Abstract
R. meliloti Rm1021 normally produces an acidic Calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide, called succinoglycan or EPS I, which is required for successful nodulation of alfalfa by this strain. At least 13 loci affecting production of EPS I were previously mapped to a cluster on the second of two symbiotic megaplasmids in Rm1021, pRmeSU47b. A putative regulatory region was originally defined by the exoG and exoJ mutations. exoG and exoJ mutants produced less exopolysaccharide than wild-type strains and induced nitrogen-fixing nodules on alfalfa with reduced efficiency compared with the wild type. These mutants appeared to produce only a low-molecular-weight form of EPS I. Mutations called exoX cause an increase in exopolysaccharide production and map in the same region as the exoG and exoJ mutations. The DNA sequence of this region reveals that it contains two open reading frames, called exoX and exoY, which have homologs in other Rhizobium species. Interestingly, the exoG insertion mutations fall in an intergenic region and may affect the expression of exoX or exoY. The exoJ mutation falls in the 3' portion of the exoX open reading frame and is probably an allele of exoX that results in altered function. exoG and exoJ mutations limit EPS I production in the presence of exoR95 or exoS96 mutations, which cause overproduction of EPS I. Gene regulation studies suggest that ExoX and ExoY constitute a system that modulates exopolysaccharide synthesis at a posttranslational level. The deduced sequence of ExoY is homologous to a protein required for an early step in xanthan gum biosynthesis, further suggesting that the modulatory system may affect the exopolysaccharide biosynthetic apparatus.
Full text
PDF

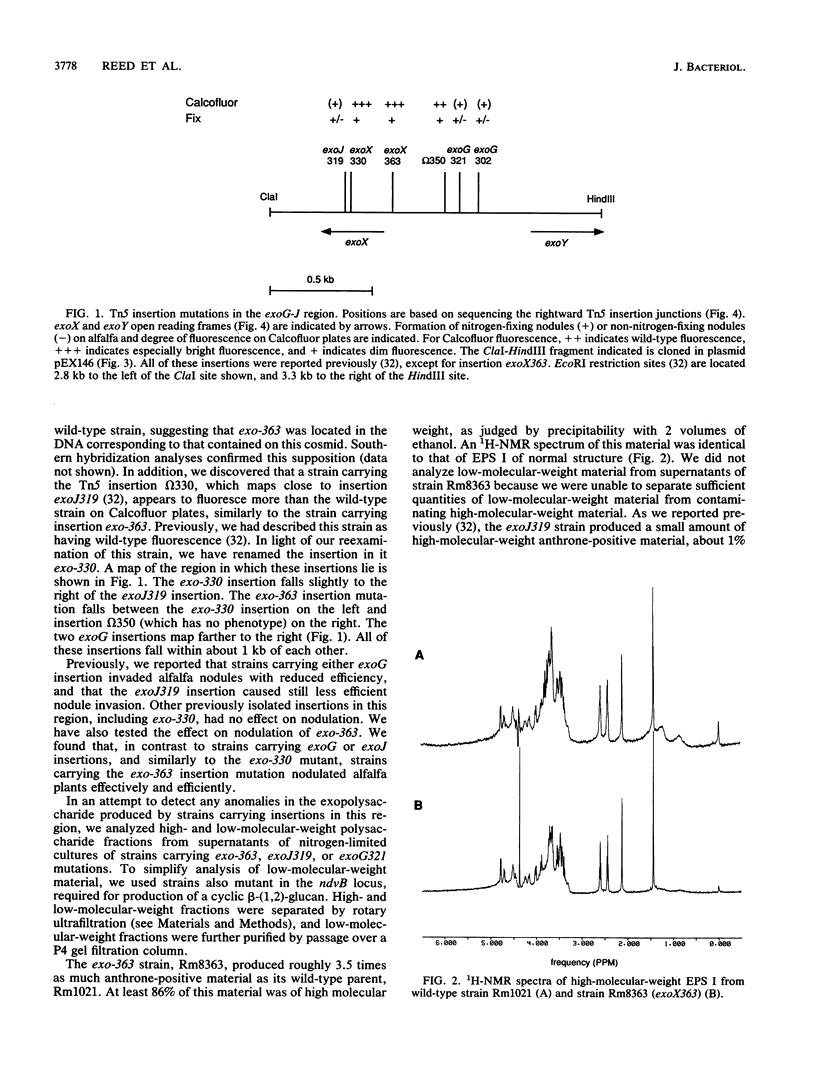








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borthakur D., Barker R. F., Latchford J. W., Rossen L., Johnston A. W. Analysis of pss genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum required for exopolysaccharide synthesis and nodulation of peas: their primary structure and their interaction with psi and other nodulation genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00333413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur D., Johnston A. W. Sequence of psi, a gene on the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium phaseoli which inhibits exopolysaccharide synthesis and nodulation and demonstration that its transcription is inhibited by psr, another gene on the symbiotic plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00331502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canter Cremers H. C., Batley M., Redmond J. W., Eydems L., Breedveld M. W., Zevehuizen L. P., Pees E., Wijffelman C. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Rhizobium leguminosarum exoB mutants are deficient in the synthesis of UDP-glucose 4'-epimerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21122–21127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G. F., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Genetic manipulations in Rhizobium meliloti utilizing two new transposon Tn5 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00331029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty D., Leigh J. A., Glazebrook J., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that overproduce the R. meliloti acidic calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4249–4256. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4249-4256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M. Genetic and physical analyses of group E exo- mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):474–477. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.474-477.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hartweig E., LeMieux K., Bergman K., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. General transduction in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):120–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.120-124.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hirsch A. M., Leigh J. A., Johansen E., Kuldau G. A., Deegan S., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that uncouple plant from bacterial differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Kunkel B., De Vos G. F., Signer E. R. Second symbiotic megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti carrying exopolysaccharide and thiamine synthesis genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.66-72.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazebrook J., Walker G. C. A novel exopolysaccharide can function in place of the calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide in nodulation of alfalfa by Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):661–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90588-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. X., Djordjevic M. A., Rolfe B. G. Two genes that regulate exopolysaccharide production in Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234: DNA sequences and resultant phenotypes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):193–203. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.193-203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. X., Rolfe B. G. Exopolysaccharide production in Rhizobium and its role in invasion. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1425–1431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. W., Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Physical and genetic map of a Rhizobium meliloti nodulation gene region and nucleotide sequence of nodC. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.469-476.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Boulnois G., Roberts I., Bitter-Suermann D., Golecki J. R., Jann B., Jann K. Expression of the Escherichia coli K5 capsular antigen: immunoelectron microscopic and biochemical studies with recombinant E. coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1085–1091. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1085-1091.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Lee C. C. Characterization of polysaccharides of Rhizobium meliloti exo mutants that form ineffective nodules. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3327–3332. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3327-3332.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Reed J. W., Hanks J. F., Hirsch A. M., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:483–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S., McCune S., Walker G. C. Symbiotic loci of Rhizobium meliloti identified by random TnphoA mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4257–4265. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4257-4265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S., Reed J. W., Himawan J., Walker G. C. Genetic analysis of a cluster of genes required for synthesis of the calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4239–4248. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4239-4248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Walker G. C. The exoD gene of Rhizobium meliloti encodes a novel function needed for alfalfa nodule invasion. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):664–677. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.664-677.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuber T. L., Long S., Walker G. C. Regulation of Rhizobium meliloti exo genes in free-living cells and in planta examined by using TnphoA fusions. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.426-434.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge R. W., Rolfe B. G. Rhizobium sp. Degradation of Legume Root Hair Cell Wall at the Site of Infection Thread Origin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):717–720. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.717-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Directed transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and complementation analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwedock J., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence and protein products of two new nodulation genes of Rhizobium meliloti, nodP and nodQ. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 Jul-Aug;2(4):181–194. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibaev V. N. Biosynthesis of bacterial polysaccharide chains composed of repeating units. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1986;44:277–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Biosynthesis and composition of gram-negative bacterial extracellular and wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:243–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Staneloni R. J., Leloir L. F. Lipid-bound saccharides in Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6751–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Staneloni R. J., Ugalde R. A., Leloir L. F. Lipid-bound sugars in Rhizobium meliloti. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Aug;203(1):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttaro A. D., Cangelosi G. A., Geremia R. A., Nester E. W., Ugalde R. A. Biochemical characterization of avirulent exoC mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1640–1646. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1640-1646.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Fear A. L., Calhoon R. D., Eichinger G. H., Mayer R., Amikam D., Benziman M., Gelfand D. H., Meade J. H., Emerick A. W. Genetic organization of the cellulose synthase operon in Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8130–8134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan H. J., Gray J. X., Levery S. B., Rolfe B. G., Leigh J. A. Functional and evolutionary relatedness of genes for exopolysaccharide synthesis in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5245–5253. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5245-5253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan H. J., Leigh J. A. Two genes that regulate exopolysaccharide production in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5254–5259. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5254-5259.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


