Abstract
Pseudotumors or tumor-like proliferations (non-neoplastic masses) and benign mimickers (non-neoplastic cellular proliferations) are rare in the testis and paratesticular structures. Clinically, these lesions (cysts, ectopic tissues, and vascular, inflammatory, or hyperplastic lesions) are of great interest for the reason that, because of the topography, they may be relevant as differential diagnoses. The purpose of this paper is to present an overview of the pseudoneoplasic entities arising in the testis and paratesticular structures; emphasis is placed on how the practicing pathologist may distinguish benign mimickers and pseudotumors from true neoplasia. These lesions can be classified as macroscopic or microscopic mimickers of neoplasia.
Keywords: Testis, Paratesticular structures, Pseudotumor, Tumor-like, Benign mimics
Introduction
There are many lesions that can simulate a neoplasm in the testis or paratesticular structures. Their incidence among tumors arising within the scrotal sac varies according to different series from 6 to 30% [16, 32]. These pseudoneoplastic lesions can be divided into those that only macroscopically imitate neoplasia (Table 1) and those that microscopically imitate neoplasia, regardless of whether they form a macroscopic mass (Table 2). The latter group causes more problems to the practicing pathologist in terms of the correct classification of a giving lesion. Hereby, we summarize main tumor-like lesions and benign mimickers that may be seen in the testis and paratesticular coverages, with emphasis on morphologic criteria for the differential diagnosis from true neoplasia.
Table 1.
Macroscopic mimickers (pseudotumors) of testicular and paratesticular neoplasia
| Vascular lesions |
| Intratesticular hemorrhage |
| Segmental testicular infarction |
| Organizad testicular hematocele |
| Cholesterol granuloma of the tunica vaginalis |
| Inflammatory lesions |
| Nonspecific infectious inflammatory lesions |
| Specific infectious inflammatory lesions |
| Non-infectious inflammatory lesions |
| Idiopathic inflammatory lesions |
| Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis |
| Testicular malakoplakia |
| Testicular sarcoidosis |
| Meconium periorchitis |
| Sperm granuloma |
| Cysts |
| Testicular cysts |
| Albuginea cysts |
| Parenchymal cysts (Epidermoid cysts) |
| Rete-testis cysts- Cystic displasia of the rete testis |
| Epididymal cysts and Spermatoceles |
| Spermatic cord cysts |
| Ectopic tissues |
| Adrenal cortical rests |
| Spleno-gonadal fusion |
| Testicular appendages |
| Miscellaneous other lesions |
| Fibrous pseudotumors; (Fibromatous periorchitis-Nodular periorchitis) |
| Amyloidosis |
| Polyorchididm |
| Sclerosing lipogranuloma |
Table 2.
Microscopic mimickers of testicular and paratesticular neoplasia
| Testicular |
| Inflammatory-reactive lesions |
| Lymphocitic orchitis (Testicular pseudolymphoma) |
| Rosai-Dorfman disease |
| Sertoli cell hyperplasia |
| Pick adenoma |
| Hamartomatous proliferation testicular feminization syndrome |
| Interstitial cell hyperplasia |
| Leydig cell hyperplasia |
| Testicular “tumor” of the adrenogenital syndrome |
| Hyperplasia of the rete testis |
| Epididymis |
| Adenomatoid hyperplasia |
| Tunicas albuginea-vaginalis |
| Mesothelial hyperplasia |
| Spermatic cord |
| Vasitis nodosa |
| Inflammatory pseudotumor (Funiculitis proliferans) |
| Miscellaneous other lesions |
Macroscopic mimickers (pseudotumors) of testicular and paratesticular neoplasia
This group of lesions refers to those that macroscopically imitate a neoplasia. Frequently, these lesions affect both compartments and are therefore difficult to establish if one or both are affected. For this reason, we classify the tumor-like lesions according to their etiology.
Vascular lesions
The majority of the vascular disorders of the male gonad are not confused with a tumor because, in addition to causing acute symptoms, they usually affect the entire gonad. However, in the rare situation in which the vascular lesion is segmental, it can simulate neoplasia, as follows:
Intratesticular hemorrhage, which occurs spontaneously [24] or in the context of anticoagulation treatment [15], may simulate a tumor at ultrasound examination.
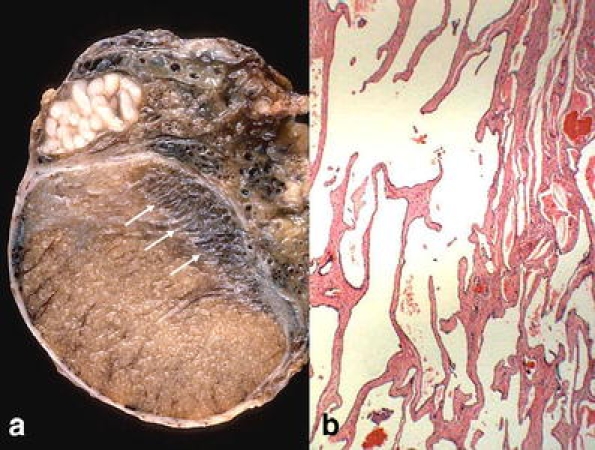
Segmental testicular infarction, a lesion clinically characterized by slight local pain unrelated to any acute episode [20], may be related to isolated or systemic vasculitis [43, 103] with morphology of polyarteritis nodosa [21], giant cell vasculitis [94], or Wegener granulomatosis [45]. Up to year 2000, 81 cases of systemic vasculitis with testicular tumor-like lesion have been recorded [45]. Other cases are seen in the context of a hematological disease (sickle cell anemia) [53] or associated with nonspecific perivascular fibrosis. Any of the phases of an infarction can be observed from acute (with hemorrhage) to healing stage (Fig. 1). Currently, the clinical diagnosis can be suspected with Doppler sonography [81], avoiding orchiectomy.
Organized testicular hematocele and other hemorrhages in the tunica vaginalis are rarely confused with a neoplasia [89], but this can happen occasionally in long-standing cases because of fibrous thickening with cholesterol granuloma formation in the tunica vaginalis (Fig. 2) [61] Exceptionally, a true testicular neoplasia presents clinically with a hematocele [86].
Fig. 1.
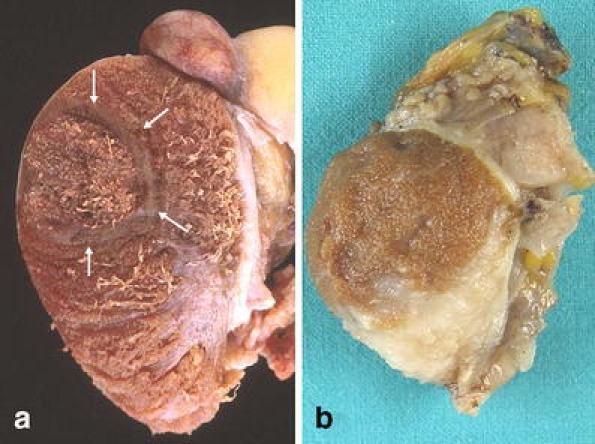
Segmental testicular infarction. a Acute hemorrhagic with reinforcement of the peripheral area (arrows). b Healing fibrosis
Fig. 2.
Cholesterol granuloma in the tunica vaginalis (H&E)
Inflammatory lesions
Similar to what was stated for vascular tumor-like lesions, inflammation that simulates a neoplasia usually has atypical clinical features; these entities can be grouped as follows:
Nonspecific infectious inflammatory lesions with a tumor-like presentation are frequently chronic processes causing progressive fibrosis, which may clinically [38] or sonographicaly [23] simulate neoplasia. Rarely a testicular, epididymal, or vas deferens abscess can look like a neoplasia [84]. Very occasionally, testicular neoplasia can clinically imitate an acute inflammatory process [44].
Specific infectious inflammatory lesions. The entities of this group that most often have been confused with neoplasias are granulomatous inflammation in tuberculosis [87], brucellosis [49], syphillis [5], fungal infections [42], and parasite diseases [9]. These lesions are usually not problematic for the pathologist.
Noninfectious inflammatory lesions. This group of tumor-like lesions include different entities among which can be highlighted:
Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis, probably of autoimmune aetiology, of which around 230 cases have been published [4], is characterized by tubular granulomas (tubular orchitis; Fig. 3) or interstitial granulomas (interstitial orchitis). The presence of intratubular giant cells differentiate this entity from infectious granulomatous orchitis [70]. Diffuse testicular hypoechoic involvement with only peripheral low-resistance flow on color Doppler sonography is a typical but not pathognomonic pattern [72].
Malakoplakia. This lesion is secondary to a mononuclear decrease in cyclin–guanine monophosphate that impairs the killing of bacteria. Fusion of the phagolysosomes with bacterial rests produces the characteristic Michaelis–Gutman bodies in the cytoplasm of the macrophages (von Hansemann cells) [1] (Fig. 4). Giant cells are occasional or absent. Testicular involvement represents only 12% of genital malakoplakia with around 388 cases in the literature [19, 56]; exceptionally, it may affect the epididymis only [31]. It has been related to idiopathic granulomatous orchitis [56, 57] and chronic xantogranulomatous inflammation of testis [85, 109, 110]; this last also reported in the spermatic cord [64, 100].
Sarcoidosis. Testicular involvement in a systemic sarcoidosis [39] is exceedingly rare, and its presentation as the primary form is even rarer; in these cases, the epididymis is affected more with the testicle being involved by contiguity [83].
Meconium periorchitis. This is an infrequent lesion (around 30 cases being reported) that typically presents in the first months of life; most times there is a clinical history with obstetric problem that has caused the passing of meconium toward the testicular surrounding structures [29]. The macroscopic appearance is a myxoid material with calcified pearls resulting from the calcification of the remains of squamous cells or lanugo hairs [107] (Fig. 5). Suspicion of neoplasia, although very uncommon in this period of life, may be caused by a scrotal mass or sonographically detectable calcifications [6]. Clinically, the peritesticular and spermatic cord enlargement can simulate a paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma.
Sperm granuloma. As its name indicates, this granulomatous lesion with few giant cells is the consequence of extravasation of spermatozoa generally postvasectomy (40% of vasectomized men and 2.5% of general population) [108]. When it produces a tumor-like lesion, it is usually located in the deferent duct or the epididymis [22] with firm nodules of 0.7 to 4 cm with occasional cysts formation.
Fig. 3.
Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis characterized by tubular granulomas (tubular orchitis)
Fig. 4.
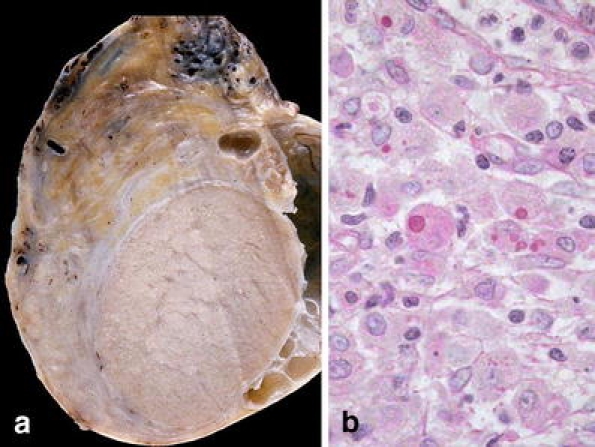
Malakoplakia. a Macroscopic appearance with a homogeneous aspect. b The characteristic Michaelis–Gutman bodies in the cytoplasm of the macrophages (von Hansemann cells) (PAS)
Fig. 5.
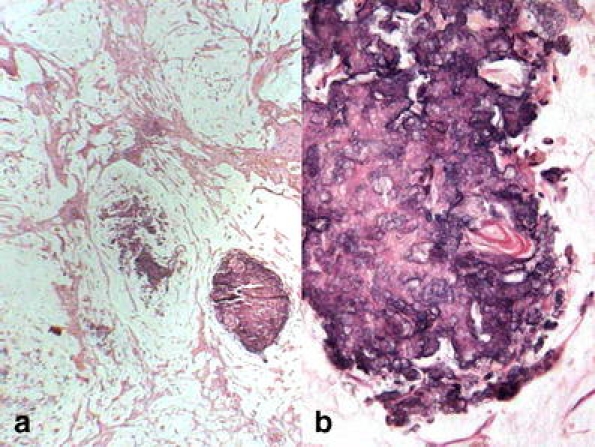
Meconium periorchitis. a calcified pearls resulting from the calcification of the remains of squamous cells or lanugo hairs. b Keratin rest in one of the calcifications (H&E)
Cysts
The majority of the cysts with a tumor-like appearance are paratesticular structures, but the testicle may occasionally have some cystic lesions that can be confused with a neoplasia.
Testicular cysts occur in approximately 8–10% of patients with a lump in the testis, including those of the tunica albuginea or the parenchyma [33].
Tunica albuginea cysts do not usually cause any diagnostic problem, unless if they are complex cysts [74].
Parenchyma testicular cysts can be more difficult to distinguish from a neoplasia and if there is the slightest suspicion of an intracystic content, one must suspect a malignant neoplasia [107]. Special consideration deserves the testicular Epidermoid cyst, which must only be lined with squamous epithelium (Fig. 6). It is recommended that the specimen is examined “in toto” to avoid underdiagnosis of any area of teratoma (especially among postpuberal patients) or intratubular germ cell neoplasia, as sonographically it is not possible to distinguish between these lesions [54, 106]. Epidermoid cysts represent 1% of the masses of the testes. Recent genetic studies have shown that there is no chromosome 12p abnormality [14], thus supporting its distinction from teratoma.
Tubular ectasia of the rete testis secondary to obstruction and generally located in the mediastinum area of the testes (Fig. 7) [69], is usually bilateral and very different from cystic dysplasia of the rete testis, a congenital lesion with complete testicular parenchyma substitution [68].
Epididymal cysts and spermatoceles are relatively frequent and the majority are in relation to the inflammatory processes. The differential diagnosis with other entities are related to its size, and similar to the other cystic formations a true neoplasia must be considered in case of observing any content in its interior [108].
Spermatic cord cysts. The majority of these cysts do not cause any diagnostic doubts, only the occasional Epidermoid cysts [46, 105] can simulate a neoplasia. These cysts can be unilocular or multilocular depending on their origin [65], and the multilocular must be distinguished from the exceptional cystadenomas of probably Müllerian origin [55].
Fig. 6.
Epidermoid cyst, which must only be lined with squamous cell epithelium (H&E)
Fig. 7.
a Tubular ectasia of the rete testis located in the mediastinum area of the testes (arrows). b Microscopic aspect (H&E)
Ectopic tissues
Ectopic adrenocortical tissue is relatively frequent in the tunica albuginea, rete testis, epididymis, and spermatic cord and occasionally reaches the size to be symptomatic. Its incidence ranges from 2.5 to 15% [17, 102]. It is made up of adrenal cortical nodes surrounded by a connective tissue band and of about 5 mm in diameter on average (Fig. 8); for which reason, they are not clinically palpable. Only in cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia or Cushing syndrome, ectopic adrenocortical tissue can be prominent and appear as a tumor-like lesion [90].
Splenic–gonadal fusion, as its name indicates, is the fusion of spleen and gonad. It is more frequent on the left side, with about 148 published cases [41]. Morphologically, the ectopic splenic tissue can be in close relation to the head of the epididymis or the upper pole of the testis (Fig. 9) or being separated from it; likewise, there may or may not be a structural continuity between the normal spleen and the ectopic tissue [30]. The same alteration has been described in women, but it is much less frequent that in men, probably because it is much easier to find it clinically in men. In about 30% of the cases, it is associated with complex malformations such as micrognathia, peromelia, or phocomelia (absence of upper portion of a limb) [30, 60, 95]. In three of the reported cases, the fusion was associated with a germ cell tumor of the testis [41].
An exceptional hepato-gonadal fusion is reported [26].
Fig. 8.
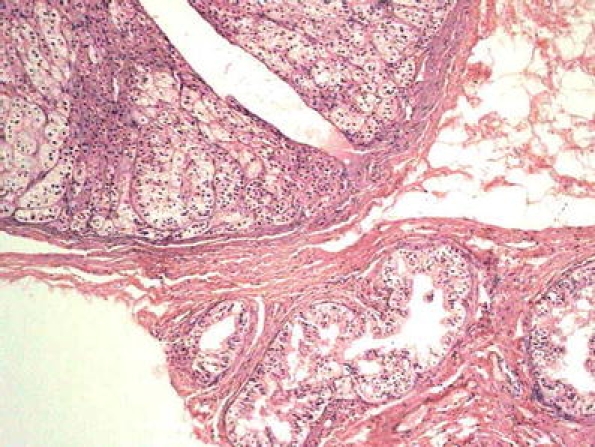
Ectopic adrenocortical tissue. Adrenal cortical nodes surrounded by a connective tissue band in continuity with epididymis. (H&E)
Fig. 9.
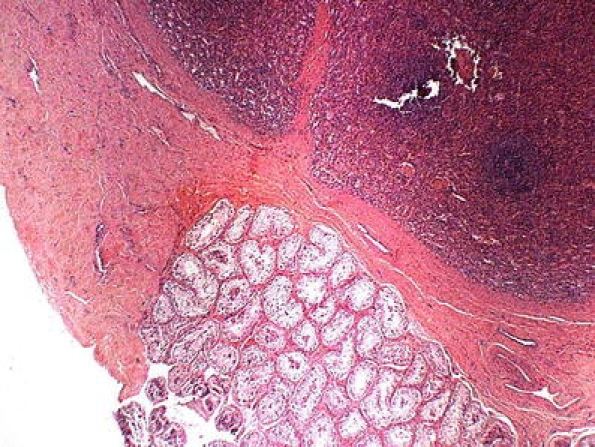
Splenic–gonadal fusion. The ectopic splenic tissue in close relation with the upper pole of the testis (H&E)
Testicular appendages
There are five testicular appendages, but for the surgical pathologist, only three can be of interest (appendix testis or hydatid of Morgagni, appendix epididymis, paradidymis or organ of Giraldes; Fig. 10). These structures are not usually the origin of a tumor-like lesion, but in rare cases of large-sized cysts, it may presents as a paratesticular mass [93]. A case of ectopic epididymal tissue in an appendix testis [101] has recently been reported.
Fig. 10.
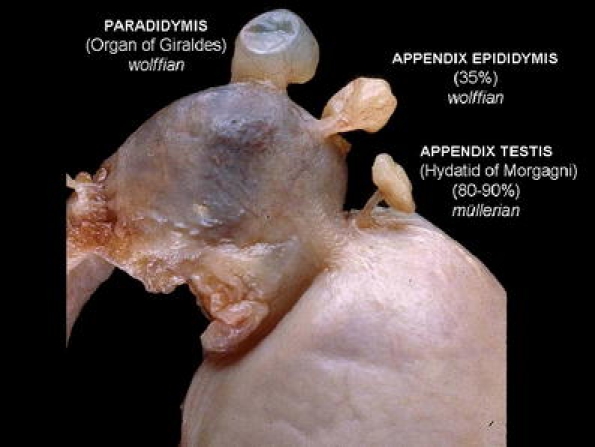
Normal testicular appendages
Miscellaneous other lesions
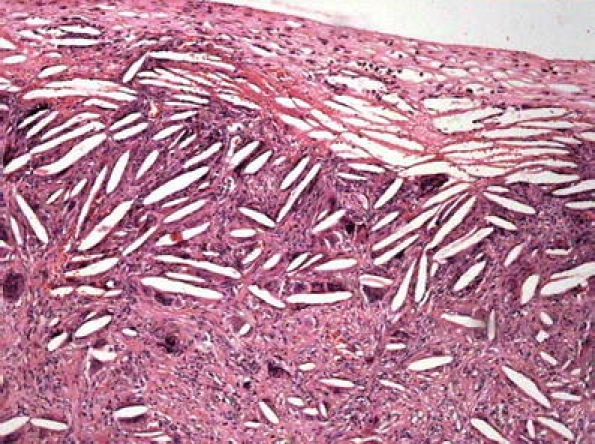
Fibrous pseudotumors. This name refers to a fibrosis phenomenon with paucicellular hyalinized collagen (Fig. 11) presenting as nodular (single or multiple) or diffuse lesion of the testicular tunics [96, 71]. Sometimes, a node can be free (scrotal mouse) [108]. This broadly considered spectrum of lesions has received diverse names: chronic periorchitis, fibromatous periorchitis, nodular periorchitis, fibrous proliferation of the tunica, nonspecific paratesticular fibrosis, granulomatous periorchitis, nodular fibrous pseudotumor, fibrous pseudotumor, inflammatory pseudotumor, fibroma, reactive periorchitis [108], indicating its controversial pathogenesis. Some cases have been reported preceded by trauma or infection, and on occasion, an inflammatory component can be observed and granulation tissue suggesting the possibility that there might be the healing of an inflammatory pseudotumor, (which will be described later on) [10]. Although radiologically, it is not difficult to recognize, upon occasion, an intraoperative frozen section becomes necessary.
Amyloidosis. It is usually bilateral and present in a patient with a prior history of amyloidosis [34]; more rarely, it is a primary form that by being a cryptorquidic patient simulates a testicular tumor [13].
Polyorchidism or supernumerary testes is a rare condition, which is easy to recognize. However, the sonography can occasionally be different from that of the normal testis, and the condition may then be tumor suspicious [79].
Fig. 11.
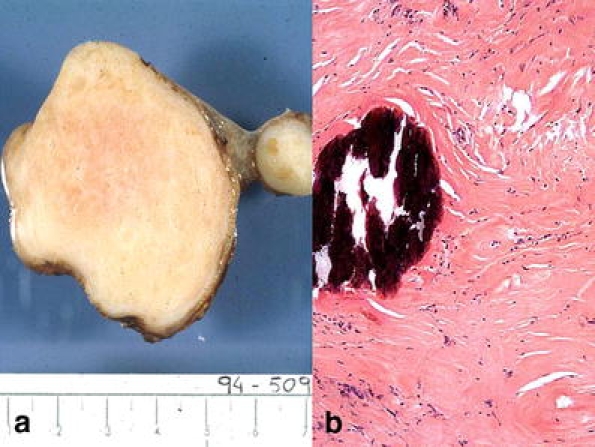
Fibrous pseudotumor. a Well outlined fibrous-like nodule. b Paucicellular hyalinized collagen with calcification
Microscopic mimickers of testicular and paratesticular neoplasia
Lesions or cellular changes that microscopically imitate a neoplasia are included under this category, whether or not they make a clinical mass. These changes are closely related to the structure of the organ in which they arises, as follows.
Testicular
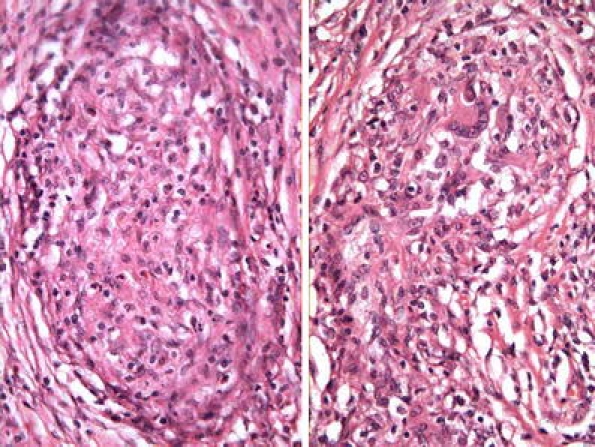
Inflammatory-reactive lesions Some lesion, already described above such as xantogranulomatous orchitis, idiopathic granulomatous orchitis and malakoplakia could be considered under this category; their microscopic confusion with a neoplasia (seminoma for example) is not currently a usual event; therefore, we preferred to include them in the macroscopic mimickers (pseudotumors). The situation is different with lymphocitic orchitis or testicular pseudolymphoma [2, 3], which is characterized by a lymphocytic and plasmocellular reaction that may be confused with a lymphoma, but immunohistochemistry will show that the cellular infiltrate is polyclonal (Fig. 12). Among these idiopathic lesions, we can include Rosai–Dorfman disease; histological examination of the testicular mass reveals an inflammatory lesion comprising lymphocytes, plasma cells, and sheets of pale staining histiocytes, some containing lymphocytes within their ample cytoplasm, suggestive of emperipolesis. The histiocytes stained positive for CD68, S100 by immunohistochemistry and negative for CD1a, while ultrastructural examination confirmed emperipolesis [25].
Fig. 12.
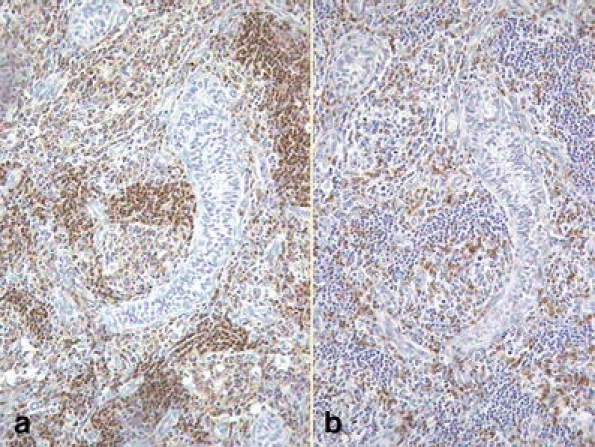
Lymphocitic orchitis. Lymphocitic cellular infiltration of polyclonal type. a CD45RA (lymphocytes B). b UCHL-1 (lymphocytes T)
Sertoli cell hyperplasia In a series of situations, nonencapsulated nodules of Sertoli cells can be found, especially known in cryptorchid testes as Pick’s adenomas (Fig. 13a) [77]. Because of their appearance, these should be distinguished from the actual Sertoli cell tumors that generally are larger and sometimes there are areas that mimic Call–Exner bodies (Fig. 13b) A differential diagnosis with a yolk-sac tumor is not usually in the scope, but the immunohistochemistry study with AFP, calretinin, α-inhibin, and CD 99 can help [40]. A special consideration merit the androgen insensitivity syndrome or testicular feminization (male pseudohermaphrodism, caused by a failure of androgen receptor binding) that in 63% of cases can have tubular hamartomas (tubules lined by immature Sertoli cells) [82] that must be differentiated from the Sertoli cell adenomas and sex cord tumor with annular tubules [76].
Fig. 13.

Sertoli cell hyperplasia. a Nonencapsulated nodules of Sertoli cells (Pick’s adenoma). b Sometimes there are areas that mimic Call–Exner bodies
Interstitial cell hyperplasia In testicles with marked tubular atrophy, such as in the Klinefelter’s syndrome, it is possible to see Leydig cell nodules that must be distinguished from Leydig cell tumors. An interstitial growth without expansive pattern favors hyperplasia (Fig. 14) [62]. Nodules of eosinophilic cells appearing to be Leydig cells are found in the patients with adrenogenital syndrome [18, 48] and Nelson’s syndrome (adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma after bilateral adrenalectomy), some of this last syndrome with excessive testosterone production [91]; proof that these interstitials cells are not only morphologically similar to Leydig cells but also have the functional property of these cells. These nodules are usually bilateral and of a large size with cellular pleomorphism and pigmentation. The clinical history and a complete endocrinological profile avoid an unnecessary orchiectomy [78] because only one case of aggressive behavior is published [18].
Fig. 14.
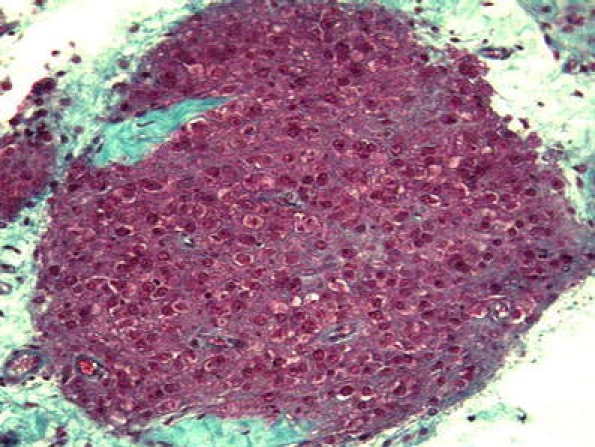
Leydig cell hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the rete testis The normal rete testis epithelium is flat, but in some hyperestrogenic situations (treatment or hepatic dysfunction), the epithelium may become columnar and rarely a micropapillary growth of bland cells can be observed. The diagnosis of rete testis hyperplasia is subjective, and adenomatous lesions are rarely seen [35, 63]. In some cases, there are intracytoplasmic hyaline eosinophilic globules resembling a yolk sac tumor, but the negative stains of α-fetoprotein or placental alkaline phosphatase help to rule this differential diagnosis [99].Pseudohyperplasia of the rete testis and epithelial reaction in case of germ cell invasion and cryptorchidism must be differentiated from real hyperplasia of the rete testis [62].
Epididymis
Benign microscopic mimickers of cancer in the epididymis are very rare. Cysts may occur but do not resemble tumors microscopically. However, some cases of adenomatoid hyperplasia of the rete testis can involve the epididymis, and occasionally, they may become macroscopically apparent [93].
Tunica albuginea and vaginalis
Non-neoplastic mesothelial lesions involving the paratesticular region include mesothelial cysts and reactive mesothelial hyperplasia [73].
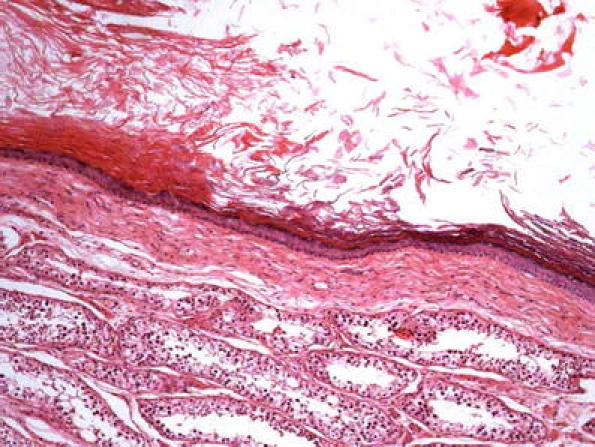
Mesothelial hyperplasia is the most important benign mimicker of the testicular tunics. It is present as a reactive lesion in hydrocele or hernia but may also be found microscopically in older men [80]. The mesothelial proliferation has an epithelial appearance, and rarely, a spindle cell proliferation can be present. In the differential diagnosis with mesothelioma, the bland nucleus, no true invasion, and associated inflammatory elements can be useful (Fig. 15) [11, 98]. Recently, a case was published with “atypical” mesothelial hyperplasia on one side and “well differentiated” mesothelioma on the contalateral [97]. This case is an example of the subjective interpretation of some mesothelial proliferative lesions because some malignant mesotheliomas lack cellular atypia. In these cases, an extensive confluence or prominent infiltration favors a malignant diagnosis. Unfortunately, the immunohistochemical expression of benign and malignant mesothelial proliferations are similar (low- and high-molecular-weight cytokeratins and vimentin) [11, 28], and only the metastatic neoplasias can be differentiated by the CEA, Ber-EP4, and B72.3 expression [27]. Only deoxyribonucleic acid ploidy can distinguish some borderline lesions [28].
Fig. 15.
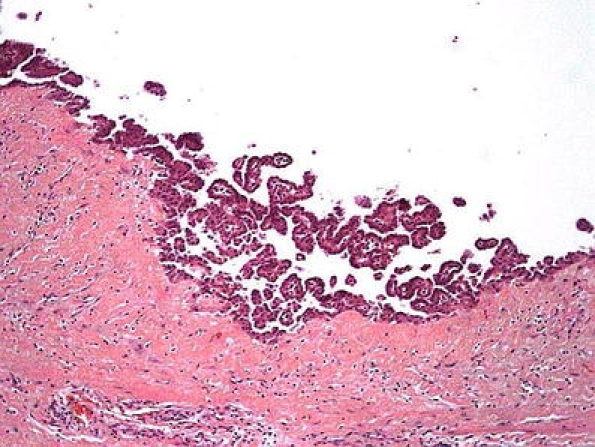
Mesothelial hyperplasia. The bland nucleus, no true invasion and associated inflammatory elements, can be useful to distinguish from malignant mesothelioma
Spermatic cord
The vas deferens and the soft tissues of spermatic cord can have benign mimickers.
Vasitis nodosa is a ductular proliferation, generally after vasectomy [36], although it can be seen following other trauma on that area, [75]. It has a microglandular morphology (Fig. 16) with mild nuclear atipia and perineural growth [7] or benign vascular invasion [8] that may be mistaken for malignancy [104]. The frequent hyperplasia of nerve fibers in the adventitia can explain the painful symptoms in some patients [36]. The coincidence with microscopic sperm granulomas and inflammatory reaction can help in the correct diagnosis. An analogous epididymal lesion also occur [88].
Proliferative funiculitis is the inflammation of the spermatic cord usually the result of an extension of vasitis. The soft tissues of the spermatic cord are also the most common site of an inflammatory pseudotumor in the male genital tract [37, 50, 58]. The lesion is ill defined, myxoid with white-gray color, and a moderate cellular proliferation with loose collagen fibers and irregular infiltration of inflammatory cells. An exceptional case has been reported that was largely infiltrated by mast cells [92]. In some cases, a prominent spindle cell proliferation mimics a sarcoma (pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation), but low mitotic index, a capillary pattern, inflammatory cells, and absence of atypical mitoses speak against a diagnosis of sarcoma. Unfortunately, immunohistochemistry is only partly helpful because the cells express actin and vimentin, less strongly desmin and exceptionally cytokeratin. Two cases of this lesion in epididymis [12, 51] and one in the rete testis [47] have been reported.
Fig. 16.
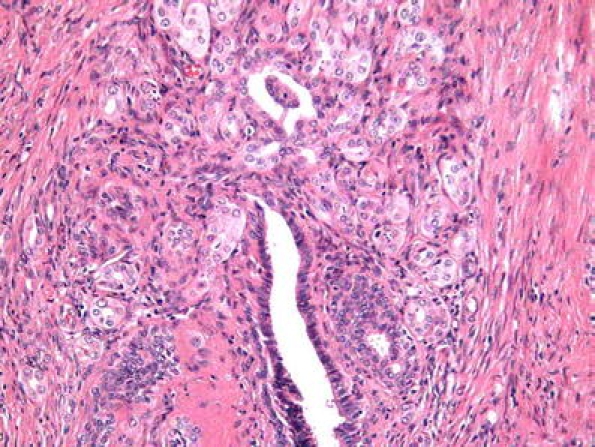
Vasitis nodosa. Ductular proliferation with a microglandular morphology
Embryonic remnants
Although ectopic tissue usually is more problematic for constituting a mass, some of them can cause microscopic diagnostic doubts for which reason they can be included in this group of benign mimics. The presence of seminiferous tubules within the tunica albuginea [67], Leydig cells in rete testis, albuginea, spermatic cord, or within sclerotic tubules [59, 66], prostate gland in the epididymis [52], and special circumstances with muscular rete testis hypertrophy [27] can mimic a neoplasia.
The lesions described constitute a large heterogeneous group, without etiological or pathogenic relations among them or with true neoplasias. However, in spite of that, the patient with one or more of these tumor-like and/or benign mimickers can have a concomitant or ulterior true neoplasm.
Footnotes
This publication is made under the auspices of the Uropathology Working Group (European Society of Pathology, ESP).
References
- 1.Abdou NI, NaPombejara C, Sagawa A, Ragland C, Stechschulte DJ, Nilsson U, Gourley W, Watanabe I, Lindsey NJ, Allen MS (1977) Malakoplakia: evidence for monocyte lysosomal abnormality correctable by cholinergic agonist in vitro and in vivo. N Engl J Med 29(297):1413–1419 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Agarwal V, Li JK, Bard R (1990) Cystic orchitis: a case report. Human Pathol 21:1080–1082 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Algaba F, Santaularia JM, Garat JM, Cubells J (1986) Testicular pseudolymphoma. Eur Urol 12:362–363 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Ameur A, al Bouzidi A, Aqira A, Benomar S, Draoui D (1998) Granulomatous orchitis. A case report and review of the literature. Prog Urol 8:410–412 [PubMed]
- 5.Archimbaud A, Bonvalet D, Levy-Klotz B, Vallet C, Civatte J (1984) Syphilitic orchiepididymitis. Apropos of a pseudotumoral case. Ann Dermatol Venereol 111:169–171 [PubMed]
- 6.Bach AM, Hann LE, Hadar O, Shi W, Yoo HH, Giess CS, Sheinfeld J, Thaler H (2001) Testicular microlithiasis: what is its association with testicular cancer? Radiology 220:70–75 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Balogh K, Travis WD (1984) The frequency of perineural ductules in vasitis nodosa. Am J Clin Pathol 82:710–713 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Balogh K, Travis WD (1985) Benign vascular invasion in vasitis nodosa. Am J Clin Pathol 83:426–430 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Bambirra EA, Andrade Jde S, Bamberg A, de Souza EA, Mitidiero CE, de Souza AF (1986) Testicular schistosomiasis mansoni: a differential diagnostic problem with testicular neoplasias. Am J Trop Med Hyg 35:791–792 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Begin LR, Frail D, Brzezinski A (1990) Myofibroblastoma of the tunica testis: evolving phase of so-called fibrous pseudotumor? Human Pathol 21:866–868 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Bolen JW, Hammar SP, McNutt MA (1986) Reactive and neoplastic serosal tissue. A light-microscopic, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 10:34–47 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Brauers A, Striepecke E, Mersdorf A, Sohn M, Fuzesi L (1997) Inflammatory pseudotumor of the epididymis. Eur Urol 32:253–255 [PubMed]
- 13.Casella R, Nudell D, Cozzolino D, Wang H, Lipshultz LI (2002) Primary testicular amyloidosis mimicking tumor in a cryptorchid testis. Urology 59:445 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Cheng L, Zhang S, MacLennan GT, Poulos CK, Sung MT, Beck SD, Foster RS (2006) Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of chromosome 12p abnormalities is useful for distinguishing epidermoid cysts of the testis from pure mature teratoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:5668–5672 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Chong J, Flynn JT (1998) Spontaneous anticoagulant-induced testicular haemorrhage mimicking a testicular tumour. Br J Urol 81:777 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Collins DH, Pugh RC (1964) Classification and frequency of testicular tumors. Br J Urol 36(Suppl):1–11 [PubMed]
- 17.Dahl EV, Bahn RC (1962) Aberrant adrenal cortical tissue near the testis in human infants. Am J Pathol 40:587–598 [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Davis JM, Woodroof J, Sadasivan R, Stephens R (1995) Case report: congenital adrenal hyperplasia and malignant Leydig cell tumor. Am J Med Sci 309:63–65 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 19.Dieckmann KP, Henke RP, Zimmer-Krolzig G (1995) Malacoplakia of the epididymis. Report of a case and review of the literature. Urol Int 55:222–225 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Doebler RW, Norbut AM (1999) Localized testicular infarction masquerading as a testicular neoplasm. Urology 54:366 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 21.Dotan ZA, Laufer M, Heldenberg E, Langevitz P, Fridman E, Duvdevani M, Ramon J (2003) Isolated testicular polyarteritis nodosa mimicking testicular neoplasm-long-term follow-up. Urology 62:352 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 22.Dunner PS, Lipsit ER, Nochomovitz LE (1982) Epididymal sperm granuloma simulating a testicular neoplasm. J Clin Ultrasound 10(7):353–355 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 23.Einstein DM, Paushter DM, Singer AA, Thomas AJ, Levin HS (1992) Fibrotic lesions of the testicle: sonographic patterns mimicking malignancy. Urol Radiol 14:205–210 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 24.Evans KJ, Teddi RJ, Weatherby E (1985) Spontaneous intratesticular hemorrhage masquerading as a testis tumor. J Urol 134:1211 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.Fernandopulle SM, Hwang JS, Kuick CH, Lui J, Tan PH, Siow WY, Wong M (2006) Rosai-Dorfman disease of the testis: an unusual entity that mimics testicular malignancy. J Clin Pathol 59(3):325–327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Ferro F, Lais A, Boldrini R, De Peppo F, Federici G, Bosman C (1996) Hepatogonadal fusion. J Pediatr Surg 31:435–436 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Fridman E, Skarda J, Ofek-Moravsky E, Cordoba M (2005) Complex multilocular cystic lesion of rete testis, accompanied by smooth muscle hyperplasia, mimicking intratesticular Leydig cell neoplasm. Virchows Arch 447(4):768–771 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Friedman MT, Gentile P, Tarectecan A, Fuchs A (1996) Malignant mesothelioma: immunohistochemistry and DNA ploidy analysis as methods to differentiate mesothelioma from benign reactive mesothelial cell proliferation and adenocarcinoma in pleural and peritoneal effusions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 120(10):959–966 [PubMed]
- 29.Garat JM, Algaba F, Parra L, Gomez L (1991) Meconium vaginalitis. Br J Urol 68:430–431 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 30.Gouw AS, Elema JD, Bink-Boelkens MT, de Jongh HJ, ten Kate LP (1985) The spectrum of splenogonadal fusion. Case report and review of 82 reported cases. Eur J Pediatr 144:316–323 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 31.Green WO Jr (1968) Malacoplakia of the epididymis (without testicular involvement). The first reported case. Arch Pathol 86:438–441 [PubMed]
- 32.Haas GP, Shumaker BP, Cerny JC (1986) The high incidente of benign testicular tumors. J Urol 136:1219–1220 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Hamm B, Fobbe F, Loy V (1988) Testicular cysts: differentiation with US and clinical findings. Radiology 168(1):19–23 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 34.Handelsman DJ, Yue DK, Turtle JR (1983) Hypogonadism and massive testicular infiltration due to amyloidosis. J Urol 129(3):610–612 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Hartwick RW, Ro JY, Srigley JR, Ordonez NG, Ayala AG (1991) Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis. A clinicopathologic study of nine cases. Am J Surg Pathol 15:350–357 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 36.Hirschowitz L, Rode J, Guillebaud J, Bounds W, Moss E (1988) Vasitis nodosa and associated clinical findings. J Clin Pathol 41(4):419–423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Hollowood K, Fletcher CD (1992) Pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferations of the spermatic cord (“proliferative funiculitis”). Histologic and immunohistochemical analysis of a distinctive entity. Am J Surg Pathol 16(5):448–454 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 38.Honore LH (1978) Nonspecific peritesticular fibrosis manifested as testicular enlargement. Clinicopathological study of nine cases. Arch Surg 113:814–816 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Hurd DS, Olsen T (2000) Cutaneous sarcoidosis presenting as a testicular mass. Cutis 66:435–438 [PubMed]
- 40.Iczkowski KA, Butler SL (2006) New immunohistochemical markers in testicular tumors. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 28:181–187 [PubMed]
- 41.Imperial SL, Sidhu JS (2002) Nonseminomatous germ cell tumor arising in splenogonadal fusion. Arch Pathol Lab Med 126:1222–1225 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Jani AN, Casibang V, Mufarrij WA (1990) Disseminated actinomycosis presenting as a testicular mass: a case report. J Urol 143:1012–1014 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Joudi FN, Austin JC, Vogelgesang SA, Jensen CS (2004) Isolated testicular vasculitis presenting as a tumor-like lesion. J Urol 171(2 Pt 1):799 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Kao HW, Wu CJ, Chen CY, Sun GH, Lee SS, Peng YJ (2005) Malignant tumor of testis imitating epididymo-orchitis. Arch Androl 51:407–411 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.Kariv R, Sidi Y, Gur H (2000) Systemic vasculitis presenting as a tumorlike lesion. Four case reports and an analysis of 77 reported cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 79:349–359 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Katergiannakis V, Lagoudianakis EE, Markogiannakis H, Manouras A (2006) Huge epidermoid cyst of the spermatic cord in an adult patient. Int J Urol 13:95–97 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Khalil KH, Ball RY, Eardley I, Ashken MH (1996) Inflammatory pseudotumor of the rete testis. J Urol Pathol 5:39–43
- 48.Knudsen JL, Savage A, Mobb GE (1991) The testicular ‘tumour’ of adrenogenital syndrome—a persistent diagnostic pitfall. Histopathology 19:468–470 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 49.Kocak I, Dundar M, Culhaci N, Unsal A (2004) Relapse of brucellosis simulating testis tumor. Int J Urol 11:683–685 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 50.Lai FM, Allen PW, Chan LW, Chan PS, Cooper JE, Mackenzie TM (1995) Aggressive fibromatosis of the spermatic cord. A typical lesion in a “new” location. Am J Clin Pathol 104(4):403–407 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51.Lam KY, Chan KW, Ho MH (1995) Inflammatory pseudotumour of the epididymis. Br J Urol 75:255–257 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Lee LY, Tzeng J, Grosman M, Unger PD (2004) Prostate gland-like epithelium in the epididymis: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 128:60–62 [PubMed]
- 53.Li M, Fogarty J, Whitney KD, Stone P (2003) Repeated testicular infarction in a patient with sickle cell disease: a possible mechanism for testicular failure. Urology 62:551 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Maizlin ZV, Belenky A, Baniel J, Gottlieb P, Sandbank J, Strauss S (2005) Epidermoid cyst and teratoma of the testis: sonographic and histologic similarities. J Ultrasound Med 24:1403–1409 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.McCluggage WG, Shah V, Nott C, Clements B, Wilson B, Hill CM (1996) Cystadenoma of spermatic cord resembling ovarian serous epithelial tumour of low malignant potential: immunohistochemical study suggesting Mullerian differentiation. Histopathology 28:77–80 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 56.McClure J (1980) Malakoplakia of the testis and its relationship to granulomatous orchitis. J Clin Pathol 33:670–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 57.Mikuz G (1973) Ultrastructural study of two cases of granulomatous orchitis. Virchows Arch A 360:223–234 [PubMed]
- 58.Milanezi MF, Schmitt F (1997) Pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation of the spermatic cord (proliferative funiculitis). Histopathology 31:387–388 [PubMed]
- 59.Mori H, Tamai M, Fushimi H, Fukuda H, Maeda T (1987) Leydig cells within the aspermatogenic seminiferous tubules. Human Pathol 18:1227–1231 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 60.Murray RS, Keeling JW, Ellis PM, FitzPatrick DR (2002) Symmetrical upper limb peromelia and lower limb phocomelia associated with a de novo apparently balanced reciprocal translocation: 44,XX,t(2; 12)(p25.1;q24.1). Clin Dysmorph 11:87–90 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 61.Nativ O, Mor Y, Nass D, Leibovitch I, Goldwasser B (1995) Cholesterol granuloma of the tunica vaginalis mimicking a neoplasm. Isr J Med Sci 31:235–236 [PubMed]
- 62.Naughton CK, Nadler RB, Basler JW, Humphrey PA (1998) Leydig cell hyperplasia. Br J Urol 81:282–289 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 63.Nistal M, Castillo MC, Regadera J, Garcia-Cabezas MA (2003) Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis. A review and report of new cases. Histol Histopathol 18(3):741–752 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 64.Nistal M, Gonzalez-Peramato P, Serrano A, Regadera J (2004) Xanthogranulomatous funiculitis and orchiepididymitis: report of 2 cases with immunohistochemical study and literature review. Arch Pathol Lab Med 128:911–914 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 65.Nistal M, Iniguez L, Paniagua R (1987) Histological classification of spermatic cord cysts in relation to their histogenesis. Eur Urol 13:327–330 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 66.Nistal M, Paniagua R (1979) Histogenesis of human extraparenchymal Leydig cells. Acta Anat (Basel) 105:188–197 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 67.Nistal M, Paniagua R, Leon L, Regadera J (1985) Ectopic seminiferous tubules in the tunica albuginea of normal and dysgenetic testes. Appl Pathol 3:123–128 [PubMed]
- 68.Nistal M, Regadera J, Paniagua R (1984) Cystic dysplasia of the testis. Light and electron microscopic study of three cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 108:579–583 [PubMed]
- 69.Older RA, Watson LR (1994) Tubular ectasia of the rete testis: a benign condition with a sonographic appearance that may be misinterpreted as malignant. J Urol 152(2 Pt 1):477–478 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 70.Osca Garcia JM, Alfaro Ferreres L, Ruiz Cerda JL, Moreno Pardo B, Martinez Jabaloyas J, Jimenez Cruz JF (1993) Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis. Actas Urol Esp 17:53–56 [PubMed]
- 71.Parveen T, Fleischmann J, Petrelli M (1992) Benign fibrous tumor of the tunica vaginalis testis. Report of a case with light, electron microscopic, and immunocytochemical study, and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 116:277–280 [PubMed]
- 72.Pekindil G, Huseyin Atakan I, Kaya E, Bilgi S, Inci O (1999) Bilateral synchronous granulomatous orchitis: gray-scale and colour Doppler sonographic findings. Eur J Radiol 31:201–203 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 73.Perez-Ordonez B, Srigley JR (2000) Mesothelial lesions of the paratesticular region. Semin Diagn Pathol 17:294–306 [PubMed]
- 74.Poster RB, Spirt BA, Tamsen A, Surya BV (1991) Complex tunica albuginea cyst simulating an intratesticular lesion. Urol Radiol 13:129–132 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 75.Ralph DJ, Lynch MJ, Pryor JP (1993) Vasitis nodosa due to torture. Br J Urol 72:515–516 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 76.Ramaswamy G, Jagadha V, Tchertkoff V (1985) A testicular tumor resembling the sex cord with annular tubules in a case of the androgen insensitivity syndrome. Cancer 55:1607–1611 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 77.Ricco R, Bufo P (1980) Histologic study of 3 cases of so-called tubular adenoma of the testis. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 56:2110–2115 [PubMed]
- 78.Rich MA, Keating MA, Levin HS, Kay R (1998) Tumors of the adrenogenital syndrome: an aggressive conservative approach. J Urol 160:1838–1841 [PubMed]
- 79.Rifkin MD, Kurtz AB, Pasto ME, Goldberg BB (1983) Polyorchidism diagnosed preoperatively by ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 2:93–94 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 80.Rosai J, Dehner LP (1975) Nodular mesothelial hyperplasia in hernia sacs: a benign reactive condition simulating a neoplastic process. Cancer 35:165–175 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 81.Ruibal M, Quintana JL, Fernández G, Zungri E (2003) Segmental testicular infarction. J Urol 170:187–188 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 82.Rutgers JL, Scully RE (1991) The androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization): a clinicopathologic study of 43 cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol 10:126–144 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 83.Ryan DM, Lesser BA, Crumley LA, Cartwright HA, Peron S, Haas GP, Bower G (1993) Epididymal sarcoidosis. J Urol 149:134–136 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 84.Ryan SP, Harte PJ (1988) Suppurative inflammation of vas deferens: an unusual groin mass. Urology 31:245–246 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 85.Salako AA, Olasode BJ, Eziyi AK, Osasan SA (2006) Xanthogranulomatous orchitis in an adult Nigerian. Int J Urol 13:186–188 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 86.Sanders LM, Levy HM, Premkumar A (1988) Malignant mixed germ cell tumor of the testis mimicking a hematocele. Am J Roentgenol 151:1253 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 87.Saw KC, Hartfall WG, Rowe RC (1993) Tuberculous prostatitis: nodularity may simulate malignancy. Br J Urol 72:249 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 88.Schned AR, Selikowitz SM (1986) Epididymitis nodosa. An epididymal lesion analogous to vasitis nodosa. Arch Pathol Lab Med 110:61–64 [PubMed]
- 89.Shamsa A, Kadkhodayan A, Feiz-zadeh B, Rasulian H (2002) Testicular hematocele mimicking a testicular tumor: a case report and review of literature. Transplant Proc 34:2141–2142 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 90.Shawker TH, Doppman JL, Choyke PL, Feuerstein IM, Nieman LK (1992) Intratesticular masses associated with abnormally functioning adrenal glands. J Clin Ultrasound 20:51–58 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 91.Shekarriz M, Schneider C, Sabanegh E, Kempter F, Waldherr R (1996) Excessive testosterone production in a patient with Nelson syndrome and bilateral testicular tumors. Urol Int 56:200–203 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 92.Shintaku M, Ukikusa M (2003) Proliferative funiculitis with a prominent infiltration of mast cells. Pathol Int 53:897–900 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 93.Srigley JR, Hartwick RW (1990) Tumors and cysts of the paratesticular region. Pathol Annu 1968(25 Pt 2):51–108 [PubMed]
- 94.Sundaram S, Smith DH (2001) Giant cell arteritis mimicking a testicular tumour. Rheumatol Int 20:215–216 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 95.Tank ES, Forsyth M (1988) Splenic gonadal fusion. J Urol 139:798–799 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 96.Thompson JE, van der Walt JD (1986) Nodular fibrous proliferation (fibrous pseudotumour) of the tunica vaginalis testis. A light, electron microscopic and immunocytochemical study of a case and review of the literature. Histopathology 10:741–748 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 97.Tolhurst SR, Lotan T, Rapp DE, Lyon MB, Orvieto MA, Gerber GS, Sokoloff MH (2006) Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma occurring in the tunica vaginalis of the testis with contralateral atypical mesothelial hyperplasia. Urol Oncol 24:36–39 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 98.Tyagi G, Munn CS, Kiser LC, Wetzner SM, Tarabulcy E (1989) Malignant mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis testis. Urology 34:102–104 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 99.Ulbright TM, Gersell DJ (1991) Rete testis hyperplasia with hyaline globule formation. A lesion simulating yolk sac tumor. Am J Surg Pathol 15:66–74 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 100.Vaidyanathan S, Mansour P, Parsons KF, Singh G, Soni BM, Subramaniam R, Oo T, Sett P (2000) Xanthogranulomatous funiculitis and epididymo-orchitis in a tetraplegic patient. Spinal Cord 38:769–772 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 101.Val-Bernal JF, Val D, Garijo MF (2006) Ectopic epididymal tissue in appendix testis. Virchows Arch 449:373–375 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 102.Vaos G, Zavras N, Boukouvalea I (2006) Ectopic adrenocortical tissue along the inguinoscrotal path of children. Int Surg 91:125–128 [PubMed]
- 103.Warfield AT, Lee SJ, Phillips SM, Pall AA (1994) Isolated testicular vasculitis mimicking a testicular neoplasm. J Clin Pathol 47:1121–1123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 104.Warner JJ, Kirchner FK Jr, Wong SW, Dao AH (1983) Vasitis nodosa presenting as a mass of the spermatic cord. J Urol 129:380–381 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 105.Wegner HE, Herbst H, Dieckmann KP (1994) Paratesticular epidermoid cyst and ipsilateral spermatic cord dermoid cyst: case report and discussion of pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. J Urol 152:2101–2103 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 106.Wiesenthal JD, Ettler H, Razvi H (2004) Testicular epidermoid cyst: a case report and review of the clinicopathologic features. Can J Urol 11:2133–2135 [PubMed]
- 107.Williams HJ, Abernethy LJ, Losty PD, Kotiloglu E (2004) Meconium periorchitis—a rare cause of a paratesticular mass. Pediatr Radiol 34:421–423 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 108.Woodward PJ, Schwab CM, Sesterhenn IA (2003) From the archives of the AFIP: extratesticular scrotal masses: radiologic–pathologic correlation. Radiographics 23:215–240 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 109.Woodward PJ, Sohaey R, O'Donoghue MJ, Green DE (2002) From the archives of the AFIP: tumors and tumorlike lesions of the testis: radiologic–pathologic correlation. Radiographics 22:189–216 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 110.Yap RL, Jang TL, Gupta R, Pins MR, Gonzalez CM (2004) Xanthogranulomatous orchitis. Urology 63:176–177 [DOI] [PubMed]


