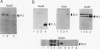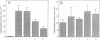Abstract
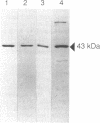
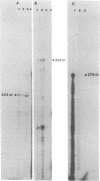
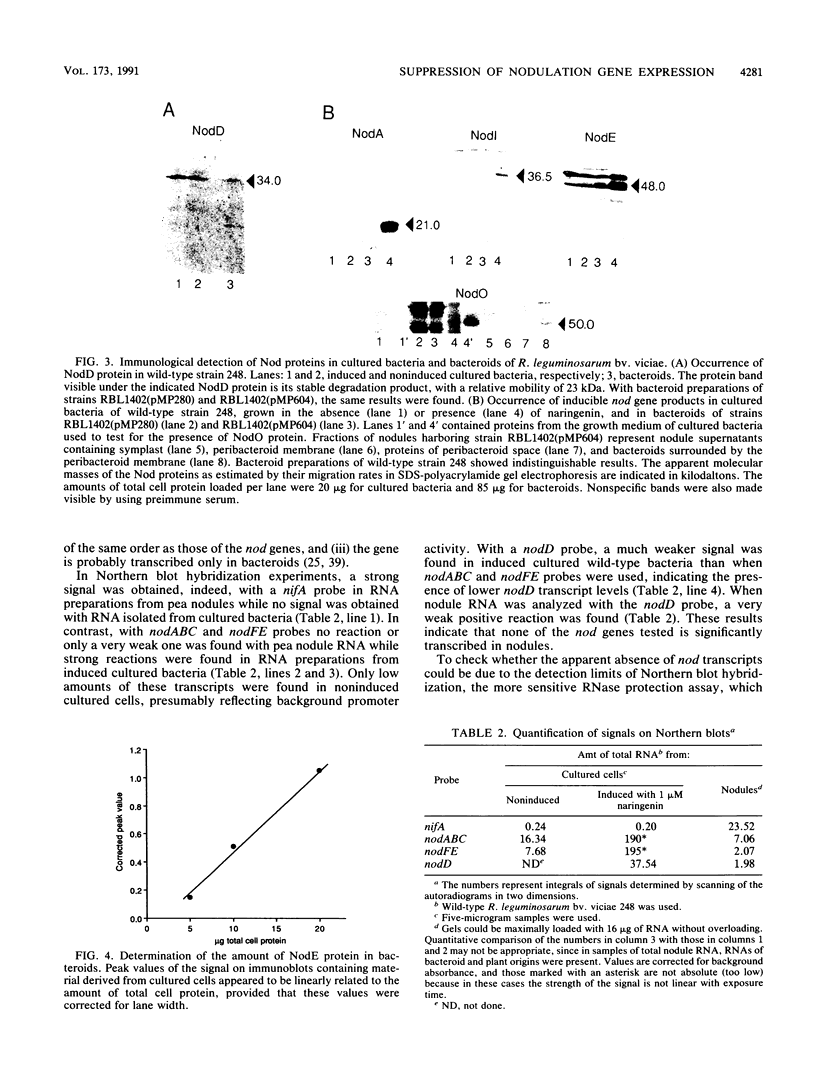
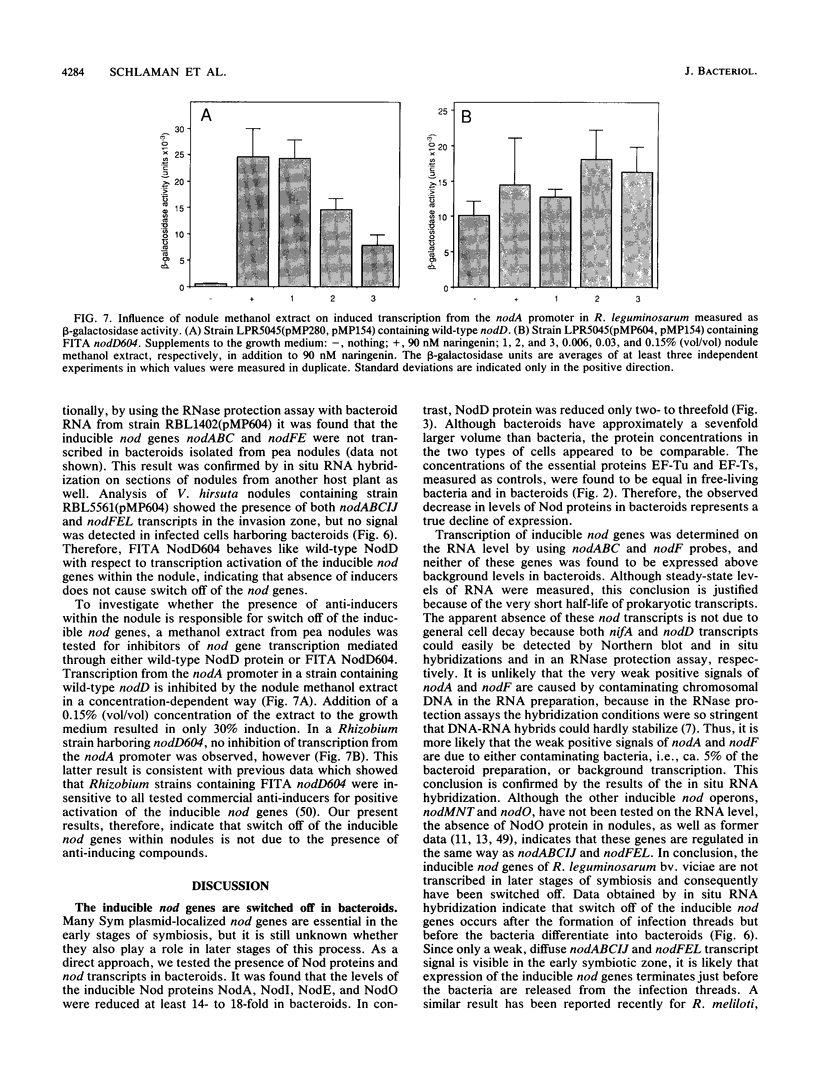
The expression of nod genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae in nodules of Pisum sativum was investigated at both the translational and transcriptional levels. By using immunoblots, it was found that the levels of NodA, NodI, NodE, and NodO proteins were reduced at least 14-fold in bacteriods compared with cultured cells, whereas NodD protein was reduced only 3-fold. Northern (RNA) blot hybridization, RNase protection assays, and in situ RNA hybridization together showed that, except for the nodD transcript, none of the other nod gene transcripts were present in bacteroids. The amount of nodD transcript in bacteroids was reduced only two- to threefold compared with that in cultured cells. Identical results were found with a Rhizobium strain harboring multicopies of nodD and with a strain containing a NodD protein (NodD604) which is activated independently of flavonoids. Furthermore, it was found that mature pea nodules contain inhibitors of induced nod gene transcription but that NodD604 was insensitive to these compounds. In situ RNA hybridization on sections from P. sativum and Vicia hirsuta nodules showed that transcription of inducible nod genes is switched off before the bacteria differentiate into bacteroids. This is unlikely to be due to limiting amounts of NodD, the absence of inducing compounds, or the presence of anti-inducers. The observed switch off of transcription during the development of symbiosis is a general phenomenon and is apparently caused by a yet unknown, negative regulation mechanism.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Production of root hair deformation factors by Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes in Escherichia coli: HsnD (NodH) is involved in the plant host-specific modification of the NodABC factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00027330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseling T., van den Bos R. C., van Kammen A. The effect of ammonium nitrate on the synthesis of nitrogenase and the concentration of leghemoglobin in pea root nodules induced by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 13;539(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canter Cremers H., Spaink H. P., Wijfjes A. H., Pees E., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Additional nodulation genes on the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;13(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00016135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R. Mapping the genetic organization of RNA by electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:239–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Redmond J. W., Batley M., Rolfe B. G. Clovers secrete specific phenolic compounds which either stimulate or repress nod gene expression in Rhizobium trifolii. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1173–1179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou A., Hamilton W. D., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium nodulation gene nodO encodes a Ca2(+)-binding protein that is exported without N-terminal cleavage and is homologous to haemolysin and related proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):349–354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Egelhoff T. T., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Specific binding of proteins from Rhizobium meliloti cell-free extracts containing NodD to DNA sequences upstream of inducible nodulation genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):282–293. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. DNA footprint analysis of the transcriptional activator proteins NodD1 and NodD3 on inducible nod gene promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5492–5502. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5492-5502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F., Burn J. E., Johnston A. W. Evidence that DNA involved in the expression of nodulation (nod) genes in Rhizobium binds to the product of the regulatory gene nodD. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9677–9690. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Snijdewint F. G., Schilperoort R. A. Identification of the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum strain 1001 and its transfer to and expression in other rhizobia and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iismaa S. E., Watson J. M. The nifA gene product from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii lacks the N-terminal domain found in other NifA proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):943–955. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondorosi E., Gyuris J., Schmidt J., John M., Duda E., Hoffmann B., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Positive and negative control of nod gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti is required for optimal nodulation. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1331–1340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIver J., Djordjevic M. A., Weinman J. J., Bender G. L., Rolfe B. G. Extension of host range of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii caused by point mutations in nodD that result in alterations in regulatory function and recognition of inducer molecules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 May-Jun;2(3):97–106. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink P. W., Hontelez J. G., van Kammen A., van den Bos R. C. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory nifA gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum PRE: transcriptional control sites and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1441–1447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Subcellular localization of the Rhizobium leguminosarum nodI gene product. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5486–5489. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5486-5489.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Spaink H. P., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Subcellular localization of the nodD gene product in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4686–4693. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4686-4693.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., John M., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nodA in Rhizobium meliloti and localization of the gene product in the cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9581–9585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Wingender R., John M., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti nodA and nodB genes are involved in generating compounds that stimulate mitosis of plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Watson J. M. DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2891–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. B., Signer E. R. Temporal and spatial regulation of the symbiotic genes of Rhizobium meliloti in planta revealed by transposon Tn5-gusA. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):344–356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Okker R. J., Wijffelman C. A., Tak T., Goosen-de Roo L., Pees E., van Brussel A. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Symbiotic properties of rhizobia containing a flavonoid-independent hybrid nodD product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4045–4053. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4045-4053.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Weinman J., Djordjevic M. A., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Genetic analysis and cellular localization of the Rhizobium host specificity-determining NodE protein. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2811–2818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surin B. P., Downie J. A. Characterization of the Rhizobium leguminosarum genes nodLMN involved in efficient host-specific nodulation. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):173–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surin B. P., Watson J. M., Hamilton W. D., Economou A., Downie J. A. Molecular characterization of the nodulation gene, nodT, from two biovars of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Schripsema J., Wijffelman C. A., van Brussel A. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Analysis of the major inducers of the Rhizobium nodA promoter from Vicia sativa root exudate and their activity with different nodD genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;13(2):175–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00016136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Wijffelman C. A., Spaink H. P., van Brussel A. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Induction of the nodA promoter of Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI by plant flavanones and flavones. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):198–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.198-204.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Spaink H. P., Pees E., Mulders I. H., Wijfjes A., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Localization and symbiotic function of a region on the Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI responsible for a secreted, flavonoid-inducible 50-kilodalton protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1151-1157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Wijfjes A. H., Spaink H. P., Ruiz-Sainz J. E., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. nodO, a new nod gene of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae sym plasmid pRL1JI, encodes a secreted protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6764–6770. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6764-6770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wiel C., Scheres B., Franssen H., van Lierop M. J., van Lammeren A., van Kammen A., Bisseling T. The early nodulin transcript ENOD2 is located in the nodule parenchyma (inner cortex) of pea and soybean root nodules. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Talens A., Bosch L. The role of EF-Tu in the expression of tufA and tufB genes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):397–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]