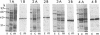Abstract
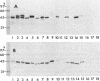
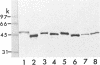
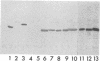
It was demonstrated that mycoplasmas, gram-negative bacteria, and certain gram-positive bacteria share a similar protein antigen with a molecular weight ranging from 42,000 to 48,000. Western blotting (immunoblotting) with an antibody specific to a 43-kDa membrane protein of Mycoplasma fermentans showed the existence of this protein antigen in all Mycoplasma spp. tested (14 species), Acholeplasma laidlawii (1 strain), and gram-negative bacteria (8 species) but only in Staphylococcus aureus of four gram-positive species tested. Neither Ureaplasma urealyticum nor mammalian cell cultures showed any cross-reactions with this antibody. These proteins were found in both cytoplasmic and membrane fractions of mycoplasma cells but were not exposed on the surface of mycoplasmal or bacterial cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blazek R., Schmitt K., Krafft U., Hadding U. Fast and simple procedure for the detection of cell culture mycoplasmas using a single monoclonal antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 7;131(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90191-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimolai N., Bryan L. E., To M., Woods D. E. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2136–2139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2136-2139.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Schmidhauser C., Parish R. W., Wettenhall R. E., Schmidt T. A mycoplasma high-affinity transport system and the in vitro invasiveness of mouse sarcoma cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3963–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Alloing G., Schmidt T., Claverys J. P., Dudler R., Hofnung M. Evidence for high affinity binding-protein dependent transport systems in gram-positive bacteria and in Mycoplasma. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3971–3974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Bonissol C., Stoiljkovic B., Ito K. Demonstration of cross-reactive antibodies to mycoplasmas in human sera by ELISA and immunoblotting. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(7):639–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Sasaki Y., Matsumura T., Oyama N., Koshimizu K. Characterization of a strain of Mycoplasma hominis lacking 120 kDa membrane protein isolated from Vero cell culture. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(5):423–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser C., Dudler R., Schmidt T., Parish R. W. A mycoplasmal protein influences tumour cell invasiveness and contact inhibition in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1990 Mar;95(Pt 3):499–506. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D. Urease color test medium U-9 for the detection and identification of "T" mycoplasms in clinical material. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):539–543. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.539-543.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]