Abstract
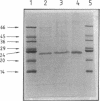
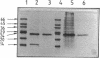
Porins were purified from cells of the anaerobic gram-negative bacterium Pelobacter venetianus grown with 20-kDa polyethylene glycol. After treatment of the cell envelope fraction with sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing solutions, the murein contained only two major peptidoglycan-associated proteins of 14 and 23 kDa. Both proteins were released from the peptidoglycan by the detergent Triton X-100. Genapol X-80 released only the 23-kDa protein. This protein was purified by chromatography on a hydroxyapatite column. It did not form sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant oligomers. Reconstituted in lipid bilayer membranes, the 23-kDa protein formed cation-selective channels with a single-channel conductance of 230 pS in 1 M KCl. The channel is not a general-diffusion pore, since its conductance depends only moderately on the salt concentration. The channel conducted ammonium much better than potassium or rubidium ions, suggesting that it is probably involved in ammonium uptake. The outer membrane of P. venetianus contains a further, non-murein-associated pore with an unknown molecular mass. It is also cationically selective and has a single-channel conductance of 1.6 nS in 1 M KCl, which suggests that its effective diameter is similar to that of porins from enteric bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Bauer K. Permeation of hydrophilic molecules through the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Review on bacterial porins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Hancock R. E. Mechanism of ion transport through the anion-selective channel of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Feb;89(2):275–295. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Boos W., Läuger P. Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;511(3):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Läuger P. Ionic selectivity of pores formed by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 8;551(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Hancock R. E. Ion selectivity of gram-negative bacterial porins. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.722-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Vos-Scheperkeuter G. H. Mechanism of sugar transport through the sugar-specific LamB channel of Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(1):21–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02209137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Wagner W., Goebel W. Pore formation by the Escherichia coli hemolysin: evidence for an association-dissociation equilibrium of the pore-forming aggregates. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):887–895. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.887-895.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K. Molecular design of PhoE porin and its functional consequences. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier C., Bremer E., Schmid A., Benz R. Pore-forming activity of the Tsx protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Demonstration of a nucleoside-specific binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2493–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Identification of the outer membrane protein of E. coli that produces transmembrane channels in reconstituted vesicle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson A. P., McQuarrie D. A. The effect of discrete charges on the electrical properties of a membrane. I. J Theor Biol. 1975 Nov;55(1):13–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(75)80106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Proteins forming large channels from bacterial and mitochondrial outer membranes: porins and phage lambda receptor protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:85–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr T. R., Jr, Poole K., Crockford G. W., Hancock R. E. Lipopolysaccharide-free Escherichia coli OmpF and Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein P porins are functionally active in lipid bilayer membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.523-526.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Stieb M. Fermentative degradation of polyethylene glycol by a strictly anaerobic, gram-negative, nonsporeforming bacterium, Pelobacter venetianus sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1905–1913. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1905-1913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Porin from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):199–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.199-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Kreusch A., Schiltz E., Nestel U., Welte W., Weckesser J., Schulz G. E. The structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus at 1.8 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):379–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Purification and properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2308–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Dimeric porin from Paracoccus denitrificans. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):430–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.430-433.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]