Abstract
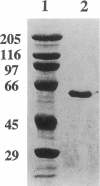
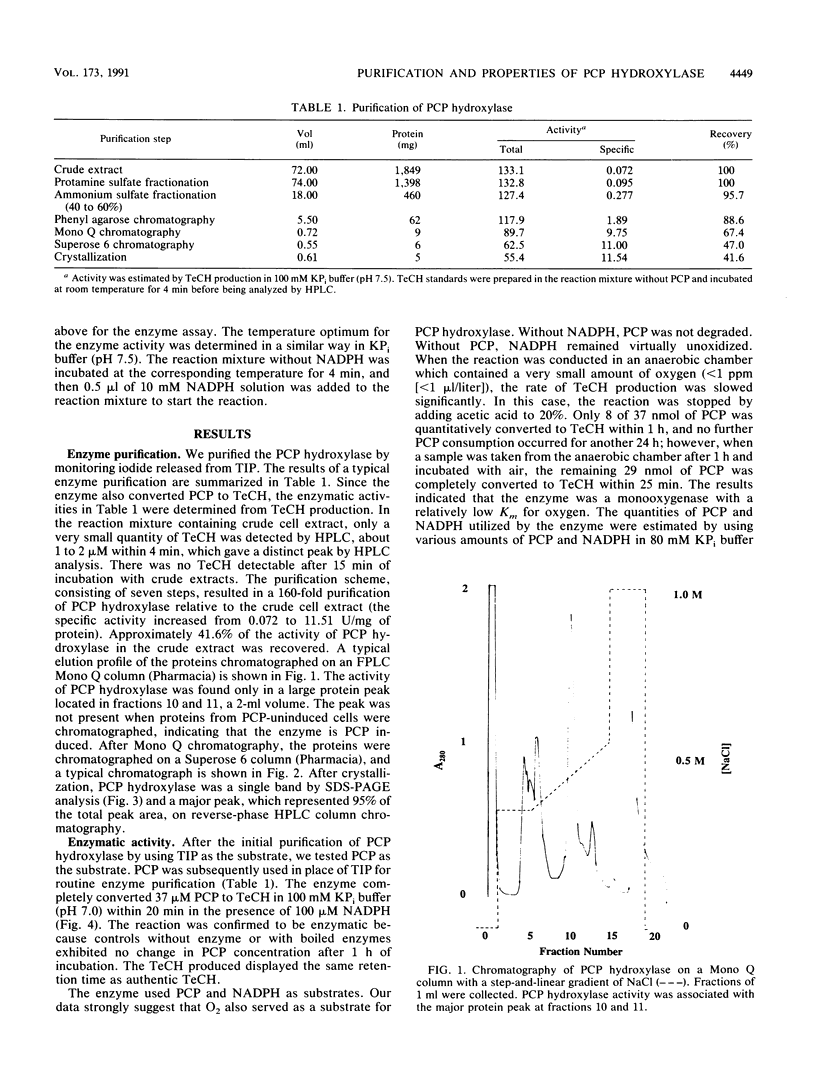
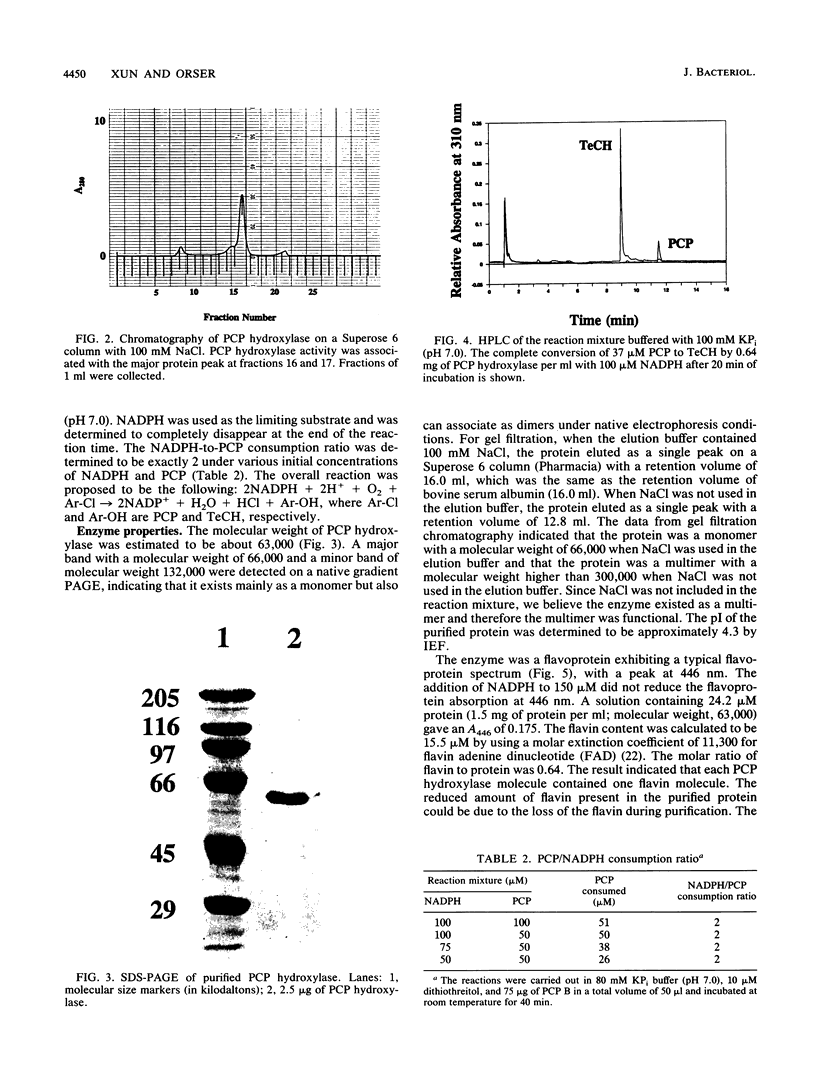
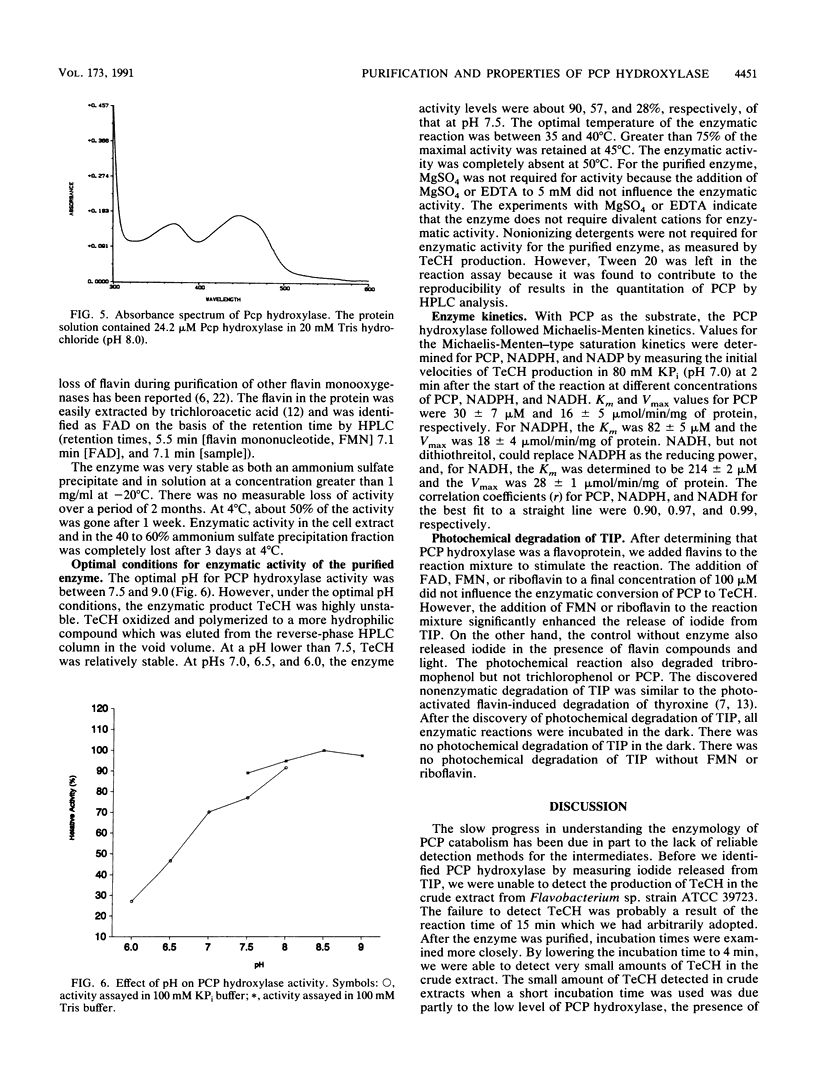
A pentachlorophenol (PCP) hydroxylase which catalyzed the conversion of PCP to 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorohydroquinone and released iodide from triiodophenol in the presence of NADPH and oxygen was identified. The enzyme was purified by protamine sulfate precipitation, ammonium sulfate precipitation, hydrophobic chromatography, anion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, and crystallization. The enzyme was a monomer with a molecular weight of 63,000. Under certain conditions, dimer and multimer conformations were also observed. The pI of the enzyme was pH 4.3. The optimal conditions for activity were a pH of 7.5 to 8.5 and a temperature of 40 degrees C. Each enzyme molecule contained one flavin adenine dinucleotide molecule. The Km for PCP was 30 microM and the Vmax was 16 mumol/min/mg of protein. The enzymatic reaction required 2 mol of NADPH per mol of halogenated substrate. On the basis of the data we present, it is likely that PCP hydroxylase is a flavoprotein monooxygenase. The addition of flavins to the reaction mixture did not stimulate the enzymatic reaction; however, we identified the photodegradation of triiodophenol and tribromophenol, but not PCP, by flavin mononucleotide or riboflavin and light.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Dechlorination and para-hydroxylation of polychlorinated phenols by Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.675-681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. P., Kirsch E. J. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by an axenic bacterial culture. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1033-1035.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALTON V. A., INGBAR S. H. A photoactivated flavin-induced degradation of thyroxine and related phenols. Endocrinology. 1962 Feb;70:210–220. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Entsch B., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Chapman P. J. Fluoride elimination from substrates in hydroxylation reactions catalyzed by p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4189–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Janke D., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Hydroxylation and Dechlorination of Tetrachlorohydroquinone by Rhodococcus sp. Strain CP-2 Cell Extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):516–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.516-519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy C. C. Melilotate hydroxylase. Purification of the enzyme and the nature of the prosthetic group. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):747–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus A., Krekel D., Lingens F. Purification and some properties of component A of the 4-chlorophenylacetate 3,4-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas species strain CBS. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12883–12888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G., Massey V. Purification and characterization of flavodoxin from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):794–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. C., Vaidyanathan C. S. Purification and properties of benzoate-4-hydroxylase from a soil pseudomonad. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber D. L., Crawford R. L. Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1512-1518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk T., Müller R., Mörsberger F., Otto M. K., Lingens F. Enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by extracts from Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5487–5491. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5487-5491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanlake G. J., Finn R. K. Isolation and characterization of a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1421–1427. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1421-1427.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Crawford R. L. Catabolism of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Pignatello J. J., Crawford R. L. Degradation of chlorinated phenols by a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):907–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.907-910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Massey V. The purification and properties of the flavoprotein melilotate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2944–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by a soil microbe. J Environ Sci Health B. 1977;12(2):113–127. doi: 10.1080/03601237709372057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L. Y., Orser C. S. Purification of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol-induced periplasmic protein (PcpA) and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene (pcpA). J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2920–2926. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2920-2926.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Biodegradation of triiodophenol by cell-free extracts of a pentachlorophenol-degrading Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90482-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]