Abstract
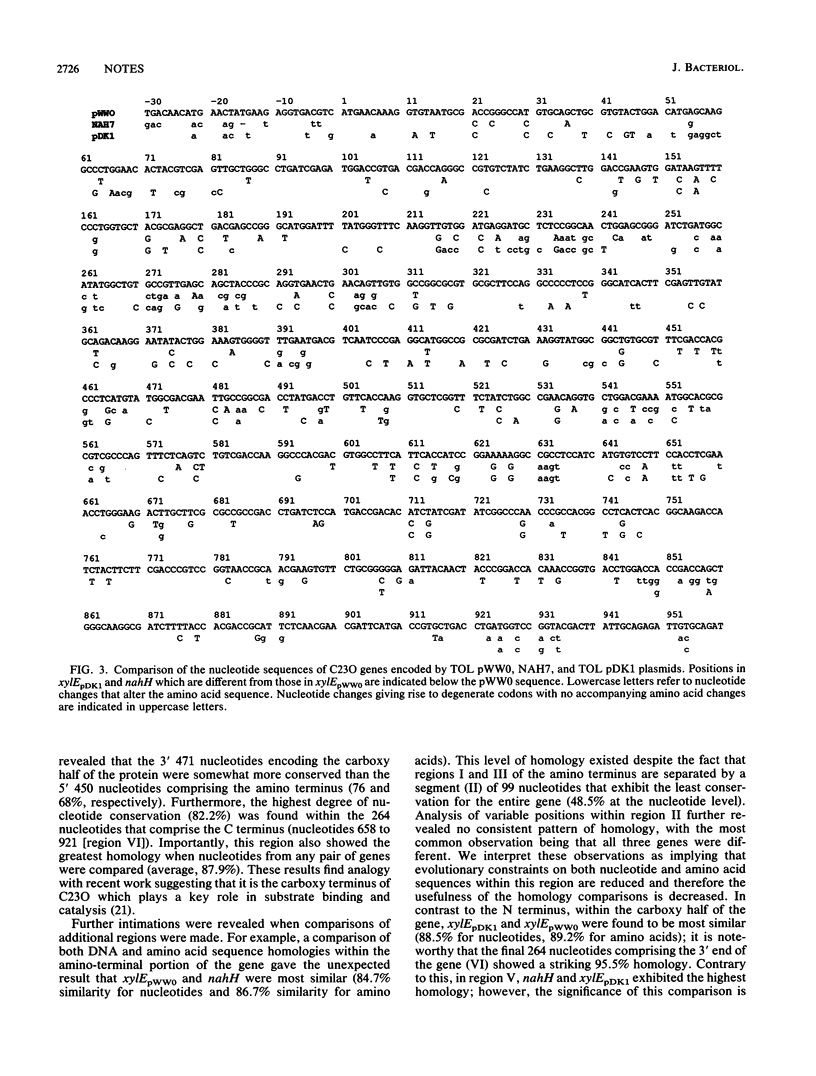
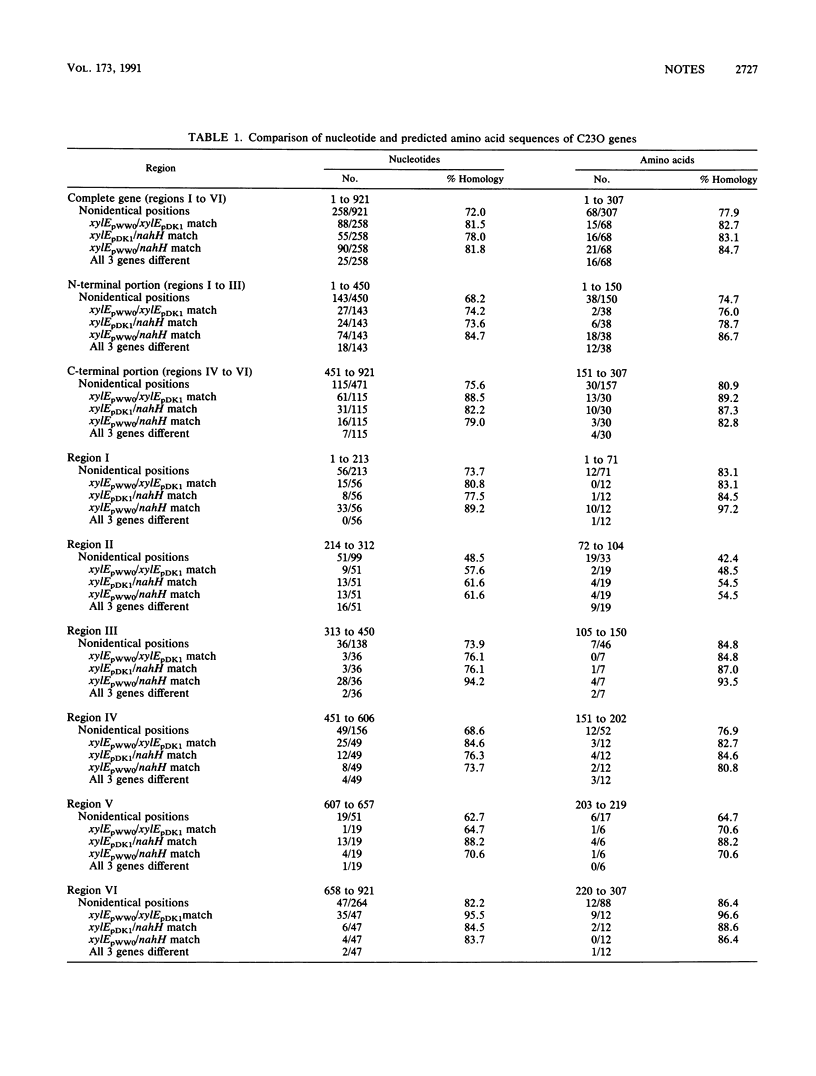
Detailed restriction and nucleotide sequence analysis of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid pDK1 xylE gene revealed significant homology with isofunctional xylE (81.5%) and nahH (78.0%) genes from the TOL pWW0 and NAH7 plasmids. The highest degrees of nucleotide and apparent amino acid conservation (82.2 and 86.4%, respectively) among all three genes were found to exist within a region comprising 264 nucleotides encoding the C terminus. A comparison of localized regions revealed significantly greater homology between xylEpWW0 and xylEpDK1 within the C-terminal region, whereas xylEpWW0 and nahH showed greater similarity at the N terminus. The possibility that xylEpWW0 may represent a genetic hybrid of xylEpDK1 and nahH is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burlage R. S., Hooper S. W., Sayler G. S. The TOL (pWW0) catabolic plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1323-1328.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield L. K., Williams P. A. Naturally occurring TOL plasmids in Pseudomonas strains carry either two homologous or two nonhomologous catechol 2,3-oxygenase genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):878–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.878-885.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the trpB gene in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Gunsalus I. C. Nucleotide sequence and expression of gene nahH of plasmid NAH7 and homology with gene xylE of TOL pWWO. Gene. 1987;55(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M., Wasserfallen A., Bairoch A. Evolutionary relationships between catabolic pathways for aromatics: conservation of gene order and nucleotide sequences of catechol oxidation genes of pWW0 and NAH7 plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00325689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L. Evolving theories of enzyme evolution. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Gunsalus I. C. Isolation of metabolic plasmid DNA from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. B., Merkel W. K., Nichols B. P. Evolution of glutamine amidotransferase genes. Nucleotide sequences of the pabA genes from Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella aerogenes and Serratia marcescens. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil H., Lebens M. R., Williams P. A. TOL plasmid pWW15 contains two nonhomologous, independently regulated catechol 2,3-oxygenase genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):248–255. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.248-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D. A., Chapman P. J. Isolation and characterization of spontaneously occurring TOL plasmid mutants of Pseudomonas putida HS1. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):952–964. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.952-964.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M., Nakazawa T., Inouye S., Ebina Y., Nakazawa A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the metapyrocatechase gene on the TOI plasmid of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2923–2928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne D. J., Pickup R. W., Williams P. A. The presence of two complete homologous meta pathway operons on TOL plasmid pWW53. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Nov;134(11):2965–2975. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-11-2965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. E., Williams P. A. Physical and functional mapping of two cointegrate plasmids derived from RP4 and TOL plasmid pDK1. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Sep;134(9):2463–2474. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-9-2463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Assinder S. J., Shaw L. E. Construction of hybrid xylE genes between the two duplicate homologous genes from TOL plasmid pWW53: comparison of the kinetic properties of the gene products. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Aug;136(8):1583–1589. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-8-1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


