Short abstract
Systemic inflammation may be the “missing link” between airway dysfunction and the extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD
Keywords: systemic inflammation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, muscle dysfunction
There is a growing recognition that chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a condition that involves multiple organs and systems.1 In addition to emphysema and airway inflammation and remodelling, COPD is associated with various local and systemic complications including cachexia, weight loss, osteoporosis, muscle wasting, heart failure, atherosclerosis, dementia, depression, and cancer.1,2,3 Strikingly, these extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD account for the vast majority of morbidity and mortality in COPD patients.4,5 Treatments that modify these complications may improve survival in patients with COPD,4,6 whereas treatments that exclusively target the airways generally do not.5,7
Skeletal muscle dysfunction
One of the important extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD is skeletal muscle dysfunction and wasting.1 With increasing severity of disease, patients with COPD lose muscle bulk, especially in their thighs and upper arms. Over time, these patients lose exercise endurance and complain of fatigue and dyspnoea with only a minimal degree of exertion.8 These symptoms curtail their ability to exercise and compromise their cardiac fitness, which further limits their exercise tolerance, creating a vicious downward spiral that can eventually lead to generalised debility and immobility.9 Not surprisingly, skeletal muscle dysfunction contributes to reduced health status of patients with COPD and substantially increases the risk of mortality, independent of traditional markers of COPD mortality such as baseline lung function, age, and cigarette smoking.10,11 Encouragingly, early interventions with exercise programmes may restore some of the lost health status related to muscle dysfunction and increase patients' exercise tolerance and stamina.7
Despite the importance of skeletal muscle performance in COPD morbidity and mortality, the pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for the muscle failure remain largely a mystery. Clearly, with advancing disease, skeletal muscle mass decreases in COPD.12 Biopsy analyses from quadriceps and elsewhere reveal a significant reduction in type I fibres and a relative increase in type II fibres compared with normal individuals, which probably contributes to the increased fatigability and reduced muscle endurance observed in COPD patients.12 Microscopically, these skeletal muscles show accelerated apoptosis, increased oxidative stress and inflammatory changes,13,14 raising the possibility that local inflammatory and oxidative milieu may be responsible for the pathological and physiological changes in the skeletal muscles in patients with COPD.
Systemic inflammation
Three papers published in this issue of Thorax raise another intriguing possibility.15,16,17 There is now a large body of data that shows that systemic inflammation exists in stable COPD and that the intensity of the inflammatory process relates to the severity of the underlying disease.18 The systemic inflammatory process has been linked with adverse cardiovascular outcomes (including sudden deaths, arrhythmias, strokes, and myocardial infarction) and excess mortality, independent of confounding factors such as age and smoking.19 These three papers indicate that systemic inflammation in COPD is a risk factor for peripheral muscle weakness, diminished workload, and reduced exercise tolerance. Although the studies were performed by three different groups using vastly different cohorts and different methodologies, the results are strikingly similar and coherent.
In the study by Yende and colleagues15 the authors analysed data from 2273 elderly participants of the Health Aging and Body Composition study, a population based cohort of well functioning elderly individuals. As might be expected from such a cohort, only 12% of the group had spirometrically proven COPD. The authors found that reduced forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) was significantly associated with reduced quadriceps strength. They also found that plasma levels of interleukin (IL)‐6, a marker of systemic inflammation, were raised in those with COPD and were inversely related to quadriceps strength. Most importantly, raised plasma IL‐6 levels were associated with poor exercise performance. Taken together, these data suggest that systemic inflammation related to COPD may in part explain the reduced muscle strength and exercise tolerance observed in COPD patients.
In the second study Broekhuizen et al16 studied 102 patients with COPD admitted to an inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation centre; most patients had severe to very severe COPD and nearly a third were on systemic corticosteroids. As in the study by Yende and colleagues, Broekhuizen et al found that reduced FEV1 was associated with systemic inflammation as reflected by increased plasma levels of C‐reactive protein (CRP) and IL‐6. They extended the observations of Yende et al by showing that raised CRP levels were associated not only with diminished muscle strength but also with reduced exercise endurance, workload, 6 minute walk distance, and poor health status and quality of life, all of which are important clinical end points. These data thus contextualise a physiological curiosity—that is, reduced muscle strength—in a clinical framework using clinical end points that matter to patients and their physicians.20
The study by Pinto‐Plata and colleagues17 takes these findings one step further. They evaluated 88 patients with COPD and 71 controls and subjected them to extensive physiological testing and a detailed review of medications. Consistent with the results reported by Broekhuizen et al, they found that serum CRP levels were inversely related to the distanced achieved in the 6 minute walk test, independent of other factors such as age, sex, and smoking history. In their cohort, 60% of the COPD patients were taking inhaled corticosteroids at the time of assessment. They found that users of inhaled corticosteroids had serum CRP levels that were on average about 40% lower than those of corticosteroid non‐users. Adjustments for potential confounders made no material impact on these results since the two groups were well balanced in terms of age, sex distribution, baseline FEV1, and smoking history. These data suggest that inhaled corticosteroids may downregulate systemic inflammation in COPD, confirming a previous observation by our group.21
Implications of these studies
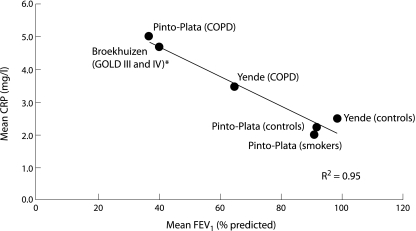
Collectively, what do these studies teach us about systemic inflammation, muscle function, and exercise performance in patients with COPD? Firstly, systemic inflammation, as measured by either CRP or IL‐6 levels, is associated with reduced FEV1. In fig 1 we have summarised the relationship between mean CRP levels and the mean FEV1 reported in the three papers. A clear (inverse) linear relationship can be seen between FEV1 and CRP, highlighting the likely importance of systemic inflammation in the progression of COPD. Secondly, systemic inflammation is associated with reduced muscle strength, exercise tolerance, and health status in COPD patients. Thirdly, inhaled corticosteroids, which downregulate airway inflammation,22 may also modulate systemic inflammation in COPD. This observation provides one plausible (but not yet proven) mechanism by which these medications improve health status and other outcomes in patients with COPD.6,7
Figure 1 Relationship between mean C‐reactive protein (CRP) levels and mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) in the three studies.15,16,17R2 of the line is 0.95. *FEV1 and CRP values were imputed based on the distribution of patients in GOLD III and IV classes and their reported CRP levels in the study.
There are, however, several important limitations to these studies that must be taken into consideration. Firstly, although the studies were well performed using validated methodologies in well characterised cohorts, they were cross sectional in design so the temporality of the relationships is uncertain. For instance, while it is tempting to ascribe systemic inflammation to muscle dysfunction, it is possible that muscle dysfunction (and perhaps the local oxidative stress and the inflammatory load within muscles) can promote systemic inflammation. The sepsis model argues in favour of systemic inflammation causing skeletal muscle dysfunction rather than the other way around.23 Moreover, there are excellent experimental models including those from transgenic mice which show that systemic inflammatory mediators and, in particular, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) can promote proteosomal degradation and catabolism of muscle fibres, probably through nuclear factor‐κB mediated pathways.24 Similarly, IL‐6 inhibits the secretion of insulin‐like growth factor I (IGF‐I) and its biological activity. IGI‐1 is an important modulator of muscle mass and function not only during the developmental period but across the entire life span.25,26
Secondly, despite the compelling logic regarding the effects of systemic inflammation on muscle dysfunction/wasting and exercise tolerance in COPD, we cannot assume that anti‐inflammatory medications will necessarily improve health outcomes in COPD. An important lesson was learned with chronic heart failure (CHF). Analogous to COPD, muscle wasting and dysfunction are common findings in advanced CHF.27 The skeletal muscles of patients with CHF, similar to COPD patients, have increased expression of TNF, IL‐6 and other inflammatory cytokines and, systemically, these cytokines are increased compared with healthy controls.27 There are now at least three published randomised controlled trials of anti‐TNF treatments (etanercept and infliximab) in CHF. Although these treatments reduce serum CRP, IL‐6 and TNF levels, they confer no measurable benefits for the patients. Two studies were terminated prematurely because of futility,28 and the one remaining study showed an increased risk of death and number of hospital admissions for heart failure in patients randomised to infliximab compared with placebo.29 These data are a sobering reminder of the enormous complexity of the inflammatory cascades and networks involved in chronic diseases such as CHF and COPD.
Notwithstanding, the three papers in this issue of Thorax have made important contributions to our current understanding of COPD. Collectively, they have extended our concept of COPD beyond the pulmonary system, provided a solid clinical and epidemiological rationale for linking systemic inflammation with peripheral muscle dysfunction, and raised the possibility of using anti‐inflammatory treatment to mitigate systemic inflammation in the hope of improving health outcomes in these patients. Systemic inflammation may well be the “missing link” between airway dysfunction and the extrapulmonary manifestations in COPD. However, we should be mindful of the enormous complexity and intricacies of the inflammatory pathways in COPD. Future research in this area will undoubtedly shed more light on this matter and also raise more questions.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: The authors have received honoraria for speaking engagements from GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and AstraZeneca and for consultative services from GSK. They have also received research funding from GSK.
References
- 1.Wouters E F. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 5: Systemic effects of COPD. Thorax 2002571067–1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wasswa‐Kintu S, Gan W Q, Man S F.et al Relationship between reduced forced expiratory volume in one second and the risk of lung cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Thorax 200560570–575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sin D D, Wu L, Man S F. The relationship between reduced lung function and cardiovascular mortality: a population‐based study and a systematic review of the literature. Chest 20051271952–1959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anthonisen N R, Skeans M A, Wise R A.et al The effects of a smoking cessation intervention on 14. 5‐year mortality: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 2005142233–239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anthonisen N R, Connett J E, Enright P L.et al Hospitalizations and mortality in the Lung Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002166333–339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sin D D, Wu L, Anderson J A.et al Inhaled corticosteroids and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 200560992–997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sin D D, McAlister F A, Man S F.et al Contemporary management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: scientific review. JAMA 20032902301–2312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sin D D, Jones R L, Mannino D M.et al Forced expiratory volume in 1 second and physical activity in the general population. Am J Med 2004117270–273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Montes de Oca M, Rassulo J, Celli B R. Respiratory muscle and cardiopulmonary function during exercise in very severe COPD. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 19961541284–1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schols A M, Broekhuizen R, Weling‐Scheepers C A.et al Body composition and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Nutr 20058253–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Marquis K, Debigare R, Lacasse Y.et al Midthigh muscle cross‐sectional area is a better predictor of mortality than body mass index in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002166809–813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mador M J, Bozkanat E. Skeletal muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res 20012216–224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Agusti A G, Sauleda J, Miralles C.et al Skeletal muscle apoptosis and weight loss in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002166485–489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Agusti A, Morla M, Sauleda J.et al NF‐kappaB activation and iNOS upregulation in skeletal muscle of patients with COPD and low body weight. Thorax 200459483–487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yende S, Waterer G W, Tolley E A.et al Inflammatory markers are associated with ventilatory limitation and muscle dysfunction in obstructive lung disease in well functioning elderly subjects. Thorax 20066110–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Broekhuizen R, Wouters E F, Creutzberg E C.et al Raised CRP levels mark metabolic and functional impairment in advanced COPD. Thorax 20066117–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pinto‐Plata V M, Mullerova H, Toso J F.et al C‐reactive protein in patients with COPD, control smokers, and non‐smokers. Thorax 20066123–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gan W Q, Man S F, Senthilselvan A.et al Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and systemic inflammation: a systematic review and a meta‐analysis. Thorax 200459574–580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tice J A, Browner W, Tracy R P.et al The relation of C‐reactive protein levels to total and cardiovascular mortality in older US women. Am J Med 2003114199–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Redelmeier D A, Bayoumi A M, Goldstein R S.et al Interpreting small differences in functional status: the six minute walk test in chronic lung disease patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 19971551278–1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sin D D, Lacy P, York E.et al Effects of fluticasone on systemic markers of inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004170760–765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gan W Q, Man S F, Sin D D. Effects of inhaled corticosteroids on sputum cell counts in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and a meta‐analysis. BMC Pulm Med 200553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Latronico N, Peli E, Botteri M. Critical illness myopathy and neuropathy. Curr Opin Crit Care 200511126–132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ladner K J, Caligiuri M A, Guttridge D C. Tumor necrosis factor‐regulated biphasic activation of NF‐kappa B is required for cytokine‐induced loss of skeletal muscle gene products. J Biol Chem 20032782294–2303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.De Benedetti F, Alonzi T, Moretta A.et al Interleukin 6 causes growth impairment in transgenic mice through a decrease in insulin like growth factor 1. J Clin Invest 199715643–650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Musaro A, McCullagh K, Paul A.et al Localized Igf‐1 transgene expression sustains hypertrophy and regeneration in senescent skeletal muscle. Nat Genet 200127195–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Drexler H, Riede U, Munzel T.et al Alterations of skeletal muscle in chronic heart failure. Circulation 1992851751–1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Anker S D, Coats A J. How to RECOVER from RENAISSANCE? The significance of the results of RECOVER, RENAISSANCE, RENEWAL and ATTACH. Int J Cardiol 200286123–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chung E S, Packer M, Lo K H.et al Randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, pilot trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor‐alpha, in patients with moderate‐to‐severe heart failure: results of the anti‐TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) trial. Circulation 20031073133–3140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]