Abstract
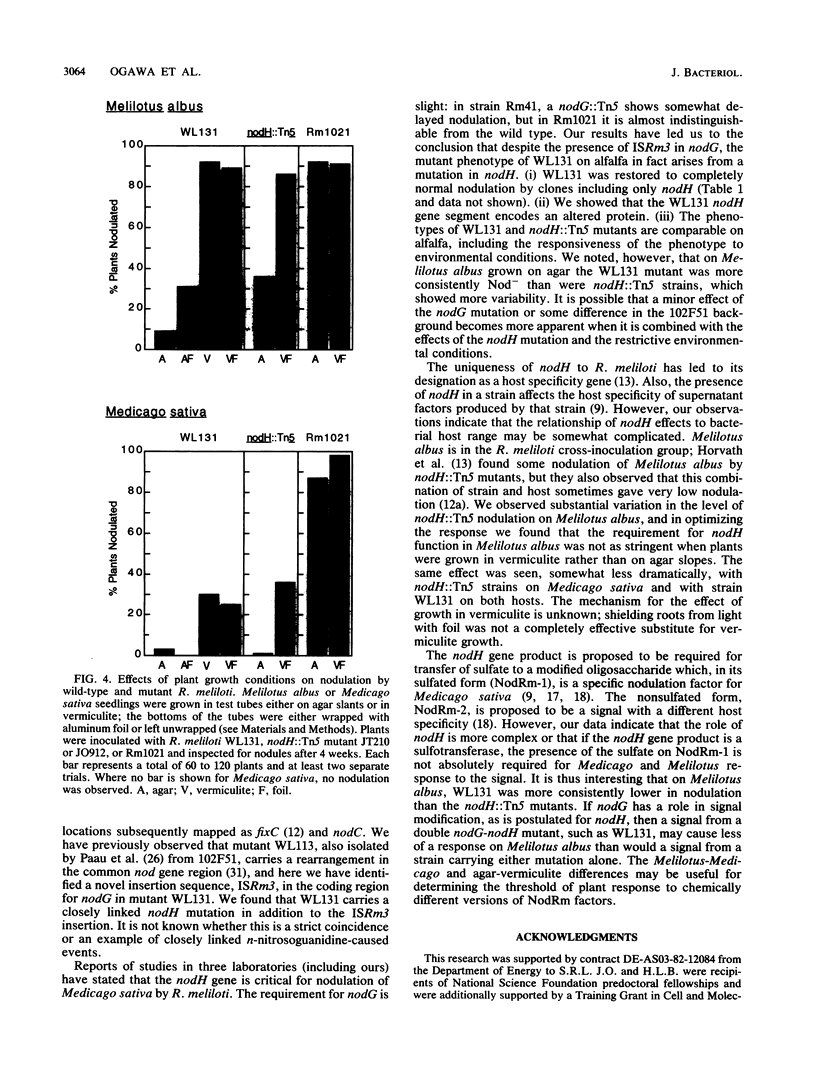
Nodulation (nod) genes are required for invasion of legumes by Rhizobium bacteria. Mutant WL131 is a derivative of 102F51 that has a severe Nod- phenotype on alfalfa. Upon examination of the extended DNA region containing host-specific nodulation genes nodFEG and nodH, we found that the nodG gene of WL131 bears a novel insertion sequence, ISRm3. Complementation studies implied, however, that the phenotype on alfalfa correlated with the nodH locus. We found that nodH in WL131 encodes an altered gene product. Correlation of the WL131 defect with nodH was also supported by phenotypic behavior. Each mutation affected nodulation more severely on alfalfa (Medicago sativa) than on sweet clover (Melilotus albus). However, we found that the degree of requirement for nodH in nodulation varied with the conditions under which the plant was grown.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes E., Sharma S. B., Maillet F., Vasse J., Truchet G., Rosenberg C. The Rhizobium meliloti host range nodQ gene encodes a protein which shares homology with translation elongation and initiation factors. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):745–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Maillet F., Martinez E., Dénarié J., Truchet G. Assignment of symbiotic developmental phenotypes to common and specific nodulation (nod) genetic loci of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1075–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1075-1086.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Sharma S. B. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti RCR2011 genes involved in host specificity of nodulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7453–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusha I., Kovalenko S., Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti insertion element ISRm2 and its use for identification of the fixX gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1403–1409. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1403-1409.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes: identification of nodDABC gene products, purification of nodA protein, and expression of nodA in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):591–599. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.591-599.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Swanson J. A., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. II. Nucleotide Sequence, Transcription Start Sites and Protein Products. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):191–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Tu J. K., Long S. R. Conserved Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1432–1435. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1432-1435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Smith C. A. Effects of Rhizobium meliloti nif and fix mutants on alfalfa root nodule development. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1137-1146.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Kondorosi E., John M., Schmidt J., Török I., Györgypal Z., Barabas I., Wieneke U., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. W., Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Physical and genetic map of a Rhizobium meliloti nodulation gene region and nucleotide sequence of nodC. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.469-476.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:483–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Signer E. R. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2076–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Leps W. T., Brill W. J. Agglutinin from Alfalfa Necessary for Binding and Nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1513–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4515.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Long S. R., Meade H. M., van den Bos R. C., Ausubel F. M. ISRm1: A Rhizobium meliloti insertion sequence that transposes preferentially into nitrogen fixation genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):405–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwedock J., Long S. R. ATP sulphurylase activity of the nodP and nodQ gene products of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):644–647. doi: 10.1038/348644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwedock J., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence and protein products of two new nodulation genes of Rhizobium meliloti, nodP and nodQ. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 Jul-Aug;2(4):181–194. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers R., LaRue T. A. Legume agglutinins that bind to Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.784-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. A., Tu J. K., Ogawa J., Sanga R., Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. I. Phenotypes of Tn5 Insertion Mutants. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):181–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]