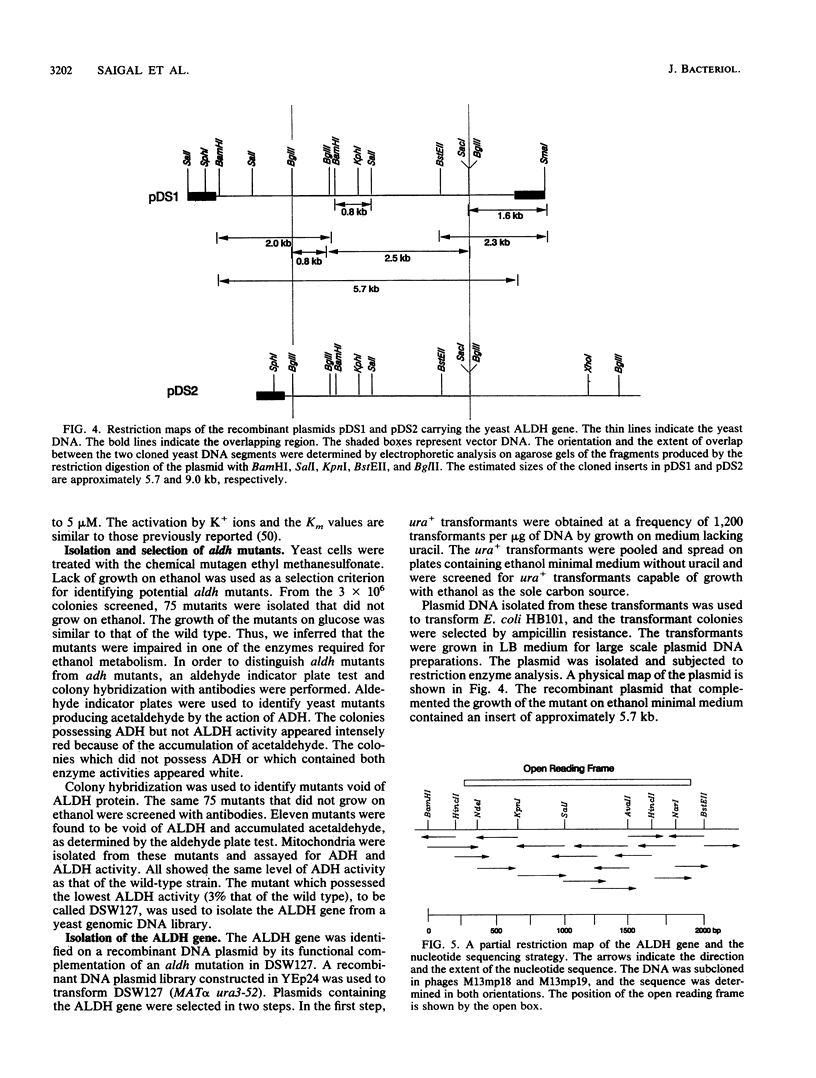
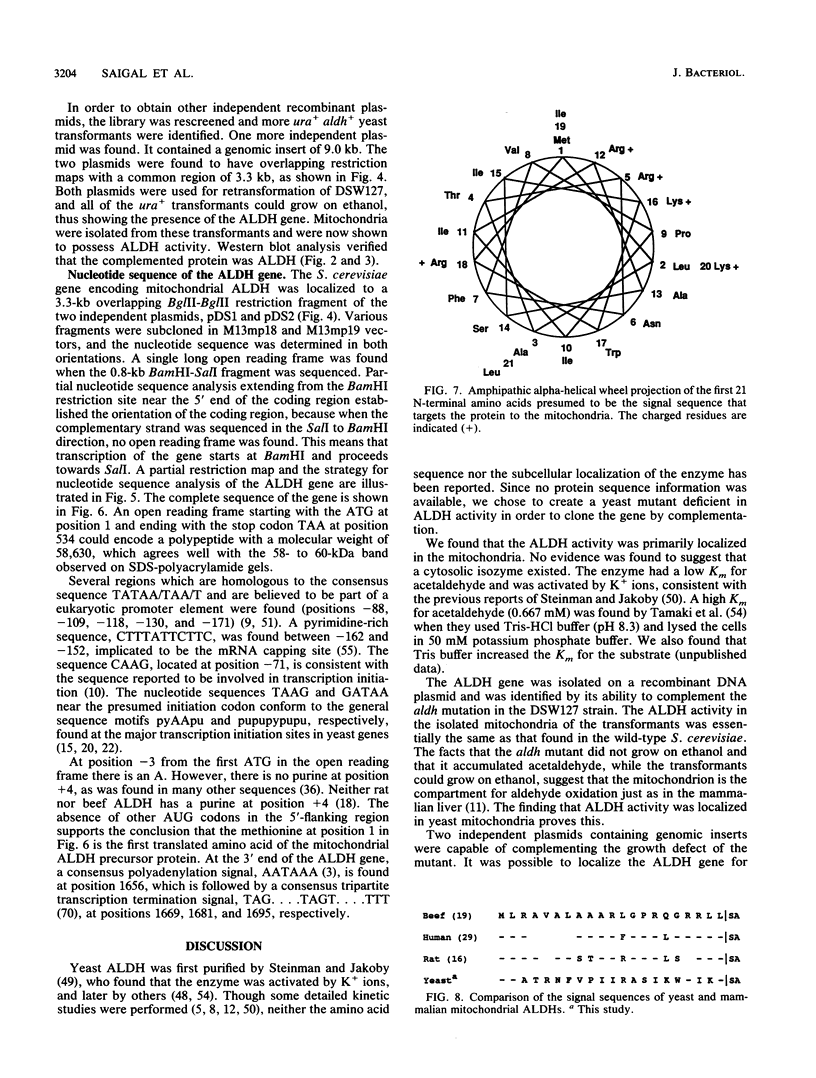
Abstract
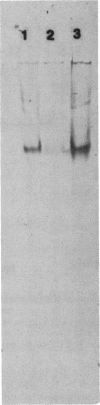
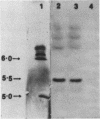
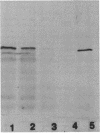
Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae deficient in mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity were isolated by chemical mutagenesis with ethyl methanesulfonate. The mutants were selected by their inability to grow on ethanol as the sole carbon source. The ALDH mutants were distinguished from alcohol dehydrogenase mutants by an aldehyde indicator plate test and by immunoscreening. The ALDH gene was isolated from a yeast genomic DNA library on a 5.7-kb insert of a recombinant DNA plasmid by functional complementation of the aldh mutation in S. cerevisiae. An open reading frame which specifies 533 codons was found within the 2.0-kb BamHI-BstEII fragment in the 5.7-kb genomic insert which can encode a protein with a molecular weight of 58,630. The N-terminal portion of the protein contains many positively charged residues which may serve as a signal sequence that targets the protein to the mitochondria. The amino acid sequence of the proposed mature yeast enzyme shows 30% identity to each of the known ALDH sequences from eukaryotes or prokaryotes. The amino acid residues corresponding to mammalian cysteine 302 and glutamates 268 and 487, implicated to be involved at the active site, were conserved. S. cerevisiae ALDH was found to be localized in the mitochondria as a tetrameric enzyme. Thus, that organelle is responsible for acetaldehyde oxidation, as was found in mammalian liver.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abriola D. P., Fields R., Stein S., MacKerell A. D., Jr, Pietruszko R. Active site of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5679–5684. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abriola D. P., MacKerell A. D., Jr, Pietruszko R. Correlation of loss of activity of human aldehyde dehydrogenase with reaction of bromoacetophenone with glutamic acid-268 and cysteine-302 residues. Partial-sites reactivity of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):179–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2660179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Betts G. F. Kinetics and reaction mechanism of potassium-activated aldehyde dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):787–798. doi: 10.1042/bj1730787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Betts G. F. Rapid purification and properties of potassium-activated aldehyde dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):773–786. doi: 10.1042/bj1730773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury S. L., Jakoby W. B. Ordered binding of substrates to yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1834–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Q. N., Tu G. C., Weiner H. Mitochondria as the primary site of acetaldehyde metabolism in beef and pig liver slices. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1988 Oct;12(5):720–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1988.tb00271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. F., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. 3. Preparation of three homogeneous species. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6065–6071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Sewell G. W., Osman Y. A., Ingram L. O. Cloning and sequencing of the alcohol dehydrogenase II gene from Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2591–2597. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2591-2597.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrés J., Guan K. L., Weiner H. Primary structures of rat and bovine liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenases deduced from cDNA sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 1;180(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Weiner H. Influence of the 5'-end region of aldehyde dehydrogenase mRNA on translational efficiency. Potential secondary structure inhibition of translation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17764–17769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Weiner H. Sequence of the precursor of bovine liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase as determined from its cDNA, its gene, and its functionality. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Mar;277(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90590-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R., Watanabe C. K., de Boer H. A. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3581–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Helser T. L., Zitomer R. S. Sequences required for transcriptional initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3785–3791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J. D., Pietruszko R. Selective chemical modification of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenases E1 and E2 by iodoacetamide. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10889–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Jörnvall H. Functional topology of aldehyde dehydrogenase structures. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;232:1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jörnvall H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Primary structure of the cytoplasmic isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Levine H. L., Goeddel D. V., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Expression of a human gene for interferon in yeast. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):717–722. doi: 10.1038/293717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. C., Bendel R. E., Yoshida A. Genomic structure of the human mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase gene. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. C., Tani K., Fujiyoshi T., Kurachi K., Yoshida A. Cloning of cDNAs for human aldehyde dehydrogenases 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn B. A., Chantler S. M. Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):104–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. K., Bernofsky C. Mitochondrial acetaldehyde dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 18;350(2):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jeck R., Woenckhaus C., Jörnvall H. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from horse liver. Correlations of the same species variants for both the cytosolic and the mitochondrial forms of an enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Jr, Brennan M. D., Hempel J., Lindahl R. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA encoding a catalytically functional tumor-associated aldehyde dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok M., Oldenhuis R., van der Linden M. P., Meulenberg C. H., Kingma J., Witholt B. The Pseudomonas oleovorans alkBAC operon encodes two structurally related rubredoxins and an aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5442–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes K. M., Midwinter G. G., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Evidence for reactivity of serine-74 with trans-4-(N,N-dimethylamino)cinnamaldehyde during oxidation by the cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 27;29(8):2070–2075. doi: 10.1021/bi00460a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S., Nelson N. An immunological method for detecting gene expression in yeast colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Reed S. I. Isolation of genes by complementation in yeast: molecular cloning of a cell-cycle gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2119–2123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M., Gwynne D. I., Buxton F. P., Elliott R., Davies R. W., Lockington R. A., Scazzocchio C., Sealy-Lewis H. M. Cloning and characterization of the aldA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Crystalline alcohol dehydrogenase from baker's yeast. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. An enrichment method for auxotrophic yeast mutants using the antibiotic 'nystatin'. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):206–207. doi: 10.1038/211206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springham M. G., Betts G. F. The activity of K + -activated yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase following rapid changes in cation environment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 5;309(1):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. I. Purification and crystallization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5019–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. II. Properties of the homogeneous enzyme preparations. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 25;243(4):730–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanas G. W., Weiner H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity as the rate-limiting factor for acetaldehyde metabolism in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90603-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H., Filmer D. L. Effects of pH on horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase: alterations in metal ion activation, number of functioning active sites, and hydrolysis of the acyl intermediate. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6225–6230. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki N., Nakamura M., Kimura K., Hama T. Purification and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biochem. 1977 Jul;82(1):73–79. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G. P., Kramer R. A., Turner K. J., Bostian K. A. Comparative analysis of the 5'-end regions of two repressible acid phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):570–579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Evidence for two distinct active sites on aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1218–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Identification of the cysteine residue in the active site of horse liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1212–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., King R. M., Burke D. C., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Regulated high efficiency expression of human interferon-alpha in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):603–608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H., Farrés J., Wang T. T., Cunningham S. J., Zheng C. F., Ghenbot G. Probing the active site of aldehyde dehydrogenase by site directed mutagenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;284:13–17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5901-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H., Lin F. P., Sanny C. G. Chemical probes for the active site of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;174:57–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger J. I., Bernofsky C. Mitochondrial alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weretilnyk E. A., Hanson A. D. Molecular cloning of a plant betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme implicated in adaptation to salinity and drought. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Paquin C. E. Homology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADH4 to an iron-activated alcohol dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):374–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00329668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Huang I. Y., Ikawa M. Molecular abnormality of an inactive aldehyde dehydrogenase variant commonly found in Orientals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):258–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr-Lindström H., Hempel J., Jörnvall H. The cytoplasmic isoenzyme of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Relationship to the corresponding human isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]