Abstract
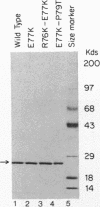
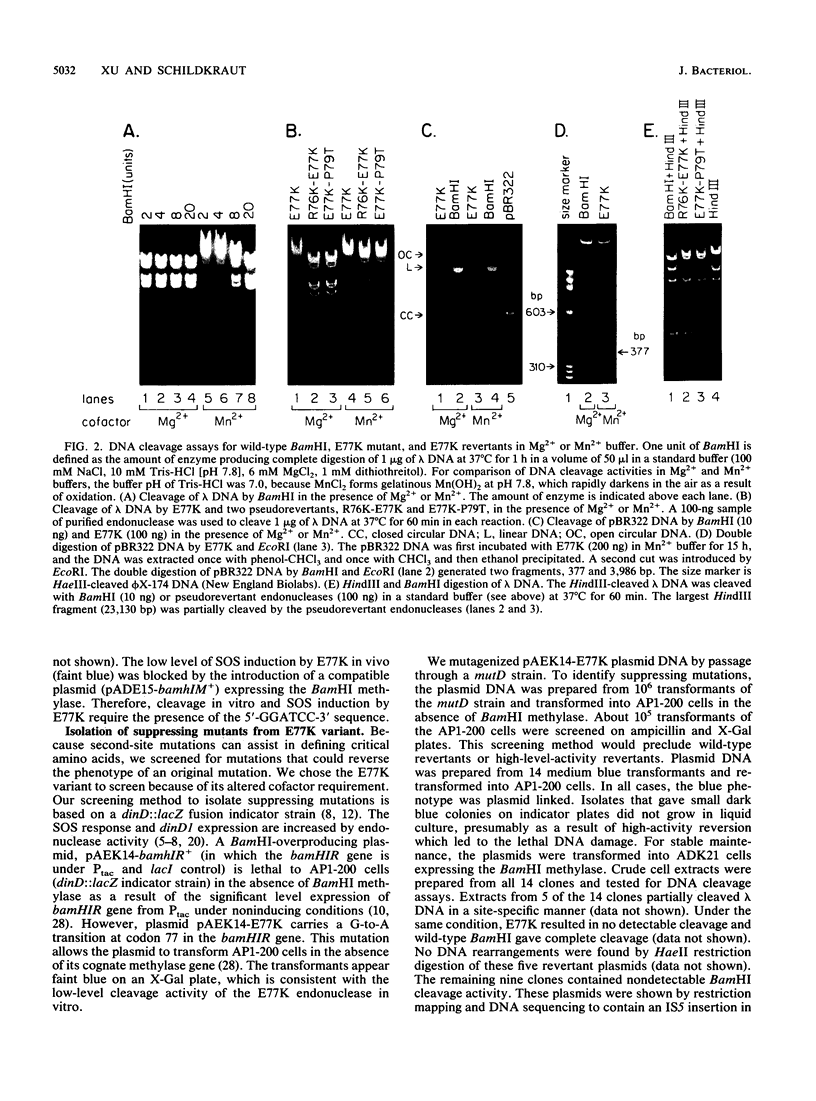
A mutant BamHI endonuclease, E77K, belongs to a class of catalytic mutants that bind DNA efficiently but cleave DNA at a rate more than 10(3)-fold lower than that of the wild-type enzyme (S. Y. Xu and I. Schildkraut, J. Biol. Chem. 266:4425-4429, 1991). The preferred cofactor for the wild-type BamHI is Mg2+. BamHI is 10-fold less active with Mn2+ as the cofactor. In contrast, the E77K variant displays an increased activity when Mn2+ is substituted for Mg2+ in the reaction buffer. Mutations that partially suppress the E77K mutation were isolated by using an Escherichia coli indicator strain containing the dinD::lacZ fusion. These pseudorevertant endonucleases induce E. coli SOS response (as evidenced by blue colony formation) and thus presumably nick or cleave chromosomal DNA in vivo. Consistent with the in vivo result, the pseudorevertant endonucleases in the crude cell extract display site-specific partial DNA cleavage activity. DNA sequencing revealed two unique suppressing mutations that were located within two amino acid residues of the original mutation. Both pseudorevertant proteins were purified and shown to increase specific activity at least 50-fold. Like the wild-type enzyme, both pseudorevertant endonucleases prefer Mg2+ as the cofactor. Thus, the second-site mutation not only restores partial cleavage activity but also suppresses the metal preference as well. These results suggest that the Glu-77 residue may play a role in metal ion binding or in enzyme activation (allosteric transition) following sequence-specific recognition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Benner J. S., Heiter D. F., Silber K. R., Sznyter L. A., Jager-Quinton T., Moran L. S., Slatko B. E., Wilson G. G., Nwankwo D. O. Cloning the BamHI restriction modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):979–997. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Nathan P. D., Landry D., Sznyter L. A., Waite-Rees P., Ives C. L., Moran L. S., Slatko B. E., Benner J. S. Characterization of the cloned BamHI restriction modification system: its nucleotide sequence, properties of the methylase, and expression in heterologous hosts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):841–850. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Model P. Mutants of the EcoRI endonuclease with promiscuous substrate specificity implicate residues involved in substrate recognition. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3369–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Model P. Substrate recognition by the EcoRI endonuclease. Proteins. 1990;7(2):185–197. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Zinder N. D., Model P. Repair of the Escherichia coli chromosome after in vivo scission by the EcoRI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack W. E., Greenough L., Dorner L. F., Xu S. Y., Strzelecka T., Aggarwal A. K., Schildkraut I. Overexpression, purification and crystallization of BamHI endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1825–1829. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. DNA-damaging agents stimulate gene expression at specific loci in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. C., Grable J. C., Love R., Greene P. J., Rosenberg J. M. Refinement of Eco RI endonuclease crystal structure: a revised protein chain tracing. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1307–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2399465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King K., Benkovic S. J., Modrich P. Glu-111 is required for activation of the DNA cleavage center of EcoRI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11807–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardone G., Chirikjian J. G. The enzymes of the BamH I restriction-modification system. Gene Amplif Anal. 1987;5:147–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Fontaine A. An endonuclease specific for single-stranded DNA selectively damages the genomic DNA and induces the SOS response. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3173–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piekarowicz A., Yuan R., Stein D. C. A new method for the rapid identification of genes encoding restriction and modification enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1831–1835. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Sancar G. B. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:29–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. A., Chirikjian J. G. Purification and characterization of the sequence-specific endonuclease Bam HI. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1003–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. H., Clarke C. H., Marinus M. G. Specificity of Escherichia coli mutD and mutL mutator strains. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90488-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. Y., Schildkraut I. Isolation of BamHI variants with reduced cleavage activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4425–4429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]