Abstract
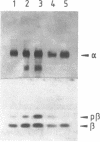
To establish the function of the periplasmic Fe-only hydrogenase in the anaerobic sulfate reducer Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough), derivatives with a reduced content of this enzyme were constructed by introduction of a plasmid that directs the synthesis of antisense RNA complementary to hydrogenase mRNA. It was demonstrated that the antisense RNA technique allowed specific suppression of the synthesis of this hydrogenase in D. vulgaris by decreasing the amount of hydrogenase mRNA but did not result in the complete elimination of the enzyme, as is usual with most conventional mutagenesis techniques. The hydrogenase content in these antisense RNA-producing D. vulgaris clones was two- to threefold lower than in the parental strain when the strains were grown in batch cultures with lactate as a substrate and sulfate as a terminal electron acceptor. Under these conditions, several differences in growth parameters were measured between the hydrogenase-suppressed clones and wild-type D. vulgaris: growth rates of the clones decreased two- to threefold, and at excess lactate, growth yields were reduced by 20%. Furthermore, the amount of hydrogen measured in the culture headspaces was reduced three- to fivefold for the clones. These observations indicate that this hydrogenase has an important function during growth on lactate and is involved in hydrogen production from protons and electrons originating from at least one of the two oxidation reactions in the conversion of lactate to acetate. The implications for the energy metabolism of D. vulgaris are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badziong W., Thauer R. K. Growth yields and growth rates of Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Marburg) growing on hydrogen plus sulfate and hydrogen plus thiosulfate as the sole energy sources. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00402310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Green P. J., Inouye M. The use of RNAs complementary to specific mRNAs to regulate the expression of individual bacterial genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauque G., Peck H. D., Jr, Moura J. J., Huynh B. H., Berlier Y., DerVartanian D. V., Teixeira M., Przybyla A. E., Lespinat P. A., Moura I. The three classes of hydrogenases from sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus Desulfovibrio. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;4(4):299–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissolo T., Choi E. S., LeGall J., Peck H. D., Jr The presence of multiple intrinsic membrane nickel-containing hydrogenases in Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):701–708. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton F. S., Conrad R., Zeikus J. G. Physiological function of hydrogen metabolism during growth of sulfidogenic bacteria on organic substrates. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):843–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.843-849.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom J. M., Peck H. D., Jr Hydrogenase, electron-transfer proteins, and energy coupling in the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:551–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde M., Fürstenau U., Mayer F., Przybyla A. E., Peck H. D., Jr, Le Gall J., Choi E. S., Menon N. K. Localization of membrane-associated (NiFe) and (NiFeSe) hydrogenases of Desulfovibrio vulgaris using immunoelectron microscopic procedures. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKLAND L. H. The determination of small quantities of bacteria by means of the biuret reaction. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):698–703. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. F., Campbell L. L., Postgate J. R. Base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid of sulfate-reducing bacteria deduced from buoyant density measurements in cesium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1073-1078.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Peck H. D., Jr Proton translocation associated with nitrite respiration in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5450–5458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traore A. S., Hatchikian C. E., Belaich J. P., Le Gall J. Microcalorimetric studies of the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria: energetics of Desulfovibrio vulgaris growth. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):191–199. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.191-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Brenner S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough). Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Hagen W. R., Krüse-Wolters K. M., van Berkel-Arts A., Veeger C. Purification and characterization of Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough) hydrogenase expressed in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Walker J. E., Brenner S. Cloning of the gene encoding the hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough) and determination of the NH2-terminal sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):509–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Westen H. M., Mayhew S. G., Veeger C. Separation of hydrogenase from intact cells of Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Purification and properties. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]