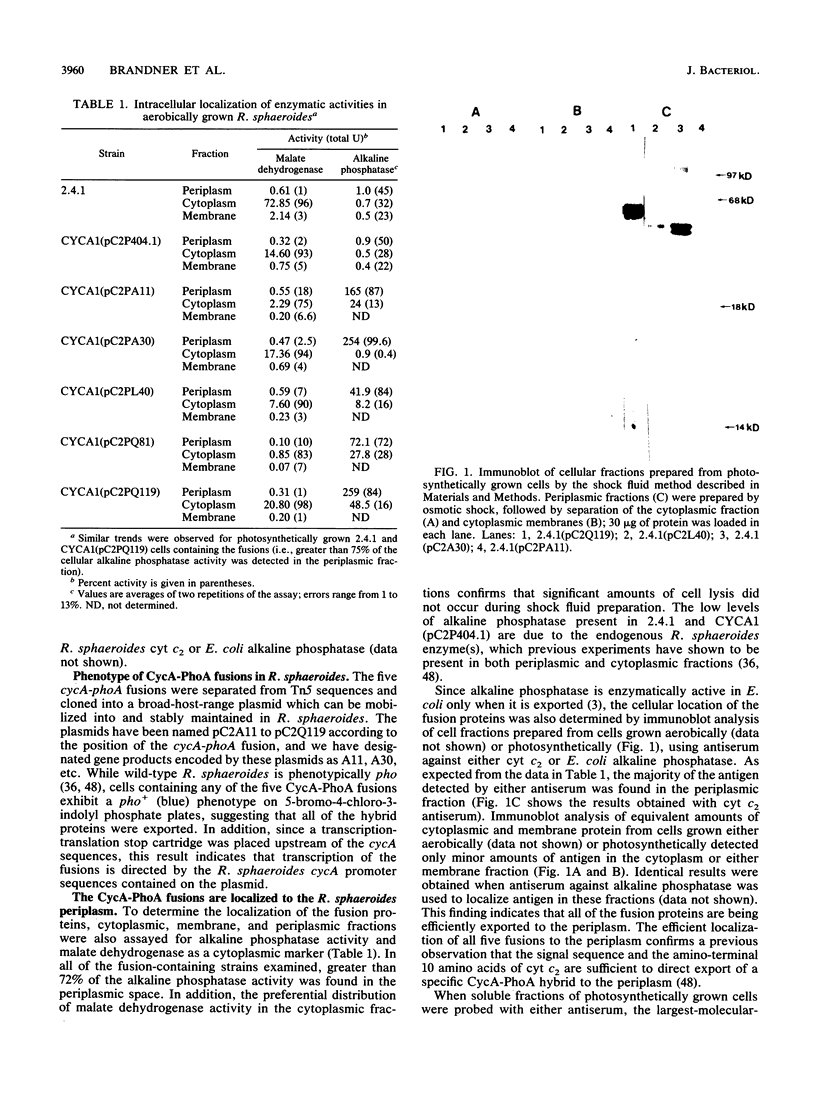
Abstract
Cytochrome c2 is a periplasmic redox protein involved in both the aerobic and photosynthetic electron transport chains of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. The process of cytochrome c2 maturation has been analyzed in order to understand the protein sequences involved in attachment of the essential heme moiety to the cytochrome c2 polypeptide and localization of the protein to the periplasm. To accomplish this, five different translational fusions which differ only in the cytochrome c2 fusion junction were constructed between cytochrome c2 and the Escherichia coli periplasmic alkaline phosphatase. All five of the fusion proteins are exported to the periplasmic space. The four fusion proteins that contain the NH2-terminal site of covalent heme attachment to cytochrome c2 are substrates for heme binding, suggesting that the COOH-terminal region of the protein is not required for heme attachment. Three of these hybrids possess heme peroxidase activity, which indicates that they are functional as electron carriers. Biological activity is possessed by one hybrid protein constructed five amino acids before the cytochrome c2 COOH terminus, since synthesis of this protein restores photosynthetic growth to a photosynthetically incompetent cytochrome c2-deficient derivative of R. sphaeroides. Biochemical analysis of these hybrids has confirmed CycA polypeptide sequences sufficient for export of the protein (A. R. Varga and S. Kaplan, J. Bacteriol. 171:5830-5839, 1989), and it has allowed us to identify regions of the protein sufficient for covalent heme attachment, heme peroxidase activity, docking to membrane-bound redox partners, or the capability to function as an electron carrier.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. Export of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase attached to an integral membrane protein, SecY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):437–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Cancedda F., Ericsson L. H., Neumann P. A., Piccoli S. P., Schlesinger M. J., Shriefer K., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3473–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandner J. P., McEwan A. G., Kaplan S., Donohue T. J. Expression of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):360–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.360-368.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Beckwith J. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Kuang W. J., Chen E. Y. Nucleotide sequence of the alkaline phosphatase gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;44(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Donohue T. J., Varga A. R., Staehelin L. A., Kaplan S. Induction of the photosynthetic membranes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: biochemical and morphological studies. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):540–554. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.540-554.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Donohue T. J., Kaplan S. Construction, characterization, and complementation of a Puf- mutant of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):320–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.320-329.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartini M., Inouye M. Interaction between two major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli: the matrix protein and the lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):329–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.329-335.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Timkovich R., Almassy R. J. The cytochrome fold and the evolution of bacterial energy metabolism. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 5;100(4):473–491. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., McEwan A. G., Kaplan S. Cloning, DNA sequence, and expression of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):962–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.962-972.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., McEwan A. G., Van Doren S., Crofts A. R., Kaplan S. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of cytochrome c2 deficient mutants of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1918–1925. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont M. E., Ernst J. F., Sherman F. Coupling of heme attachment to import of cytochrome c into yeast mitochondria. Studies with heme lyase-deficient mitochondria and altered apocytochromes c. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15928–15937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Molecular components of the signal sequence that function in the initiation of protein export. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):689–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzel B. C., Poulos T. L., Kraut J. Crystal structure of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase refined at 1.7-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13027–13036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis R. T., Jr, Becker R. R. Specific indication of hemoproteins in polyacrylamide gels using a double-staining process. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennis R. B., Casey R. P., Azzi A., Ludwig B. Purification and characterization of the cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Zha X. H., Durham B., O'Brien P., Vieira B., Davis D., Okamura M., Millett F. Reaction of cytochromes c and c2 with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction center involves the heme crevice domain. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4494–4500. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Zha X. H., Yu L., Yu C. A., Millett F. The binding domain on horse cytochrome c and Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 for the Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome bc1 complex. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4501–4504. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampsey D. M., Das G., Sherman F. Amino acid replacements in yeast iso-1-cytochrome c. Comparison with the phylogenetic series and the tertiary structure of related cytochromes c. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3259–3271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan T., Khan A. U. Phototoxicity of the tetracyclines: photosensitized emission of singlet delta dioxygen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4604–4606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry G. A., Houghton J. D., Jones O. T. The cytochromes in microsomal fractions of germinating mung beans. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):743–751. doi: 10.1042/bj1940743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Tamaki S., Kobayashi D., Trollinger D. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell J. P., Lascelles J. Membrane-bound, pyridine nucleotide-independent L-lactate dehydrogenase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.593-600.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwan A. G., Kaplan S., Donohue T. J. Synthesis of Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jun;50(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochrome composition of the purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 31;807(3):308–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D. New perspectives on c-type cytochromes. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:105–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60469-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Kaplan S. Construction of TnphoA gene fusions in Rhodobacter sphaeroides: isolation and characterization of a respiratory mutant unable to utilize dimethyl sulfoxide as a terminal electron acceptor during anaerobic growth in the dark on glucose. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4385–4394. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4385-4394.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overfield R. E., Wraight C. A., Devault D. Microsecond photooxidation kinetics of cytochrome c2 from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: in vivo and solution studies. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80903-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Baccarini-Melandri A., Hauska G. A., Melandri B. A., Crofts A. R. Asymmetry of an energy transducing membrane the location of cytochrome c2 in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 15;387(2):212–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Cogdell R. J., Crofts A. R. The photo-oxidation of horse heart cytochrome c and native cytochrome c2 by reaction centres from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides R26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 23;347(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:778–785. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Werner P. K., Müller M. Insertion of proteins into bacterial membranes: mechanism, characteristics, and comparisons with the eucaryotic process. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):333–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.333-366.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Beckwith J. An Escherichia coli mutation preventing degradation of abnormal periplasmic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. P., Kaplan S. Intracellular localization of phospholipid transfer activity in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and a possible role in membrane biogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):181–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.181-186.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga A. R., Kaplan S. Construction, expression, and localization of a CycA::PhoA fusion protein in Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5830–5839. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5830-5839.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Protoplast formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):668–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.668-670.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Paluch U., Neupert W. Cell-free synthesis of cytochrome c. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]