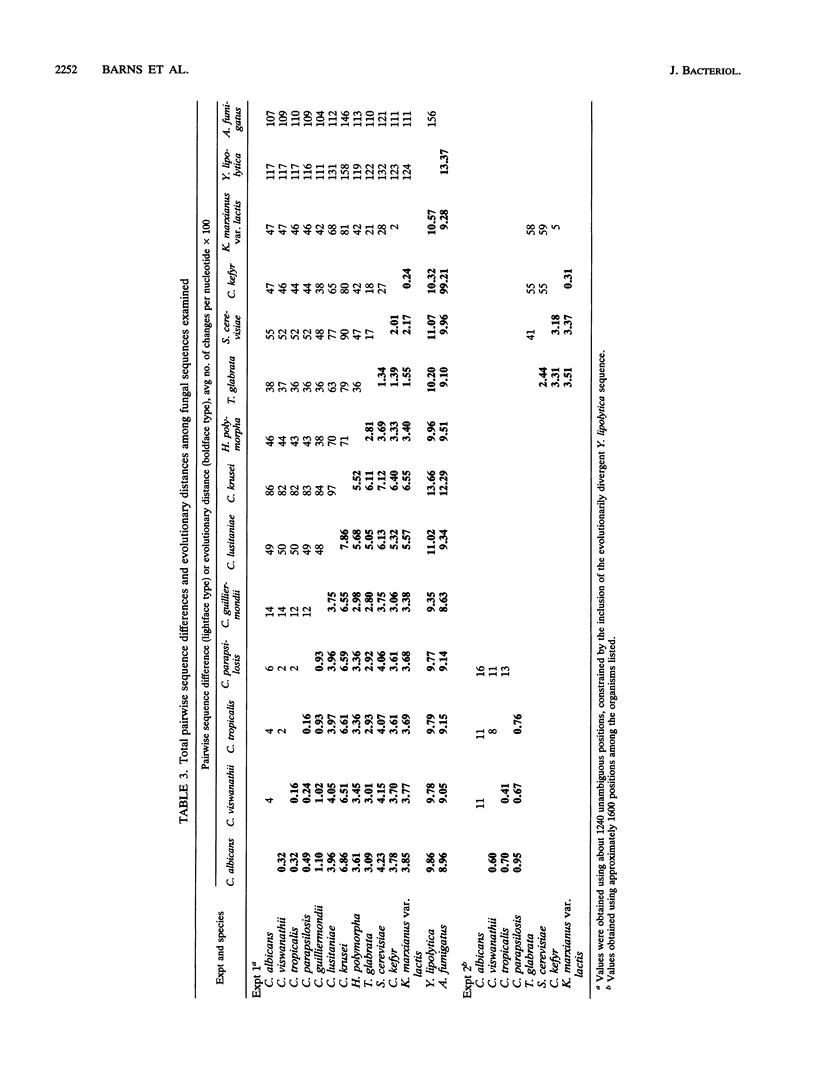
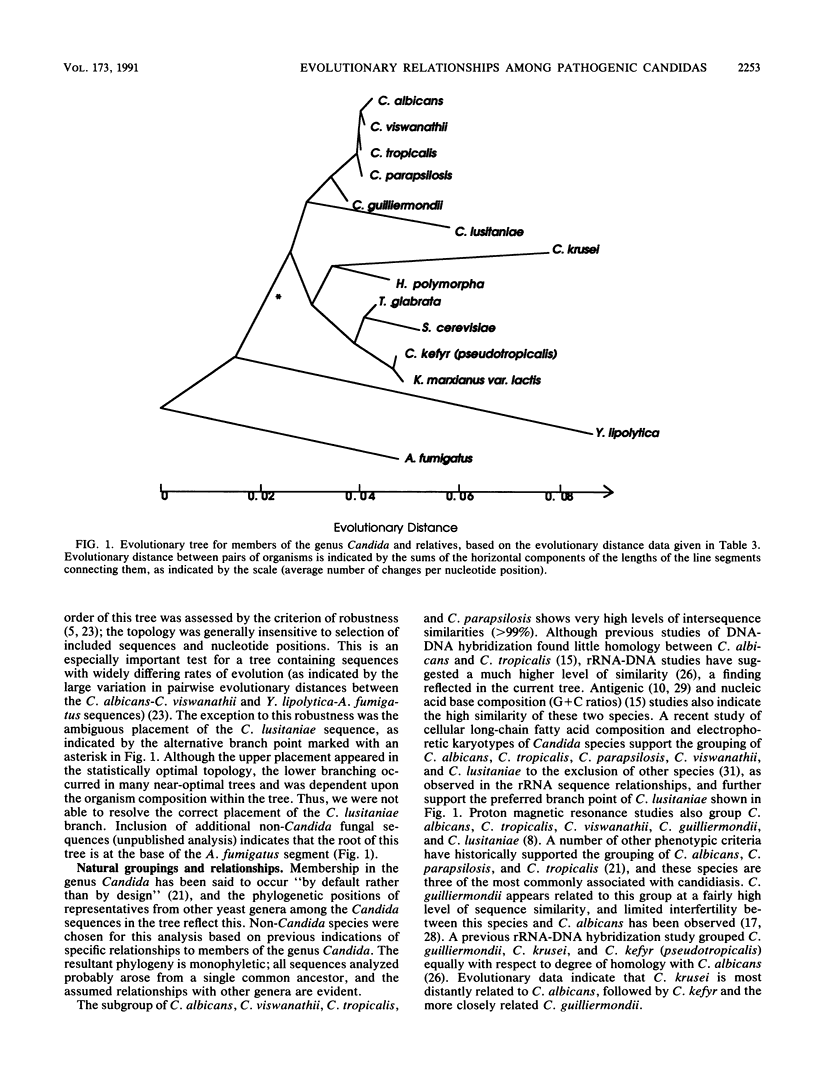
Abstract
Small subunit rRNA sequences have been determined for 10 of the most clinically important pathogenic species of the yeast genus Candida (including Torulopsis [Candida] glabrata and Yarrowia [Candida] lipolytica) and for Hansenula polymorpha. Phylogenetic analyses of these sequences and those of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces marxianus var. lactis, and Aspergillus fumigatus indicate that Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. viswanathii form a subgroup within the genus. The remaining significant pathogen, T. glabrata, falls into a second, distinct subgroup and is specifically related to S. cerevisiae and more distantly related to C. kefyr (psuedotropicalis) and K. marxianus var. lactis. The 18S rRNA sequence of Y. lipolytica has evolved rapidly in relation to the other Candida sequences examined and appears to be only distantly related to them. As anticipated, species of several other genera appear to bear specific relationships to members of the genus Candida.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak A. L., Stenderup A. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology in yeasts. Genetic relatedness within the genus Candida. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;59(1):21–30. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwood H. J., Olsen G. J., Sogin M. L. The small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences from the hypotrichous ciliates Oxytricha nova and Stylonychia pustulata. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Sep;2(5):399–410. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field K. G., Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Ghiselin M. T., Raff E. C., Pace N. R., Raff R. A. Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):748–753. doi: 10.1126/science.3277277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Margoliash E. Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):279–284. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O., LOEWE J. Antigenic studies of Candida. II. Antigenic relation of Candida albicans group A and group B to Candida stellatoidea and Candida tropicalis. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:574–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.574-577.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman C. P. Synonomy of the yeast genera Hansenula and Pichia demonstrated through comparisons of deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1984;50(3):209–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02342132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Rikkerink E. H., Magee B. B. Methods for the genetics and molecular biology of Candida albicans. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleszka R., Clark-Walker G. D. Sequence of the gene for the cytoplasmic ribosomal RNA small subunit from Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1889–1889. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medlin L., Elwood H. J., Stickel S., Sogin M. L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Earliest phylogenetic branchings: comparing rRNA-based evolutionary trees inferred with various techniques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:825–837. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Phylogenetic analysis using ribosomal RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:793–812. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Eylan E. Genetic relatedness of Candida albicans to asporogenous and ascosporogenous yeasts as reflected by nucleic acid homologies. Microbios. 1974 Jan;9(33):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Miotto K., Miller L. Primary structure of the Neurospora crassa small subunit ribosomal RNA coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9540–9540. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Rogers A. L., Magee P. T. Inter- and intra-species crosses between Candida albicans and Candida guilliermondii. Yeast. 1986 Mar;2(1):53–58. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C. E., Kaufman L. Application of agglutinins for the rapid and accurate identification of medically important Candida species. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):830–836. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.830-836.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. What are mycoplasmas: the relationship of tempo and mode in bacterial evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02115648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters J., Erdmann V. A. Compilation of 5S rRNA and 5S rRNA gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r1–70. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heerikhuizen H., Ykema A., Klootwijk J., Gaillardin C., Ballas C., Fournier P. Heterogeneity in the ribosomal RNA genes of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica; cloning and analysis of two size classes of repeats. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


