Abstract
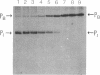
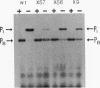
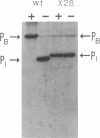
We have developed an in vitro transcription system in which purified TrpI protein and indoleglycerol phosphate (InGP) activate transcription initiation at the trpBA promoter (trpPB) and repress initiation at the trpI promoter (trpPI) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The phenotypes resulting from mutations in the -10 region of both promoters indicate that the -10 region consensus sequence in P. aeruginosa is probably the same as that in Escherichia coli. Furthermore, in the absence of TrpI and InGP, the activities of the two promoters are inversely correlated: down mutations in trpPI lead to increased activity of trpPB, and up mutations in trpPB cause a decrease in trpPI activity. These results are a consequence of the fact that the two promoters overlap, so that RNA polymerase cannot form open complexes with both promoters simultaneously. Thus, in theory, by preventing RNA polymerase from binding at trpPI, TrpI protein could indirectly activate trpPB. However, oligonucleotide-induced mutations that completely inactivate trpPI do not relieve the requirement for TrpI and InGP to activate trpPB. Therefore, activation of trpPB is mediated by a direct effect of TrpI on transcription initiation at trpPB. In addition, the oligonucleotide-induced mutations in trpPI alter site II, the weaker of two TrpI binding sites identified in DNase I and hydroxyl radical footprinting studies (M. Chang and I. P. Crawford, Nucleic Acids Res. 18:979-988, 1990). Since these mutations prevent full activation of trpPB, we conclude that specific base pairs in site II are required for activation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Garges S. Positive control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10797–10800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
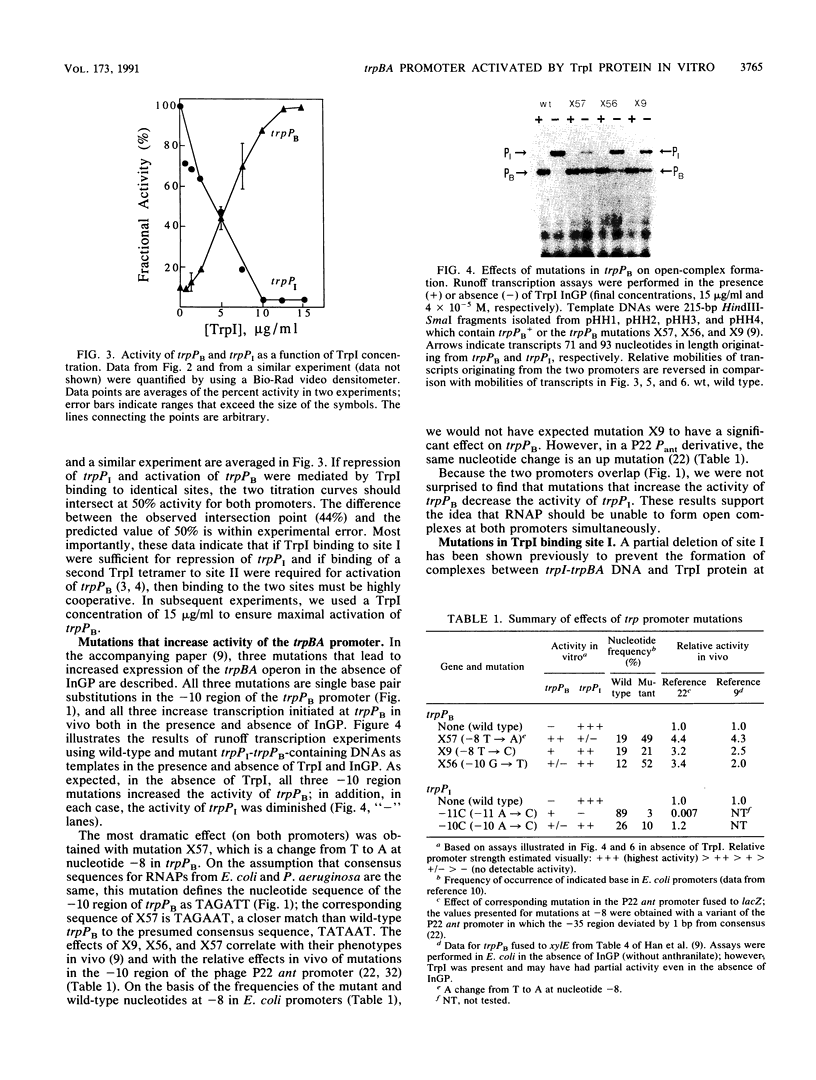
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. In vitro determination of the effect of indoleglycerol phosphate on the interaction of purified TrpI protein with its DNA-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1590-1597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. The roles of indoleglycerol phosphate and the TrpI protein in the expression of trpBA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):979–988. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Hadero A., Crawford I. P. Sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa trpI activator gene and relatedness of trpI to other procaryotic regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):172–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.172-183.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Evolution of a biosynthetic pathway: the tryptophan paradigm. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:567–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Gunsalus I. C. Inducibility of tryptophan synthetase in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):717–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J. G., Gussin G. N. RNA polymerases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas syringae respond to Escherichia coli activator proteins. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):394–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.394-397.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C. Y., Crawford I. P., Harwood C. S. Up-promoter mutations in the trpBA operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3756–3762. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3756-3762.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Mechanism of activation of transcription initiation from the lambda PRM promoter. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):493–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Rosenberg M. Characterization of a third, cII-dependent, coordinately activated promoter on phage lambda involved in lysogenic development. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11838–11844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. J., Gussin G. N. Interactions between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and lambda repressor. Mutations in PRM affect repression of PR. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):735–739. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konyecsni W. M., Deretic V. Broad-host-range plasmid and M13 bacteriophage-derived vectors for promoter analysis in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Francklyn C., Hamilton E. P. Arabinose-induced binding of AraC protein to araI2 activates the araBAD operon promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8814–8818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobell R. B., Schleif R. F. DNA looping and unlooping by AraC protein. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):528–532. doi: 10.1126/science.2237403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manch J. N., Crawford I. P. Genetic evidence for a positive-acting regulatory factor mediating induction in the tryptophan pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle H., Waldburger C., Susskind M. M. Hierarchies of base pair preferences in the P22 ant promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1944–1950. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1944-1950.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran T. V., Frantz B., Shin M. K., Ralston D. M., Wright J. G. The MerR heavy metal receptor mediates positive activation in a topologically novel transcription complex. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y. L., Garges S., Adhya S., Krakow J. S. Cooperative DNA binding of heterologous proteins: evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Gussin G. N. Role of cII protein in stimulating transcription initiation at the lambda PRE promoter. Enhanced formation and stabilization of open complexes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):489–506. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Synergy between Escherichia coli CAP protein and RNA polymerase in the lac promoter open complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O. Organization, expression, and evolution of genes for mercury resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:607–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hatfield G. W. Transcriptional activation at adjacent operators in the divergent-overlapping ilvY and ilvC promoters of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):643–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Bouvier S., Susskind M. M. Sequence determinants of promoter activity. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]