Abstract
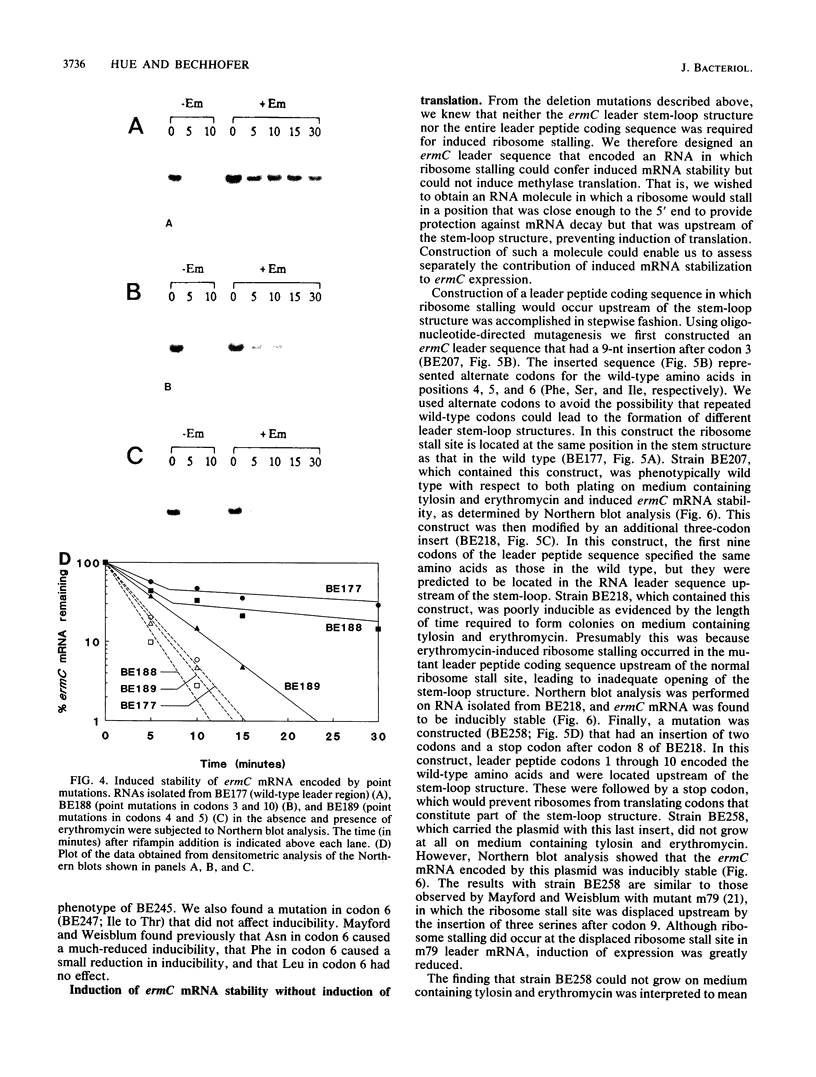
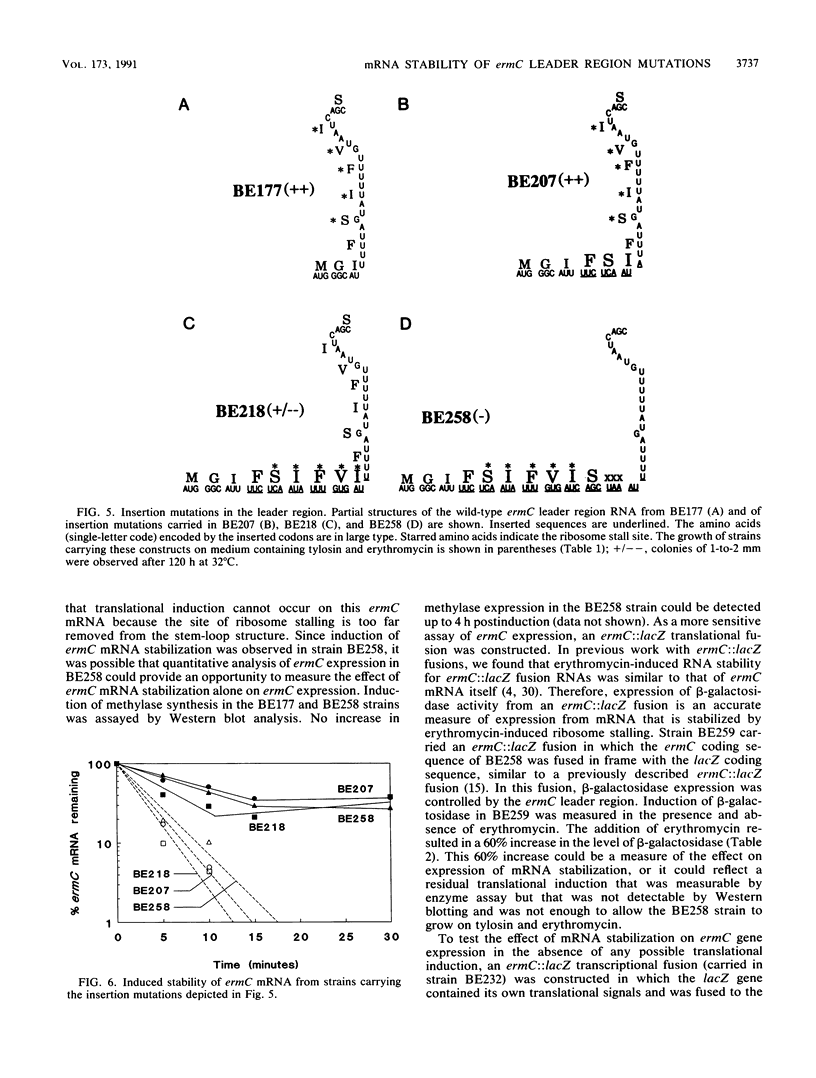
Induction of translation of the ermC gene product in Bacillus subtilis occurs upon exposure to erythromycin and is a result of ribosome stalling in the ermC leader peptide coding sequence. Another result of ribosome stalling is stabilization of ermC mRNA. The effect of leader RNA secondary structure, methylase translation, and leader peptide translation on induced ermC mRNA stability was examined by constructing various mutations in the ermC leader region. Analysis of deletion mutations showed that ribosome stalling causes induction of ermC mRNA stability in the absence of methylase translation and ermC leader RNA secondary structure. Furthermore, deletions that removed much of the leader peptide coding sequence had no effect on induced ermC mRNA stability. A leader region mutation was constructed such that ribosome stalling occurred in a position upstream of the natural stall site, resulting in induced mRNA stability without induction of translation. This mutation was used to measure the effect of mRNA stabilization on ermC gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Kurland C. G. Elongating ribosomes in vivo are refractory to erythromycin. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):901–904. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H. A method for sequencing polymerase chain reaction products can be used to sequence Bacillus subtilis "miniprep" plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):17-9, 20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Induced mRNA stability in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Zen K. H. Mechanism of erythromycin-induced ermC mRNA stability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5803–5811. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5803-5811.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breidt F., Dubnau D. Identification of cis-acting sequences required for translational autoregulation of the ermC methylase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3661–3668. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3661-3668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraro V. J., Subbarao M. N., Kennell D. Specific endonucleolytic cleavage sites for decay of Escherichia coli mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):257–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contente S., Dubnau D. Marker rescue transformation by linear plasmid DNA in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):555–571. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Translational autoregulation of ermC 23S rRNA methyltransferase expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1133–1141. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1133-1141.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Grandi G., Hahn J., Grandi R., Dubnau D. Conformational alteration of mRNA structure and the posttranscriptional regulation of erythromycin-induced drug resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6081–6097. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Hahn J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Replication and incompatibility properties of plasmid pE194 in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):722–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.722-735.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Israeli-Reches M., Dubnau D. Induction of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance requires ribosomes able to bind inducer. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(3):357–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00425544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Grandi G., Gryczan T. J., Dubnau D. Translational attenuation of ermC: a deletion analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):204–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00331851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Schmidt F. H. The role of mRNA and protein stability in gene expression. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2360–2370. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. The control region for erythromycin resistance: free energy changes related to induction and mutation to constitutive expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):341–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00269681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. Conformational alterations in the ermC transcript in vivo during induction. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4307–4314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. The ermC leader peptide: amino acid alterations leading to differential efficiency of induction by macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3772–3779. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3772-3779.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. ermC leader peptide. Amino acid sequence critical for induction by translational attenuation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan C. S., Dubnau D. An in vitro study of the translational attenuation model of ermC regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1756–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. B., Youngman P. J. Construction and properties of Tn917-lac, a transposon derivative that mediates transcriptional gene fusions in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):140–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced ribosome stall in the ermA leader: a barricade to 5'-to-3' nucleolytic cleavage of the ermA transcript. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6680–6688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6680-6688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced stabilization of ermA messenger RNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar A. G., Hahn J., Grandi G., Kozlov Y., Dubnau D. Posttranscriptional regulation of an erythromycin resistance protein specified by plasmic pE194. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vester B., Garrett R. A. A plasmid-coded and site-directed mutation in Escherichia coli 23S RNA that confers resistance to erythromycin: implications for the mechanism of action of erythromycin. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]