Abstract
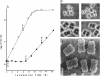
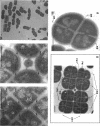
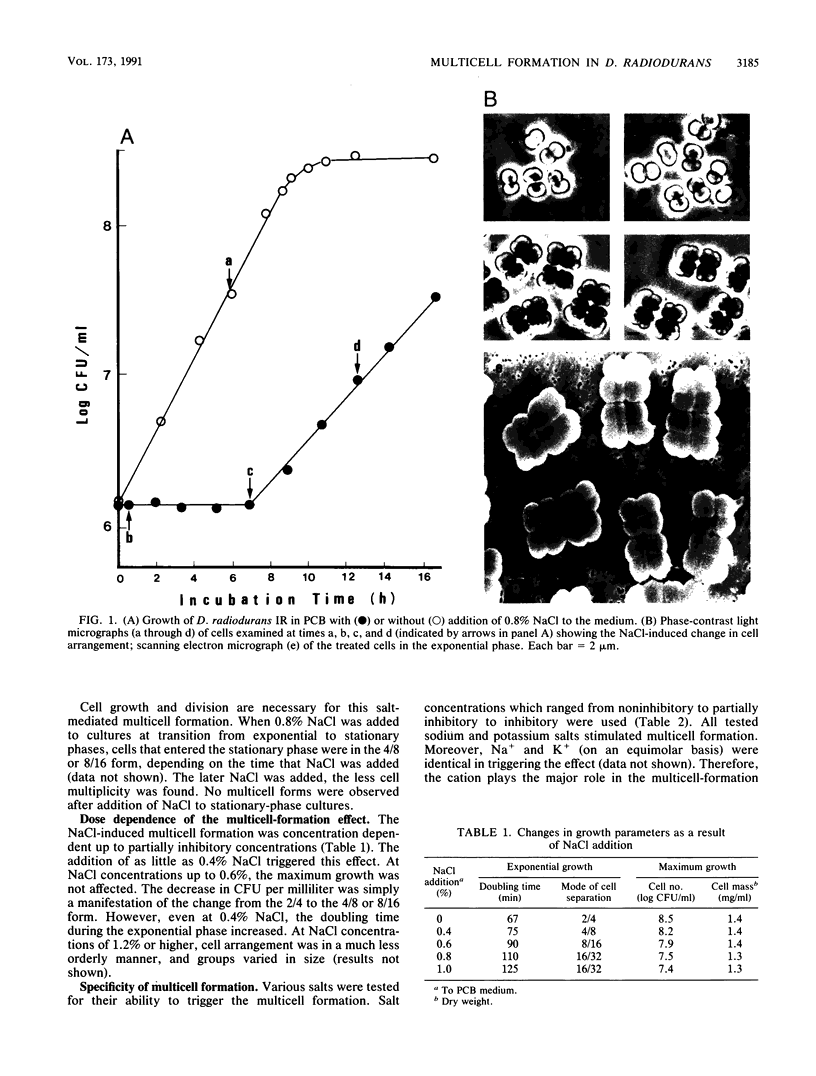
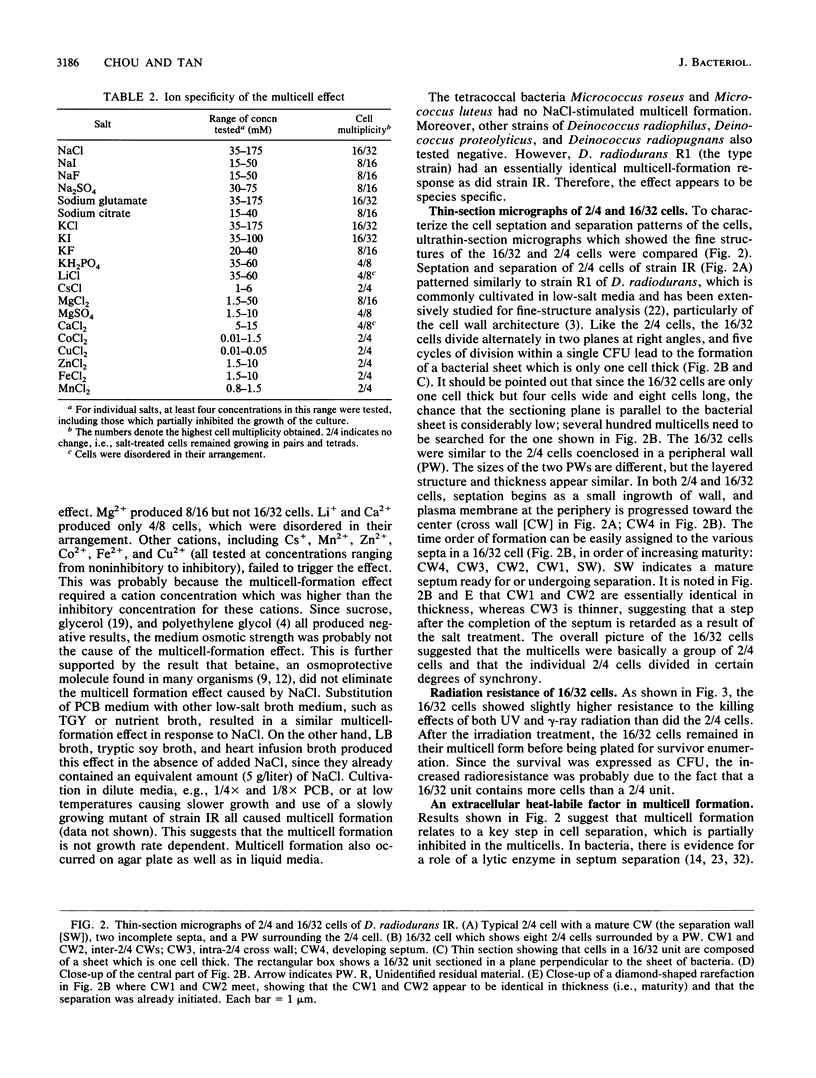
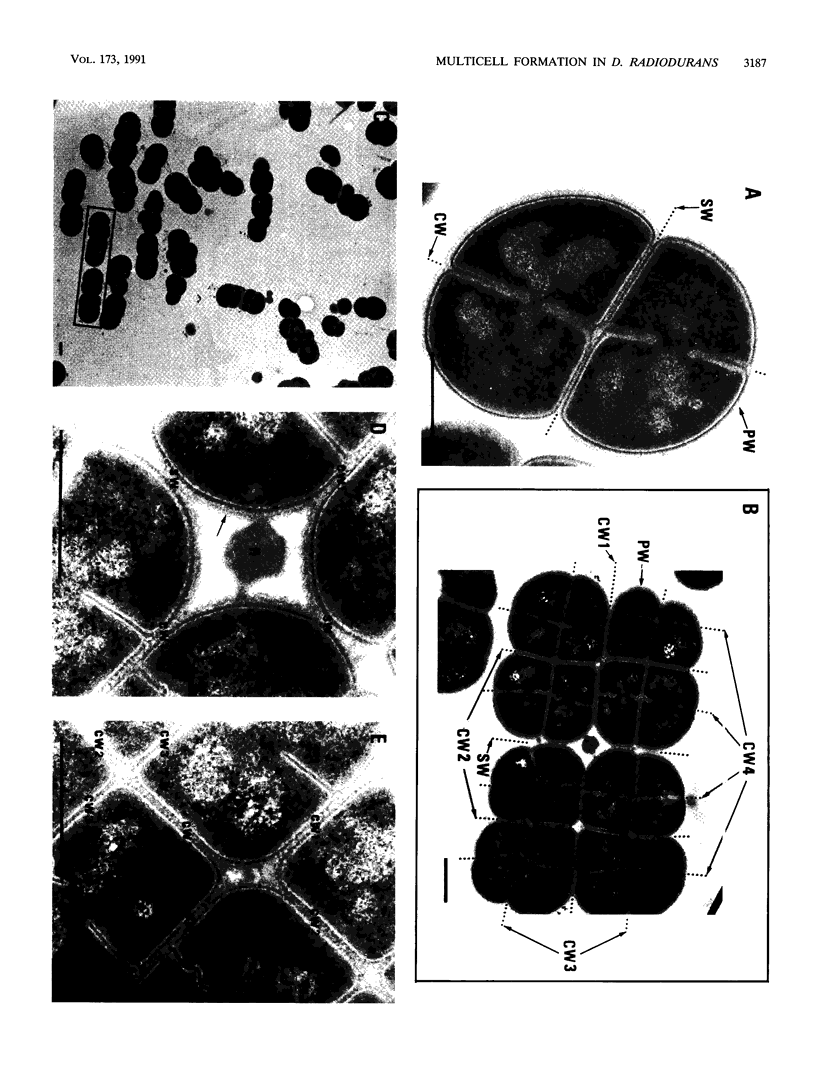
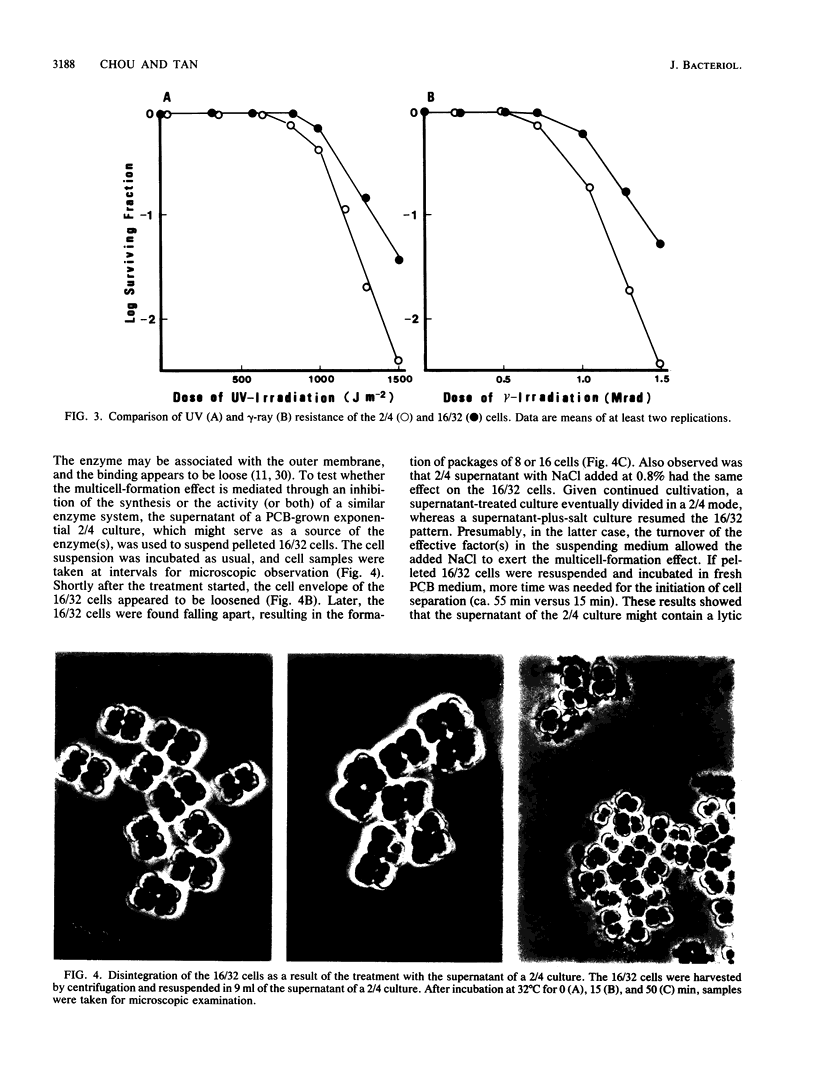
The highly radiation-resistant tetracoccal bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans exhibited a reversible multi-cell-form transition which depended on the NaCl concentration in the medium. In response to 0.8% NaCl addition into the medium, the pair/tetrad (designated 2/4) cells in a young culture grew and divided but did not separate and became 8-, 16-, and 32-cell units successively. In exponential growth phase, the cells divided in a 16/32 pattern. Potassium ions were equally effective as Na+ in mediating this multicell-formation effect; Mg2+, Li+, and Ca2+ also worked but produced less multiplicity. This effect appears to be species specific. This-section micrographs revealed that in a 16/32-cell unit, eight 2/4 cells were encased in an orderly manner within a large peripheral wall, showing five cycles of septation. Our results suggest the presence of a salt-sensitive mechanism for controlling cell separation in D. radiodurans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin W. W., Sheu M. J., Bankston P. W., Woldringh C. L. Changes in buoyant density and cell size of Escherichia coli in response to osmotic shocks. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):452–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.452-455.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister W., Barth M., Hegerl R., Guckenberger R., Hahn M., Saxton W. O. Three-dimensional structure of the regular surface layer (HPI layer) of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse M. D., Bottomley P. J. Growth and Nodulation Responses of Rhizobium meliloti to Water Stress Induced by Permeating and Nonpermeating Solutes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2431–2436. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2431-2436.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou F. I., Tan S. T. Manganese(II) induces cell division and increases in superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in an aging deinococcal culture. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2029–2035. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2029-2035.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J. The regulation of DNA replication and cell division in E. coli B-r. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:823–838. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoul M., Bernard T., Cormier M. Evidence that Escherichia coli accumulates glycine betaine from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):551–554. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.551-554.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Silverman C. S., Adams N. J., Awkard W. S. Extracellular cell wall lytic enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus: purification and partial characterization. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):761–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.761-769.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutkins R. W., Ellefson W. L., Kashket E. R. Betaine Transport Imparts Osmotolerance on a Strain of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2275–2281. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2275-2281.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOMINSKI I., CAMERON J., WYLLIE G. Chaining and unchaining Streptococcus faecalis; a hypothesis of the mechanism of bacterial cell separation. Nature. 1958 May 24;181(4621):1477–1477. doi: 10.1038/1811477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOMINSKI I., GRAY S. Inhibition of lysozyme by 'Suramin'. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:683–683. doi: 10.1038/192683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson A. T., Sprott G. D., McDonald I. J., Tessier H. Some properties of an unidentified halophile: growth characteristics, internal salt concentration, and morphology. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):780–786. doi: 10.1139/m76-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Mundy A. R., Blackford H. N., Stephenson T. P. Transvesical phenolisation of the pelvic plexuses: a simple technique for the treatment of refractory detrusor instability and hyperreflexia. Urol Int. 1986;41(3):202–206. doi: 10.1159/000281198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. G., Hall M., Thompson B. G. Cell division in Deinococcus radiodurans and a method for displaying septa. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Oct;29(10):1412–1423. doi: 10.1139/m83-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. H., Chudek J. A., Foster R., Gadd G. M. Osmotic significance of glycerol accumulation in exponentially growing yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2119–2123. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2119-2123.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Bacterial growth and the cell envelope. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):194–214. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.194-214.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Kocur M., Glauert A. M., Thornley M. J. A study by freeze-etching of the fine structure of Micrococcus radiodurans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 4;94(1):77–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00414079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. F., Donachie W. D. Transcriptional organization within an Escherichia coli cell division gene cluster: direction of transcription of the cell separation gene envA. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.724-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Maxcy R. B. Simple method to demonstrate radiation-inducible radiation resistance in microbial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):88–90. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.88-90.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Maxcy R. B., Thompson T. L. Paper replication method for isolation of radiation-sensitive mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.233-236.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao L., Tanzer J. M., MacAlister T. J. Bicarbonate and potassium regulation of the shape of Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449S. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2543–2547. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2543-2547.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. AMINO ACIDS OF WALLS OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1107–1109. doi: 10.1038/2011107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Normark S. Evidence for a role of N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase in septum separation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):580–586. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.580-586.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heijenoort J., Parquet C., Flouret B., van Heijenoort Y. Envelope-bound N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase of Escherichia coli K 12. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):611–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]