Abstract
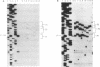
We have generated a series of deletions in the downstream region of the lac promoter. The promoter activities of these mutations were compared by measuring the levels of beta-galactosidase gene expression in vivo. Our results show that deletion of downstream lac promoter sequences changes the promoter strength only two- to threefold. The effects of these deletions on transcription initiation site location were studied through primer extension assay of in vivo mRNAs. We found that the transcription start sites are primarily chosen as an approximate distance from the -10 region of the lac promoter; however, starts are sometimes manifested at a GAATT(C) sequence, which is identical to the wild-type preferred start site. lac promoter P2 and a newly identified promoter, P3, are transcribed in vivo at low levels. Catabolite activator protein complexed with cyclic AMP represses P2 and P3 expression in vivo. The secondary catabolite activator protein binding site plays at most a modest role in catabolite repression in vivo.
Full text
PDF
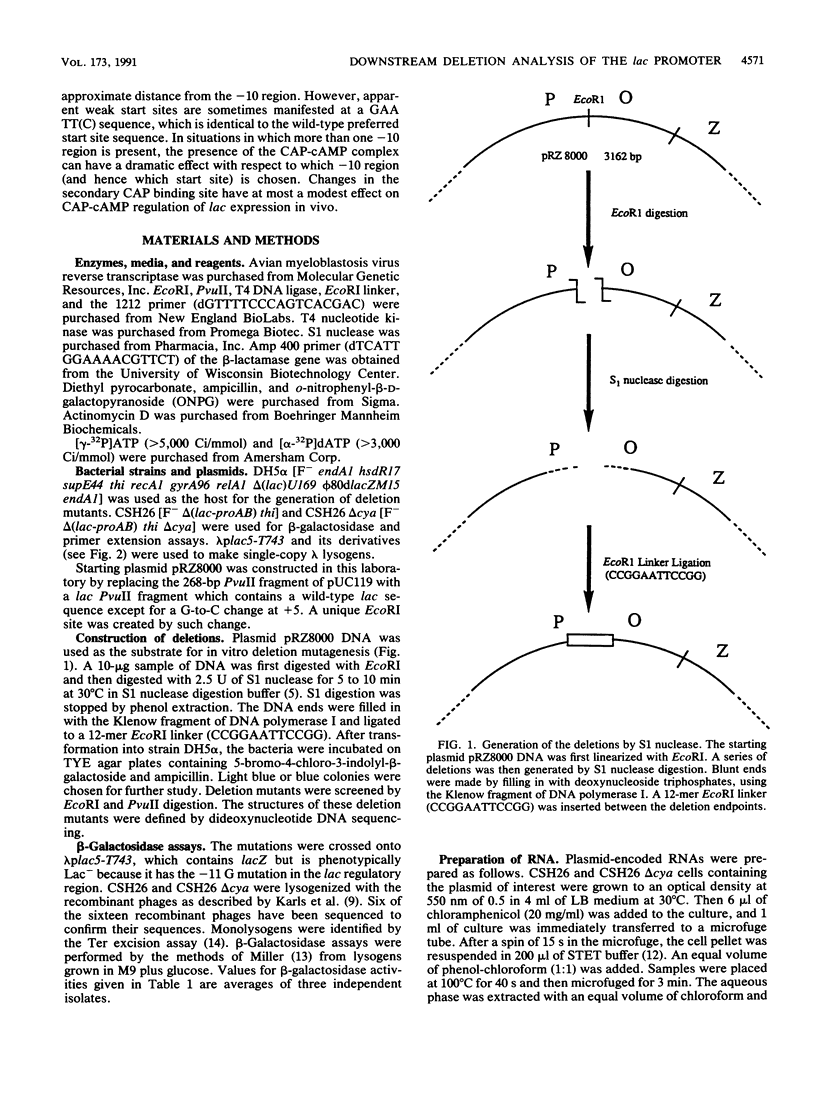


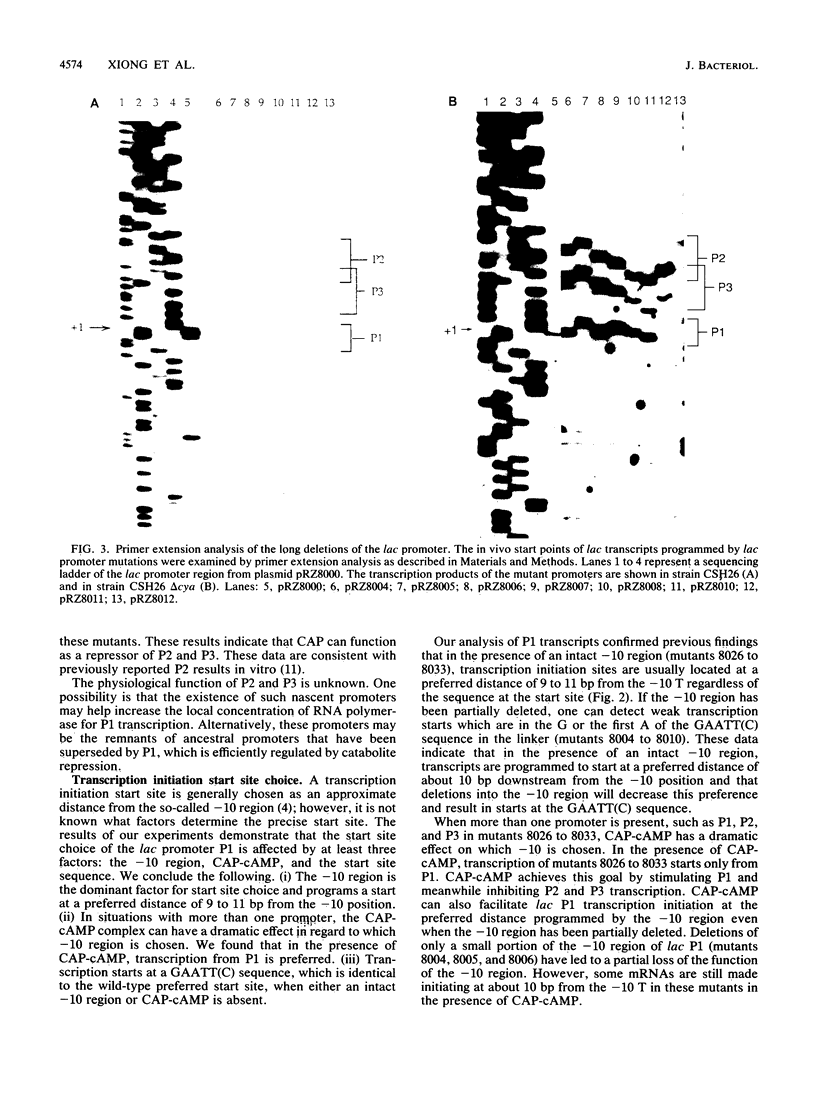


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donnelly C. E., Reznikoff W. S. Mutations in the lac P2 promoter. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1812–1817. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1812-1817.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. M., Fried M. G. Co-operative interactions between the catabolite gene activator protein and the lac repressor at the lactose promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):381–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90188-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karls R., Schulz V., Jovanovich S. B., Flynn S., Pak A., Reznikoff W. S. Pseudorevertants of a lac promoter mutation reveal overlapping nascent promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3927–3949. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer D. D., Cao J. L., Revzin A. Specific sequences downstream from -6 are not essential for proper and efficient in vitro utilization of the Escherichia coli lactose promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., McClure W. R. Dual promoter control of the Escherichia coli lactose operon. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Thomas R. Ter, a function which generates the ends of the mature lambda chromosome. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):242–244. doi: 10.1038/221242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Reznikoff W. S. Properties of lac P2 in vivo and in vitro. An overlapping RNA polymerase binding site within the lactose promoter. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A. Cyclic AMP receptor proteins interacts with lactose operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]