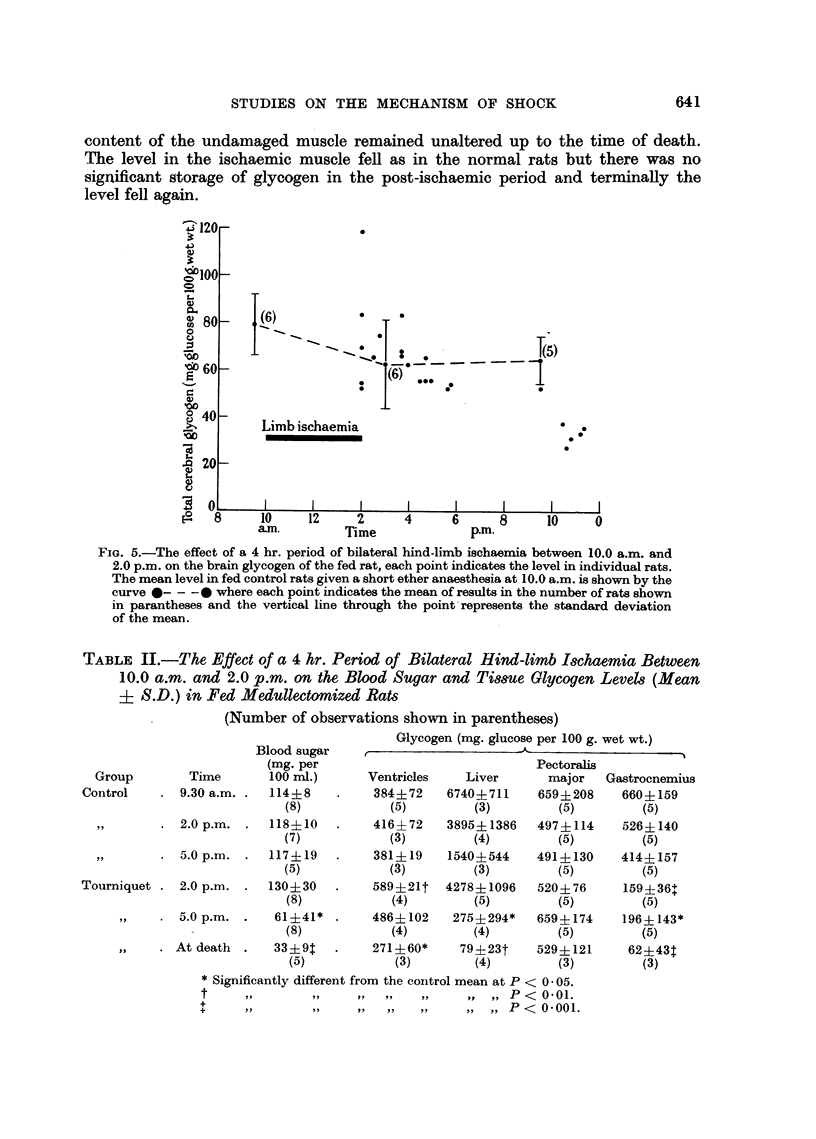
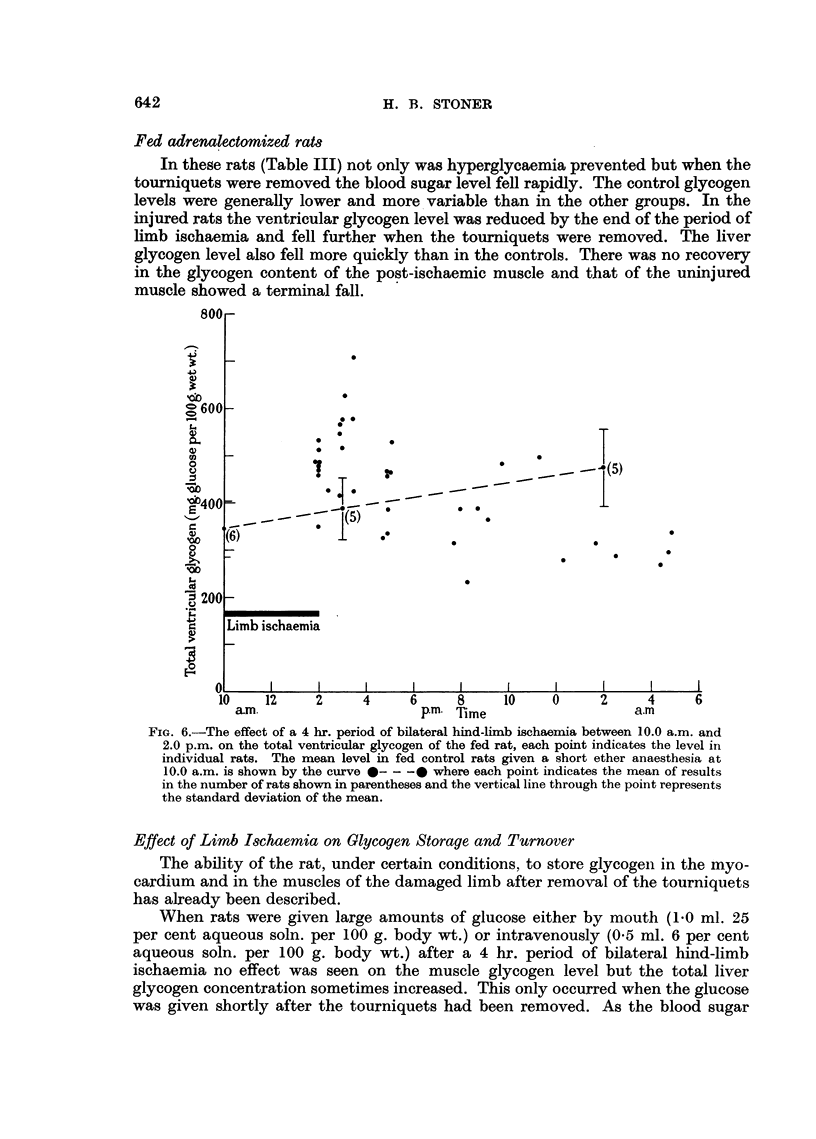
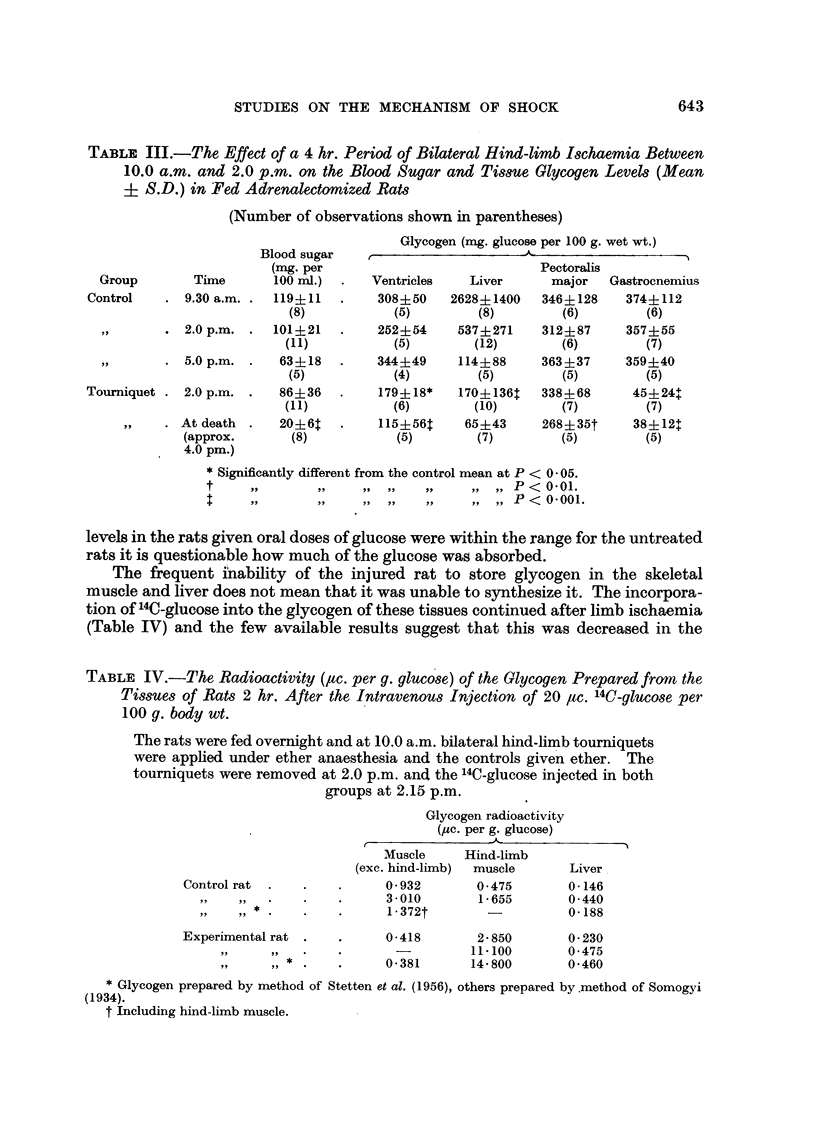
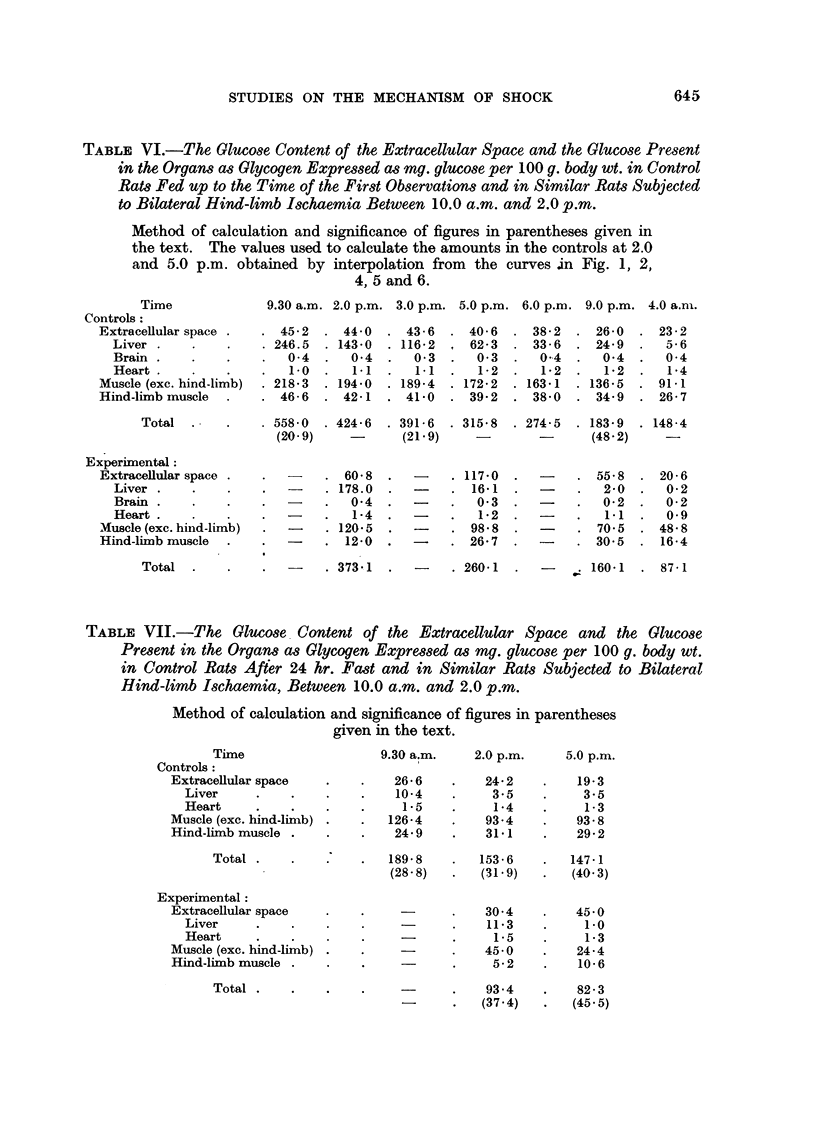
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM W. L., LEWIS G. T., SCHUMPERT M. Z., SHEN T. M. Glycogen fractions of liver and muscle. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):631–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUCE H. M., PARKES A. S. Feeding and breeding of laboratory animals; a complete cubed diet for mice and rats. J Hyg (Lond) 1949 Jun;47(2):202–208. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400014479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTER W. O., PONCELET J., SIMON A. B., ARMSTRONG W. D. Tissue weights of the rat. I. Normal values determined by dissection and chemical methods. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):122–126. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPENHAVER W. M., MOORE D. H., RUSKA H. Electron microscopic and histochemical observations of muscle degeneration after tourniquet. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Nov 25;2(6):755–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.6.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDIER D., DESSAUX G. Variations de la réserve glycogénique cardiaque au cours du choc ischémique (tourniquet shock). C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1954 Feb;148(3-4):363–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEXTER D., STONER H. B. The role of the adrenal medulla in water diuresis in rats. J Physiol. 1952 Dec;118(4):486–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies F., Francis E. T., Stoner H. B. The distribution of nucleotide, phosphocreatine and glycogen in the heart. J Physiol. 1947 Jun 2;106(2):154–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL F. L., FREDERICKS J. Contribution to understanding of mechanism of permissive action of corticoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):593–596. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haist R. E., Hamilton J. I. Reversibility of carbohydrate and other changes in rats shocked by a clamping technique. J Physiol. 1944 Apr 4;102(4):471–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZEN H. M., STETTEN D., Jr, STETTEN M. R. Metabolic inhomogeneity of glycogen as a function of molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):587–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACH A. G., TAKACS L., MANYHART J., IRANYI M., KALMAR Z. Phosphorylation of glycogen in shock. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1952;3(2):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANERY J. F. Water and electrolyte metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1954 Apr;34(2):334–417. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONER H. B., THRELFALL C. J., GREEN H. N. Studies on the mechanism of shock, Carbohydrate metabolism in nucleotide and ischaemic shock. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Apr;33(2):131–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THRELFALL C. J., STONER H. B. Studies on the mechanism of shock, the effect of limb ischaemia on the phosphates of muscle. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Aug;38(4):339–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTERNITZ W. W., DINTZIS R., LONG C. N. Further studies on the adrenal cortex and carbohydrate metabolism. Endocrinology. 1957 Dec;61(6):724–741. doi: 10.1210/endo-61-6-724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


