Abstract
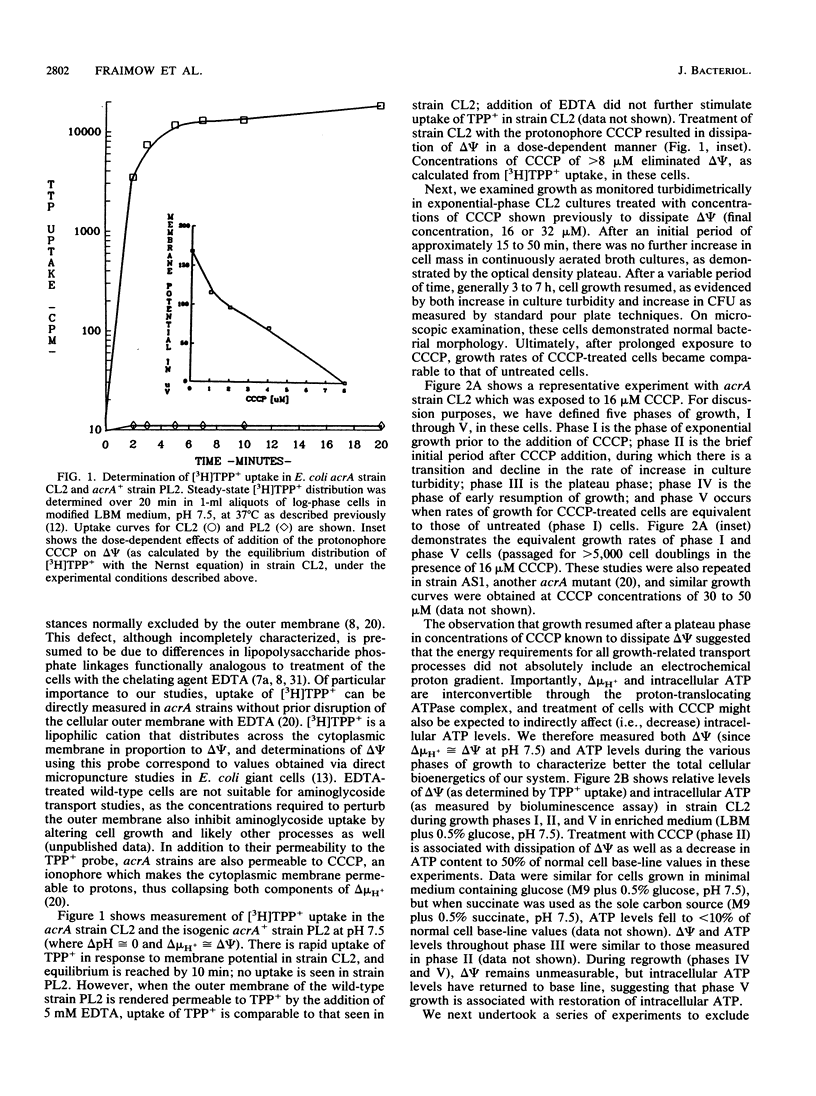
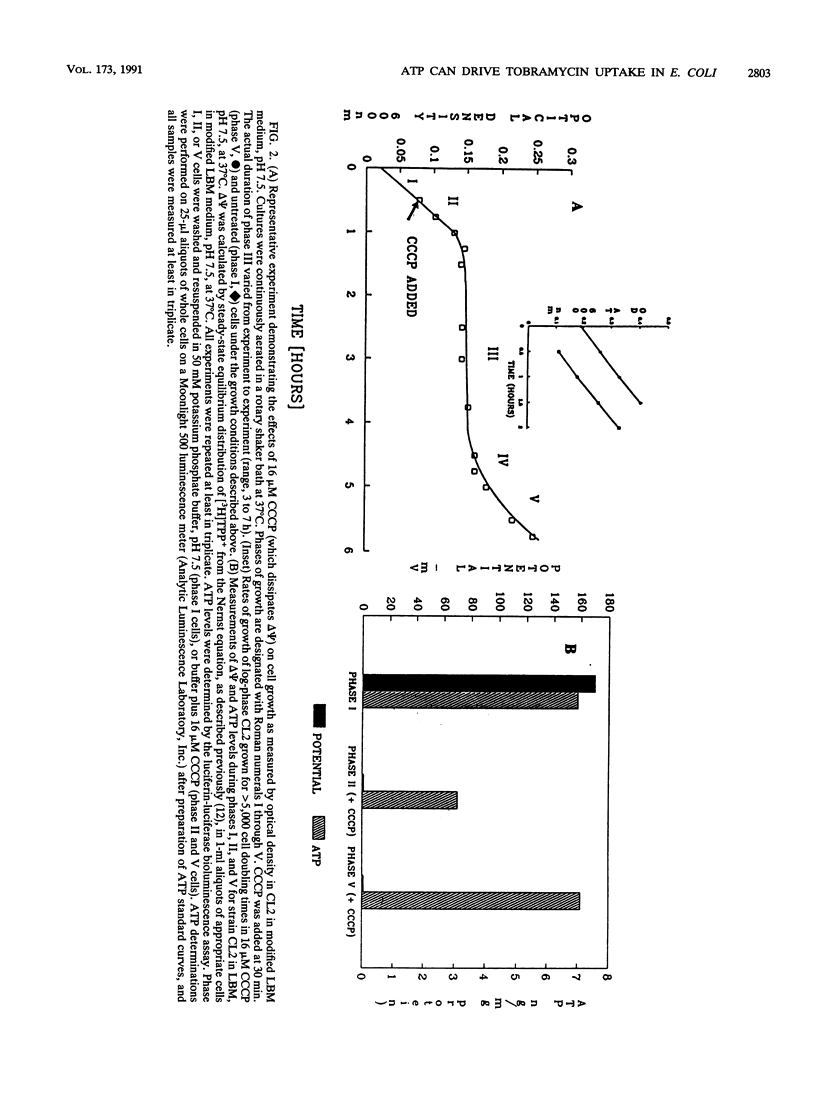
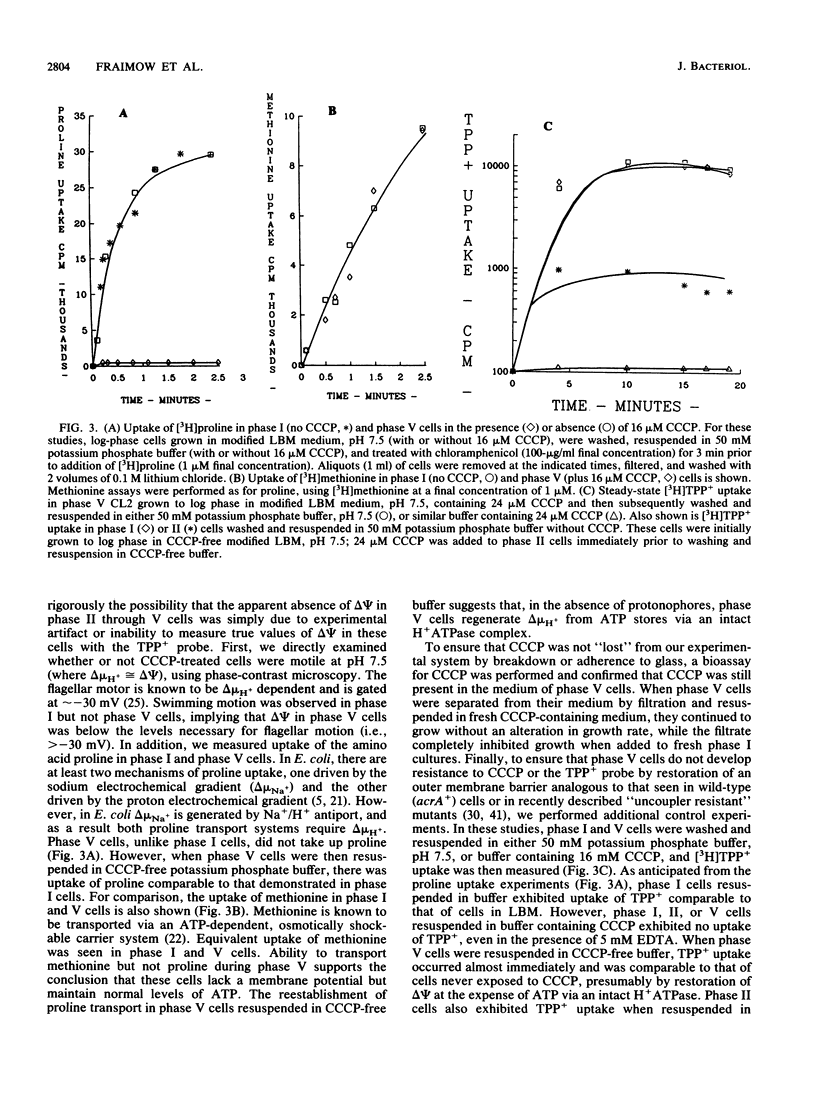
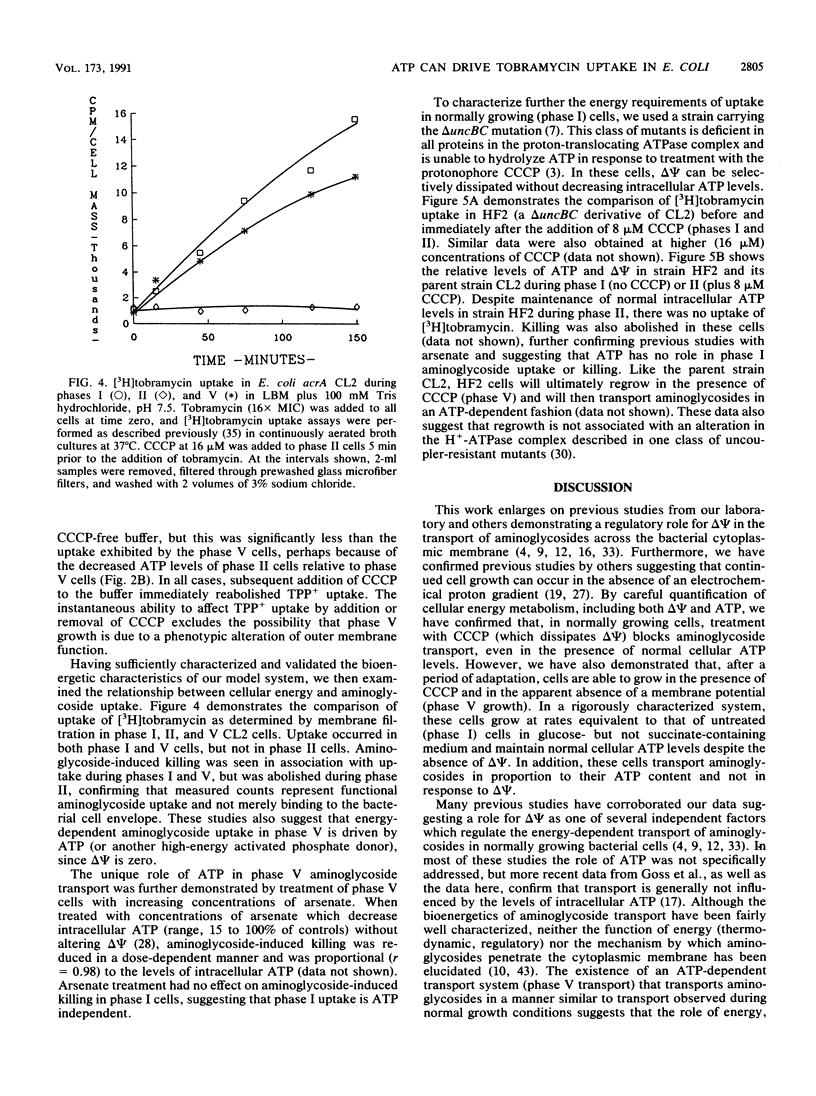
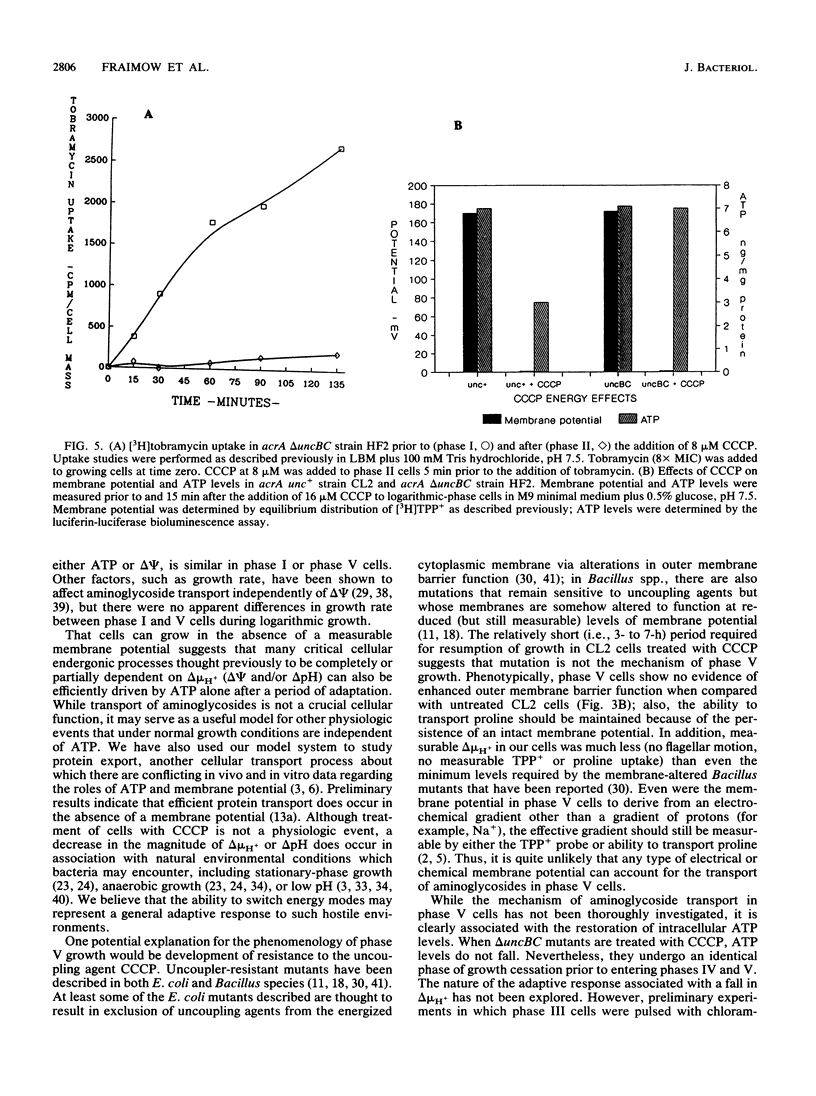
Aminoglycoside antibiotics such as streptomycin and tobramycin must traverse the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane prior to initiating lethal effects. Previous data on Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis have demonstrated that transport of aminoglycosides is regulated by delta psi, the electrical component of the proton motive force. However, several laboratories have observed that growth of bacterial cells can occur in the apparent absence of delta psi, and we wished to confirm these studies with E. coli and further investigate whether transport of aminoglycosides could occur in the absence of a membrane potential. Treatment of acrA strain CL2 with the protonophore carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) dissipated delta psi, decreased intracellular ATP levels, and resulted in cessation of growth; after a variable period of time (3 to 7 h), growth resumed, ultimately achieving growth rates comparable to those of untreated cells. Absence of delta psi in these cells was confirmed by absence of [3H]tetraphenyl phosphonium+ uptake as measured by membrane filtration, lack of flagellar motion, and inability of these cells to transport proline (but not methionine). Regrowth was associated with restoration of normal intracellular ATP as measured by luciferin-luciferase bioluminescence assay. Unlike unacclimatized CL2 cells treated with CCCP, these cells transported [3H]tobramycin similarly to untreated cells; aminoglycoside-induced killing was seen in association with transport. These studies suggest that under certain circumstances aminoglycoside transport can be driven by ATP (or other high-energy activated phosphate donors) alone, in the absence of a measurable delta psi. delta uncBC mutants of CL2 incapable of interconverting delta psi and ATP were treated with CCCP, resulting in dissipation of delta psi but no alteration in ATP content. Despite maintenance of normal ATP, there was no transport of [3H] bramycin, confirming that under normal growth conditions ATP has no role in the transport of aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Randall L. L. The requirement for energy during export of beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is fulfilled by the total protonmotive force. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):895–900. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):835–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Higgins C. F., Booth I. R. Proline uptake through the major transport system of Salmonella typhimurium is coupled to sodium ions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.22-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. ATP is essential for protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. Effects of nucleotides on ATP-dependent protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):828–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.828-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. G., Jr, Leive L. Two mutations which affect the barrier function of the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):899–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.899-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damper P. D., Epstein W. Role of the membrane potential in bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):803–808. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. Mechanism of bactericidal action of aminoglycosides. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):341–350. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.341-350.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Lang D. R. Mutants of Bacillus megaterium resistant to uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5936–5938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Quantitative association between electrical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane and early gentamicin uptake and killing in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):863–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.863-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Porter J. S., Slayman C. L., Kaback H. R. Quantitative measurements of membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I., Kaback H. R. Electrochemical proton gradient in Micrococcus lysodeikticus cells and membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):651–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.651-658.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman S., Saunders V. A. Accumulation of gentamicin by Staphylococcus aureus: the role of the transmembrane electrical potential. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jan;17(1):37–44. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. R., Spicer A. B., Nichols W. W. Bioenergetics of dihydrostreptomycin transport by Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Clejan S., Falk L. H., Hicks D. B., Krulwich T. A. Isolation and characterization of uncoupler-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4469–4478. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4469-4478.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Van Brunt J. Circulation of H+ and K+ across the plasma membrane is not obligatory for bacterial growth. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):372–373. doi: 10.1126/science.69317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Matsuura S., Mochizuki N., Mutoh N., Imae Y. Use of lipophilic cation-permeable mutants for measurement of transmembrane electrical potential in metabolizing cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):399–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.399-405.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Winkler H. H. Energy coupling for methionine transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.985-991.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Effects of aerobiosis and nitrogen source on the proton motive force in growing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):377–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.377-384.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.369-376.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. Proton chemical potential, proton electrical potential and bacterial motility. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):599–614. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Unemoto T., Kobayashi H. Proton motive force is not obligatory for growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1074–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1074-1077.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L., Boyer P. D. Energization of active transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M., Harris M. Effects of streptomycin in bacterial cultures growing at different rates; interaction with bacterial ribosomes in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1969 May 1;9(1):42–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Quirk P. G., Guffanti A. A. Uncoupler-resistant mutants of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):52–65. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.52-65.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential in anaerobically growing Staphylococcus aureus and its relationship to gentamicin uptake. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):526–530. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir M. E., Ballesteros M., Wallace B. J. Respiration rate, growth rate and the accumulation of streptomycin in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2573–2579. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir M. E., van Heeswyck R. S., Wallace B. J. Effect of growth rate on streptomycin accumulation by Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2015–2022. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk P. G., Jones M. R., Haworth R. S., Beechey R. B., Campbell I. D. Uncoupler resistance in Escherichia coli: the role of cellular respiration. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Oct;135(10):2577–2587. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-10-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber H. W., Mueller J. P., Miller P. F., Arrow A. S. Bacterial uptake of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):439–457. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.439-457.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


