Abstract
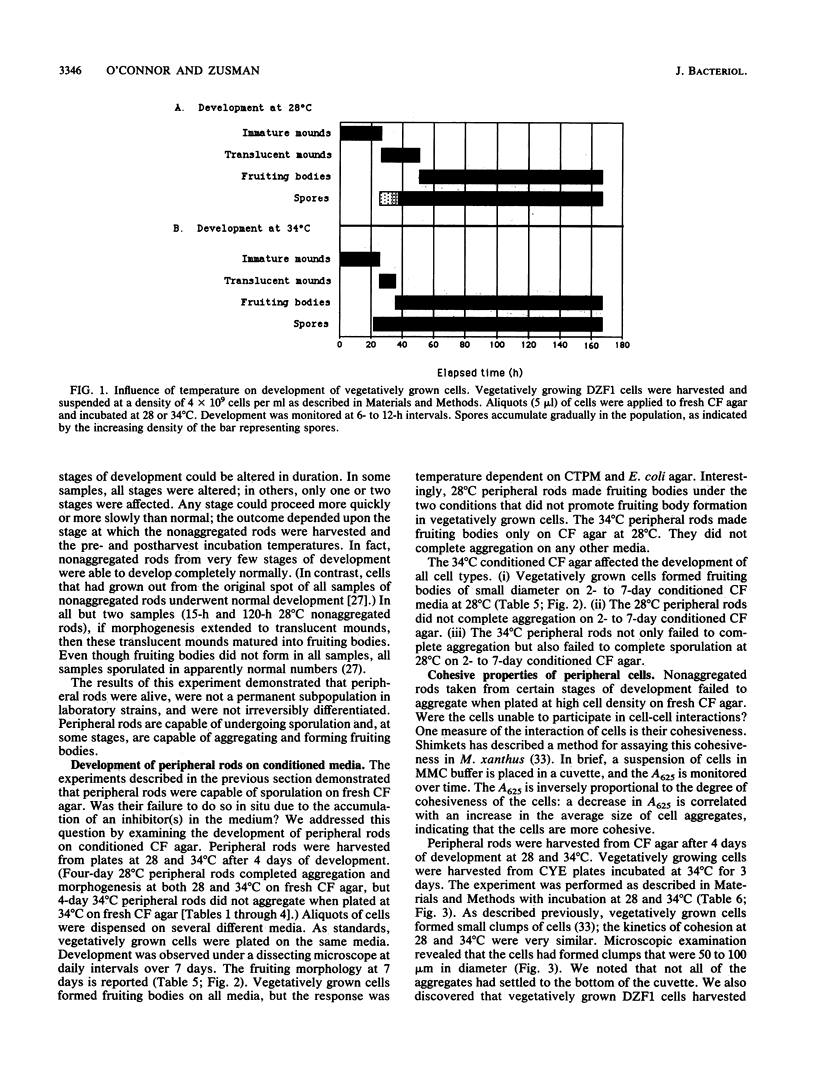
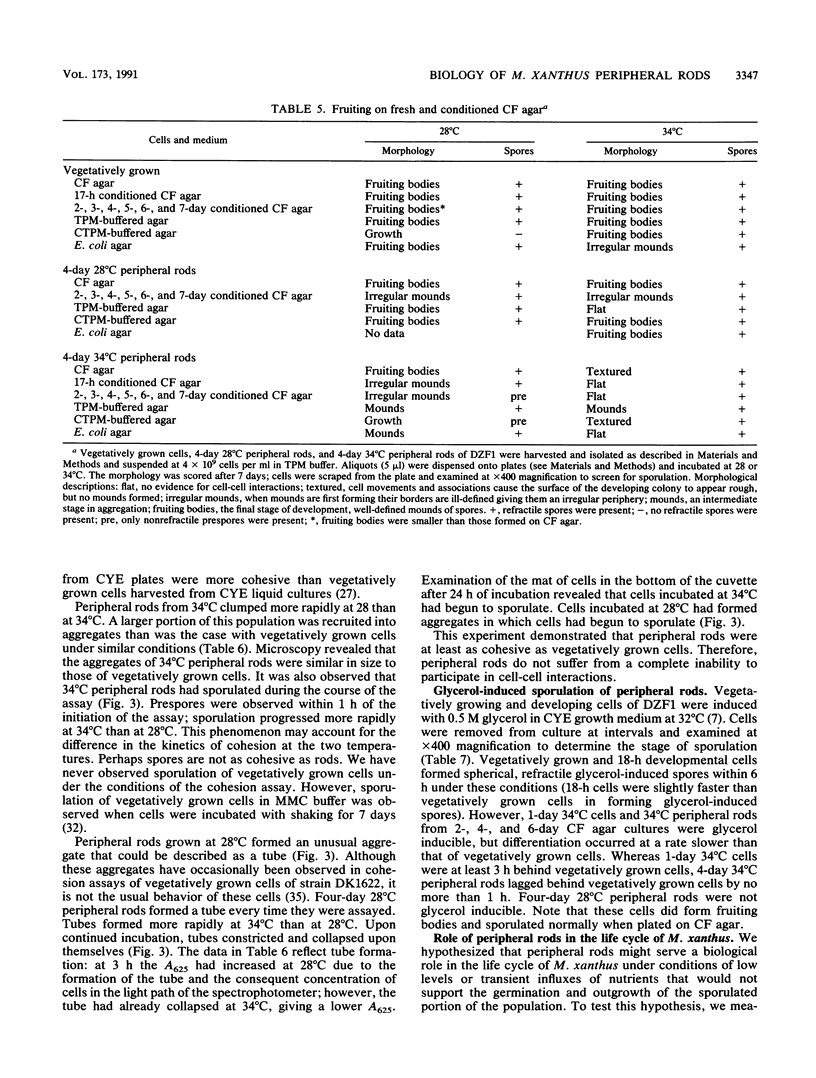
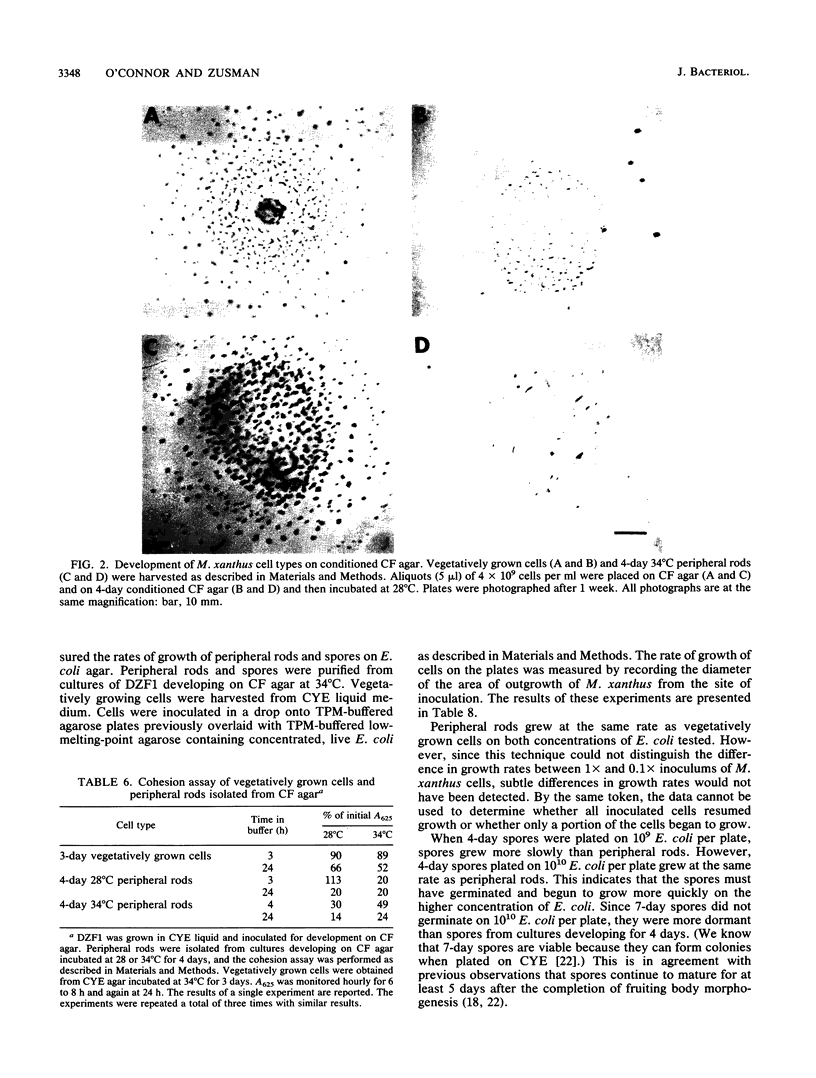
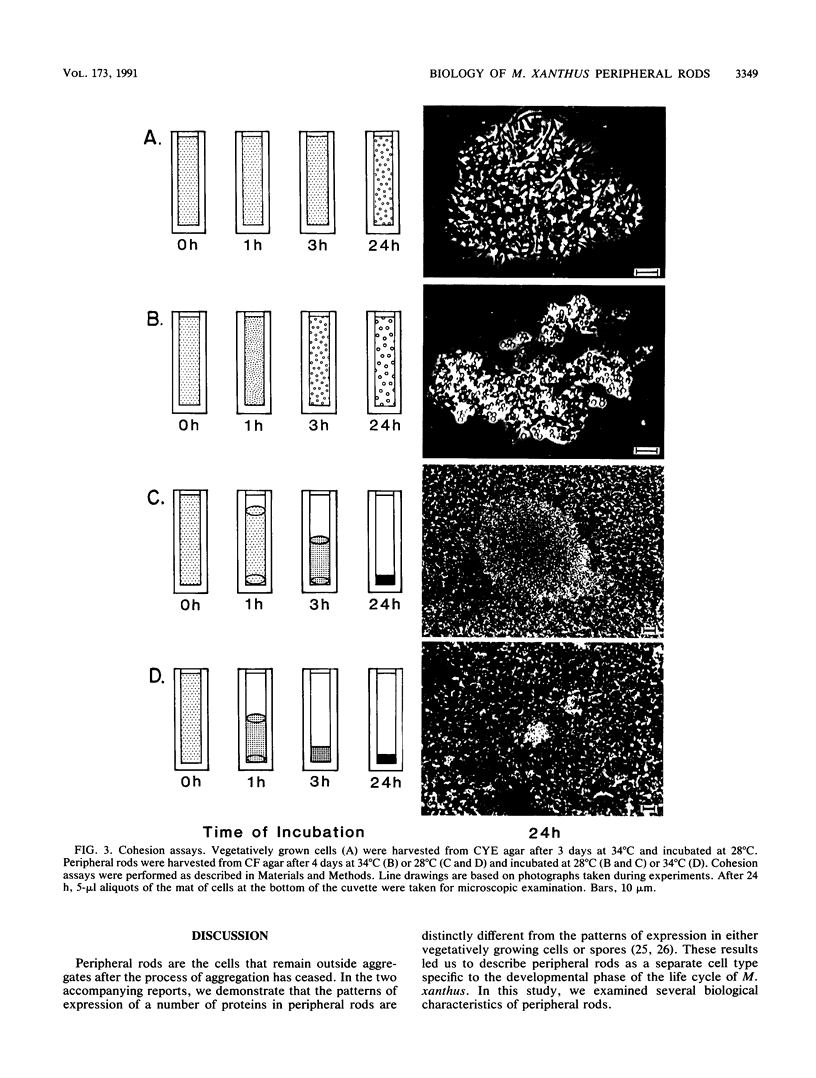
Myxococcus xanthus is a gram-negative bacterium with a complex life cycle including a developmental phase in which cells aggregate and sporulate in response to starvation. In previous papers, we have described a heretofore unsuspected layer of complexity in the development of M. xanthus: vegetatively growing cells differentiate into two cell types during development. In addition to the differentiation of spores within fruiting bodies, a second cell type, peripheral rods, arises outside fruiting bodies. The pattern of expression of proteins in peripheral rods is different from that of either vegetatively growing cells or spores, and peripheral rods express a number of recognized developmental markers. In this report, we examine four aspects of the biology of peripheral rods: (i) the influence of nutrients on the proportion of peripheral rods in a population of developing cells, (ii) the capacity of peripheral rods to recapitulate development, (iii) the development of peripheral rods on conditioned medium, and (iv) the ability of peripheral rods to resume growth on low amounts of exogenously added nutrients. The results of these studies suggest that peripheral rods play a significant role in the life cycle of M. xanthus by allowing the exploitation of low amounts or transient influxes of nutrients without the investment of energy in spore germination. The differentiation of vegetatively growing cells into two cell types that differ significantly in biology, shape, and localization within the population has been incorporated into a model of the life cycle of M. xanthus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Zusman D. R. Regulation of development in Myxococcus xanthus: effect of 3':5'-cyclic AMP, ADP, and nutrition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):518–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schultz J. E., Zychlinsky E., Bockman A., Matin A. Starvation proteins in Escherichia coli: kinetics of synthesis and role in starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.486-493.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Effect of temperature on the growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):561–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.561-562.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Chaisson S. A., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2779–2781. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2779-2781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Schultz J. E., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3910–3914. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3910-3914.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Auger E. A., Blum P. H., Schultz J. E. Genetic basis of starvation survival in nondifferentiating bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:293–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride M. J., Zusman D. R. Trehalose accumulation in vegetative cells and spores of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6383–6386. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6383-6386.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., Esmon B., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus protein C is a major spore surface protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2141–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2141-2145.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Analysis of Myxococcus xanthus cell types by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3334–3341. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3334-3341.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Development in Myxococcus xanthus involves differentiation into two cell types, peripheral rods and spores. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3318–3333. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3318-3333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Genetic analysis of tag mutants of Myxococcus xanthus provides evidence for two developmental aggregation systems. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3868–3878. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3868-3878.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Patterns of cellular interactions during fruiting-body formation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6013–6024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6013-6024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Reexamination of the role of autolysis in the development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4103–4112. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4103-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve C. A., Bockman A. T., Matin A. Role of protein degradation in the survival of carbon-starved Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.758-763.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Filer D., Zafriti D., Kindler S. H. Aspartokinase activity and the developmental cycle of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.29-34.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Autocide AMI rescues development in dsg mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1513–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1513-1518.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus in liquid shake flask cultures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4521–4524. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4521-4524.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Correlation of energy-dependent cell cohesion with social motility in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.837-841.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Aliabadi Z., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Global control in Salmonella typhimurium: two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of starvation-, anaerobiosis-, and heat shock-inducible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):420–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.420-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Park Y. K., Tirgari S., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Identification and characterization of starvation-regulated genetic loci in Salmonella typhimurium by using Mu d-directed lacZ operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.345-351.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. Alkaline, acid, and neutral phosphatase activities are induced during development in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2294–2302. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2294-2302.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Developmentally induced autolysis during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.798-802.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Morphogenesis and developmental interactions in myxobacteria. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):516–523. doi: 10.1126/science.806967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]