments, which were separated by contour-clamped homogeneous electric field electrophoresis, purified, and radiolabeled. Each AseI fragment was hybridized to SpeI-digested DNA and to an M. xanthus genomic library contained in yeast artificial chromosomes. Some SpeI restriction fragments and yeast artificial chromosome clones contained AseI sites and hybridized with two different AseI restriction fragments, providing evidence for the juxtaposition of these AseI restriction fragments in the chromosome. The deduced AseI physical map is circular, suggesting that this bacterium contains a single, circular chromosome. Transposable elements shown by transduction to be in or near genes of interest were located on specific AseI restriction fragments by restriction analysis and Southern hybridization. Most AseI restriction fragments contained genes involved in social and developmental behaviors.
Full text
PDF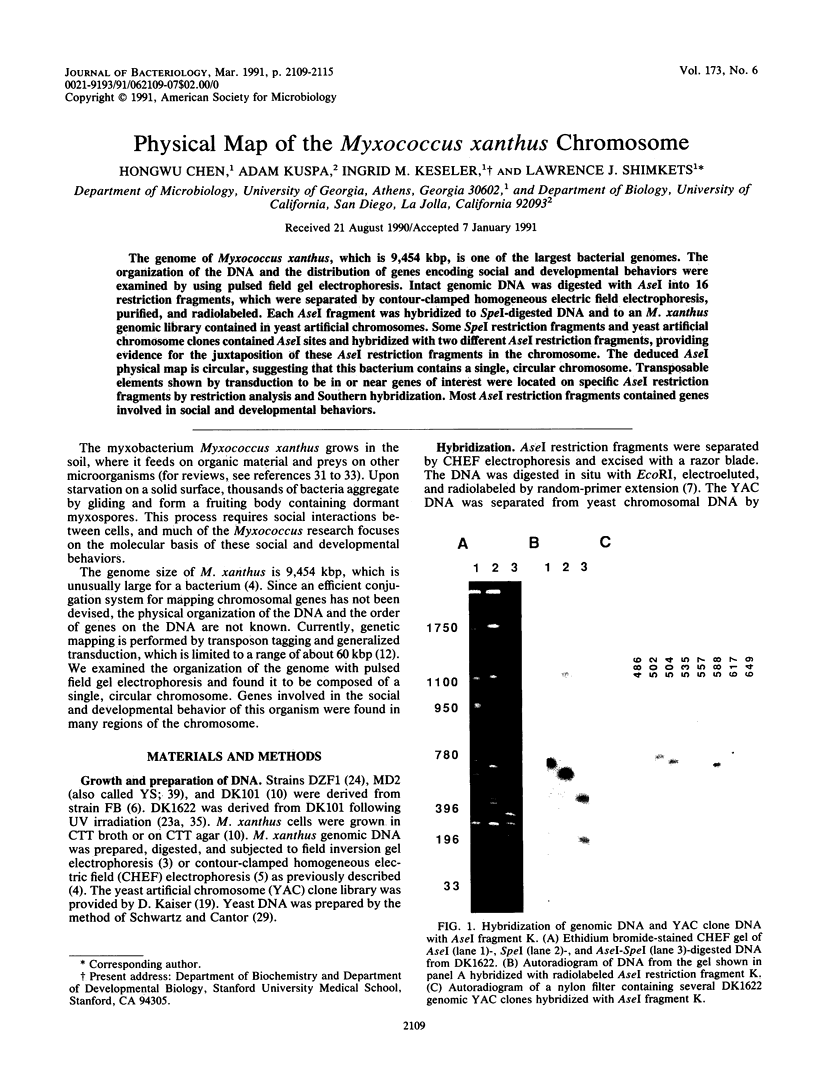






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackhart B. D., Zusman D. R. Cloning and complementation analysis of the "Frizzy" genes of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00383002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Keseler I. M., Shimkets L. J. Genome size of Myxococcus xanthus determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4206–4213. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4206-4213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. M., Kalos M., Zissler J. F. Isolation of cell surface antigen mutants of Myxococcus xanthus by use of monoclonal antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2033–2041. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2033-2041.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G., Fly S. Genetic identification and cloning of a gene required for developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5279–5288. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5279-5288.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalos M., Zissler J. F. Defects in contact-stimulated gliding during aggregation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6476–6493. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6476-6493.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. A global analysis of developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):252–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Introduction of transposon Tn5 into Myxococcus for analysis of developmental and other nonselectable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):425–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Genes required for developmental signalling in Myxococcus xanthus: three asg loci. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2762-2772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Vollrath D., Cheng Y., Kaiser D. Physical mapping of the Myxococcus xanthus genome by random cloning in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R., Kuner J., Hagen D., Manoil C., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions of Myxococcus xanthus: analysis of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1394–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1394-1404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Kaiser D. Accumulation of guanosine tetraphosphate and guanosine pentaphosphate in Myxococcus xanthus during starvation and myxospore formation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):297–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.297-304.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Sodergren E., Masuda T., Kaiser D. Systematic isolation of transducing phages for Myxococcus xanthus. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):44–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Genetic analysis of tag mutants of Myxococcus xanthus provides evidence for two developmental aggregation systems. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3868–3878. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3868-3878.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhie H. G., Shimkets L. J. Developmental bypass suppression of Myxococcus xanthus csgA mutations. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3268-3276.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Zusman D. R. Cloning of the gene for myxobacterial hemagglutinin and isolation and analysis of structural gene mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3801–3808. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3801-3808.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Role of autocide AMI in development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4307–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4307-4314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Asher S. J. Use of recombination techniques to examine the structure of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00338394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Induction of coordinated movement of Myxococcus xanthus cells. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):451–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.451-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Role of cell cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body formation. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.842-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. The role of the cell surface in social and adventurous behaviour of myxobacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1295–1299. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodergren E., Kaiser D. Insertions of Tn5 near genes that govern stimulatable cell motility in Myxococcus. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starich T., Cordes P., Zissler J. Transposon tagging to detect a latent virus in Myxococcus xanthus. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):541–543. doi: 10.1126/science.2996138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starich T., Zissler J. Movement of multiple DNA units between Myxococcus xanthus cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2323–2336. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2323-2336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Morphogenesis and developmental interactions in myxobacteria. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):516–523. doi: 10.1126/science.806967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




