Abstract
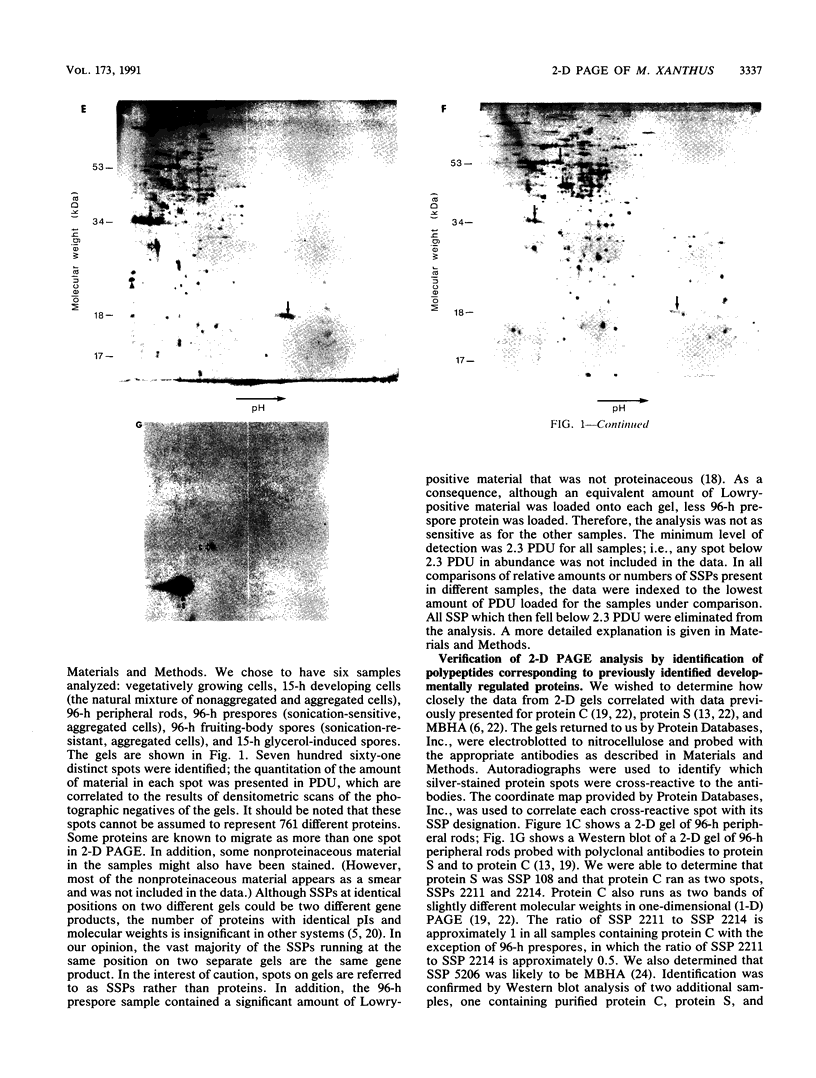
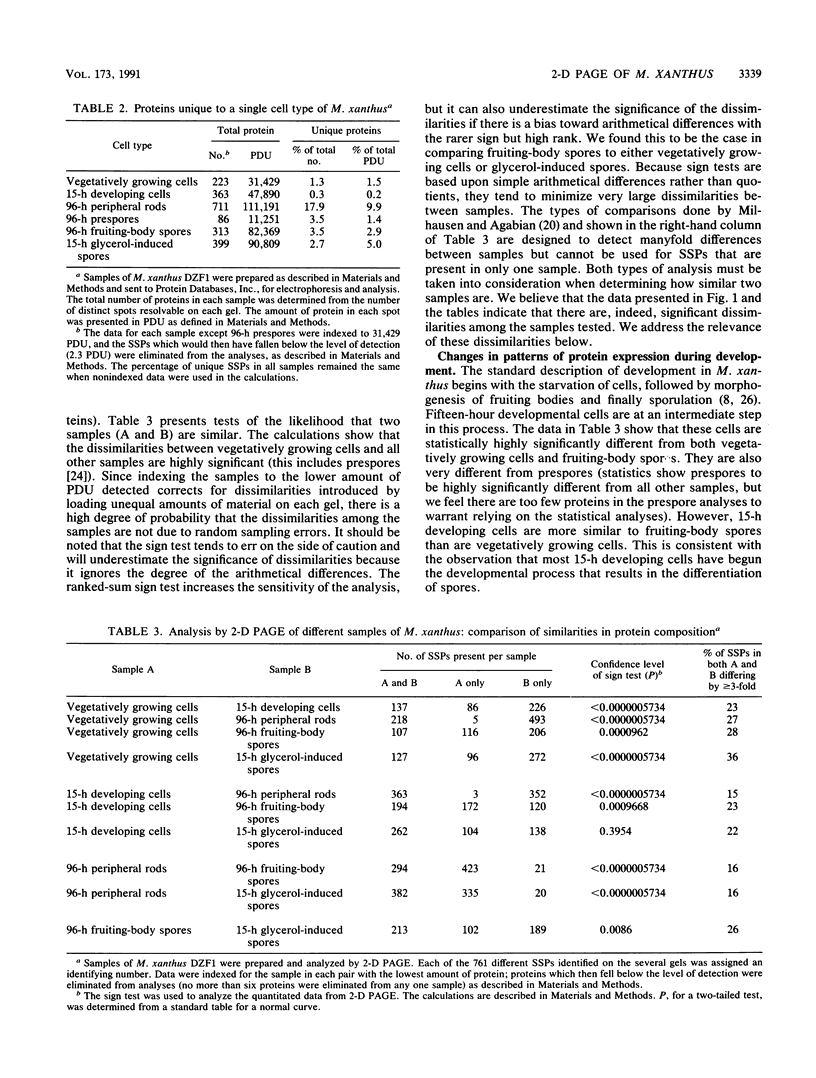
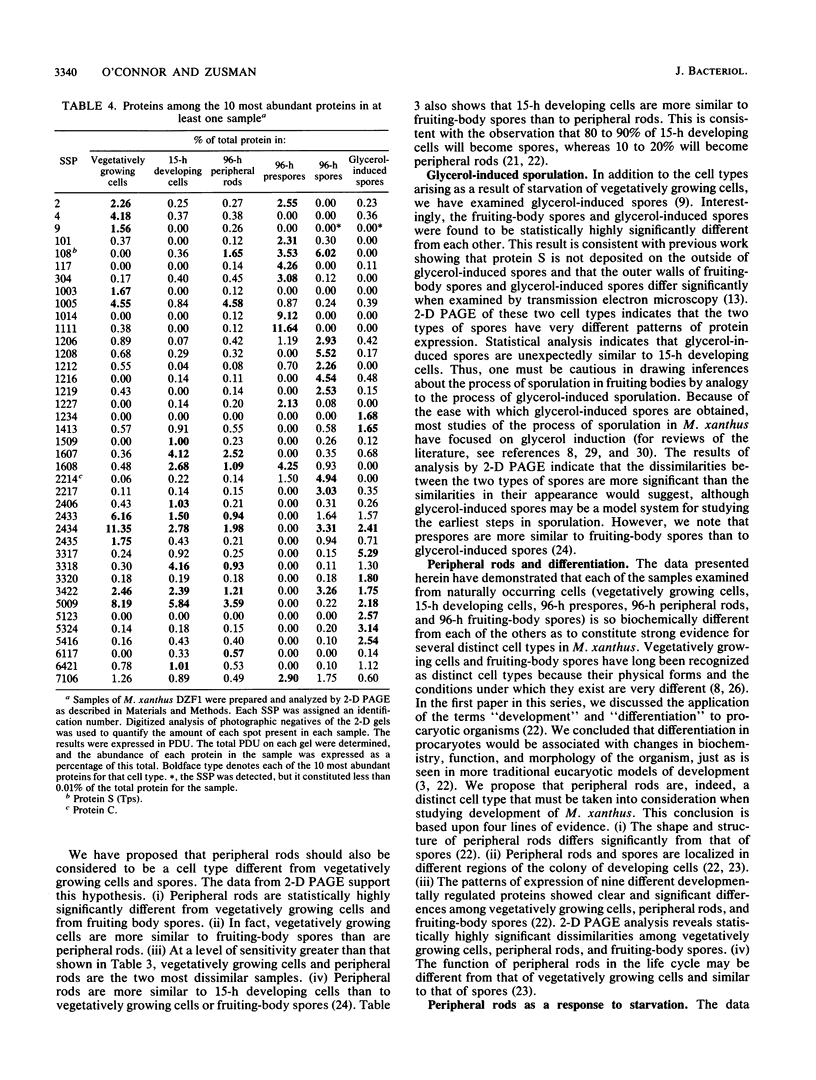
Myxococcus xanthus is a gram-negative, soil-dwelling bacterium that undergoes development in response to depletion of nutrients. Whereas most cells aggregate into multicellular mounds in which they differentiate into spores, 10 to 20% of the developing cells remain outside fruiting bodies as peripheral rods. We used two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to analyze the global expression of polypeptides in cells taken from six stages in the life cycle: vegetatively growing cells, cells 15 h after the induction of development, peripheral rods, prespores (sonication-sensitive, aggregated cells), fruiting-body spores (sonication-resistant, aggregated cells) 96 h after the induction of development, and glycerol-induced spores 15 h after induction. Seven hundred sixty-one discrete sample spots (SSPs) were identified among the six gels. Comparisons among the samples revealed that each sample had some unique SSPs, ranging from 0.3% of the 15-h developing cell SSPs to 17.9% of 96-h peripheral rod SSPs. Sixty-eight SSPs were ubiquitously distributed, but the relative amounts of these SSPs varied among the samples. Statistical analyses of the distribution and relative quantities of the SSPs indicate that, within a confidence level of greater than 99.99%, peripheral rods are significantly different from vegetatively growing cells, 15-h developing cells, prespores, fruiting-body spores, and glycerol-induced spores. In fact, among the six samples studied, only 15-h developing cells and glycerol-induced spores were similar to each other within a confidence level of P greater than or equal to 0.05. These results are consistent with the description of peripheral rods as a distinct developmental cell type.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campos J. M., Zusman D. R. Regulation of development in Myxococcus xanthus: effect of 3':5'-cyclic AMP, ADP, and nutrition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):518–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schultz J. E., Zychlinsky E., Bockman A., Matin A. Starvation proteins in Escherichia coli: kinetics of synthesis and role in starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.486-493.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus: pattern of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Chaisson S. A., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2779–2781. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2779-2781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Schultz J. E., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3910–3914. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3910-3914.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., Esmon B., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus protein C is a major spore surface protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2141–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2141-2145.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Agabian N. Regulation of polypeptide synthesis during Caulobacter development: two-dimensional gel analysis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.163-173.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Behavior of peripheral rods and their role in the life cycle of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3342–3355. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3342-3355.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Development in Myxococcus xanthus involves differentiation into two cell types, peripheral rods and spores. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3318–3333. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3318-3333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Reexamination of the role of autolysis in the development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4103–4112. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4103-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve C. A., Bockman A. T., Matin A. Role of protein degradation in the survival of carbon-starved Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.758-763.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Aliabadi Z., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Global control in Salmonella typhimurium: two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of starvation-, anaerobiosis-, and heat shock-inducible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):420–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.420-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Park Y. K., Tirgari S., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Identification and characterization of starvation-regulated genetic loci in Salmonella typhimurium by using Mu d-directed lacZ operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.345-351.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Morphogenesis and developmental interactions in myxobacteria. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):516–523. doi: 10.1126/science.806967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]