Full text
PDF




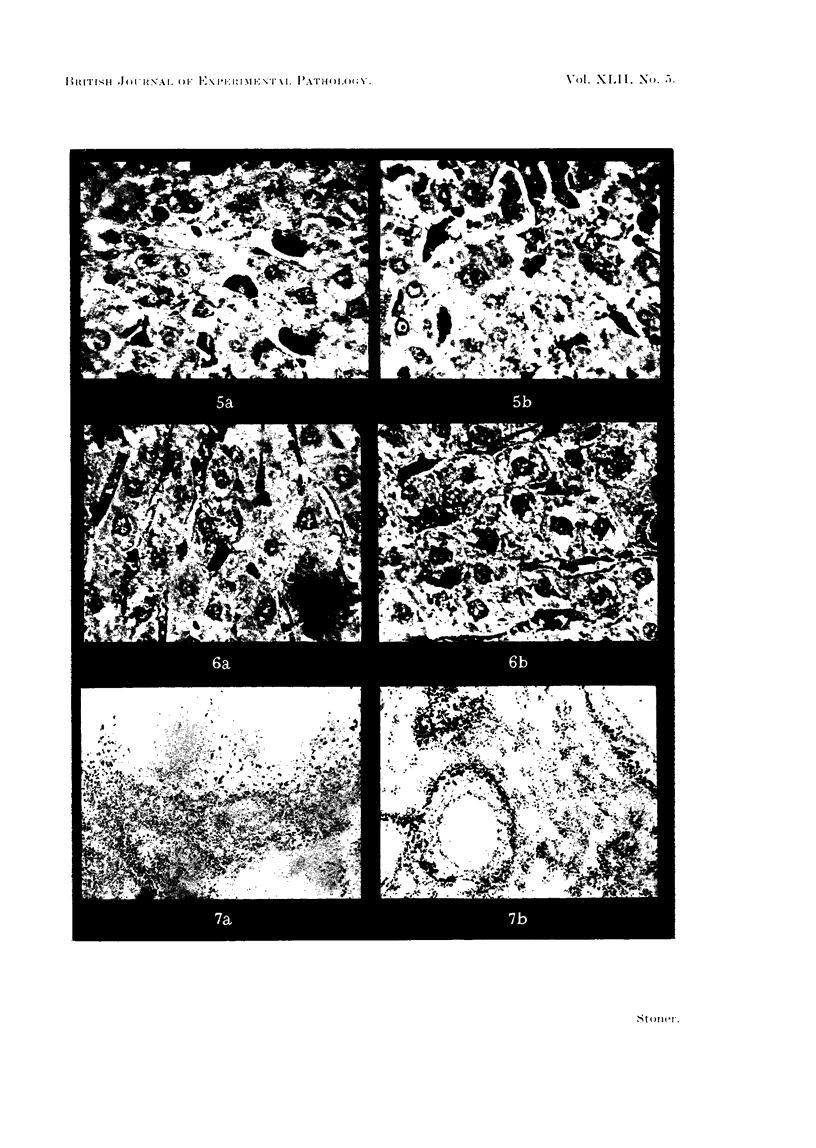

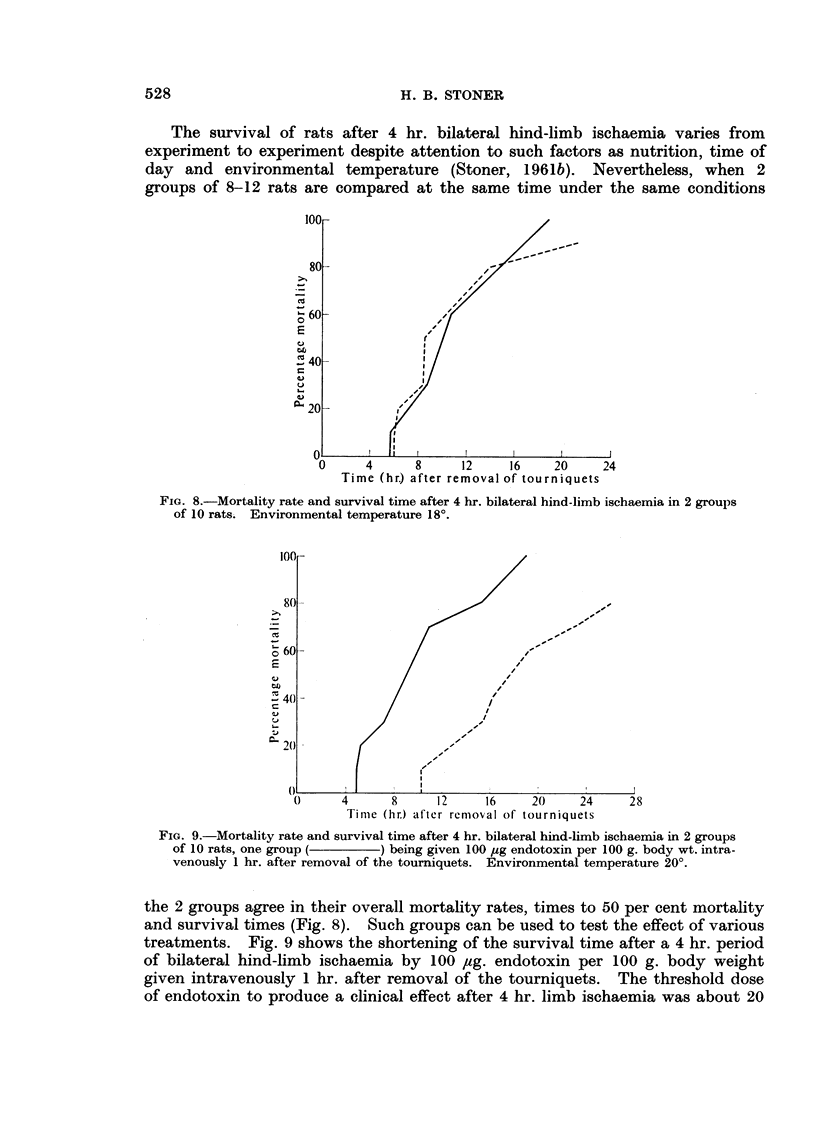

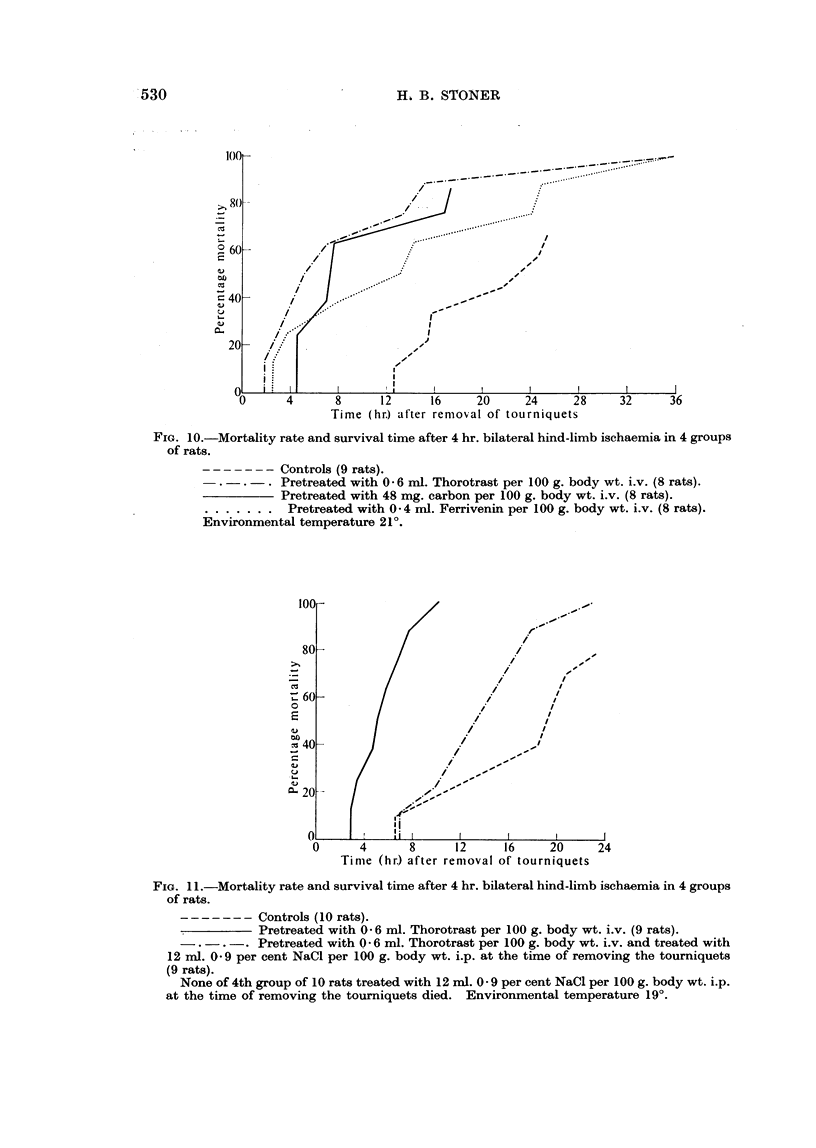
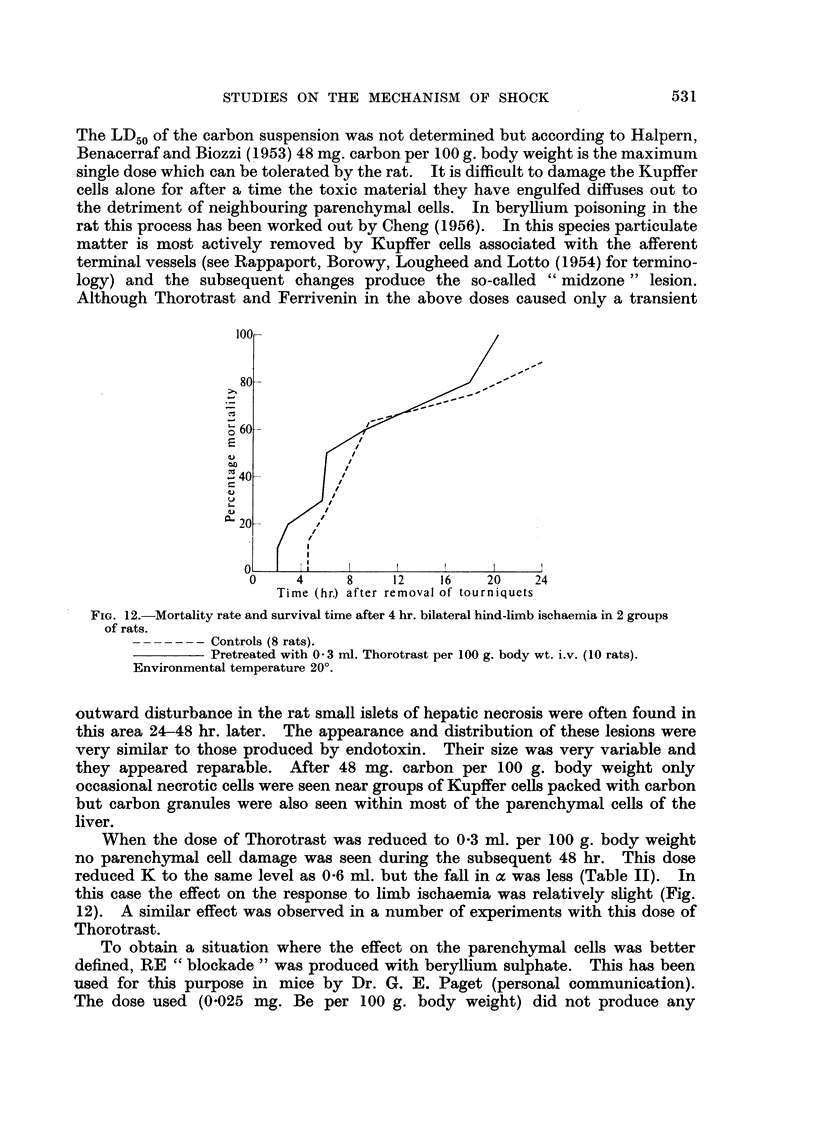
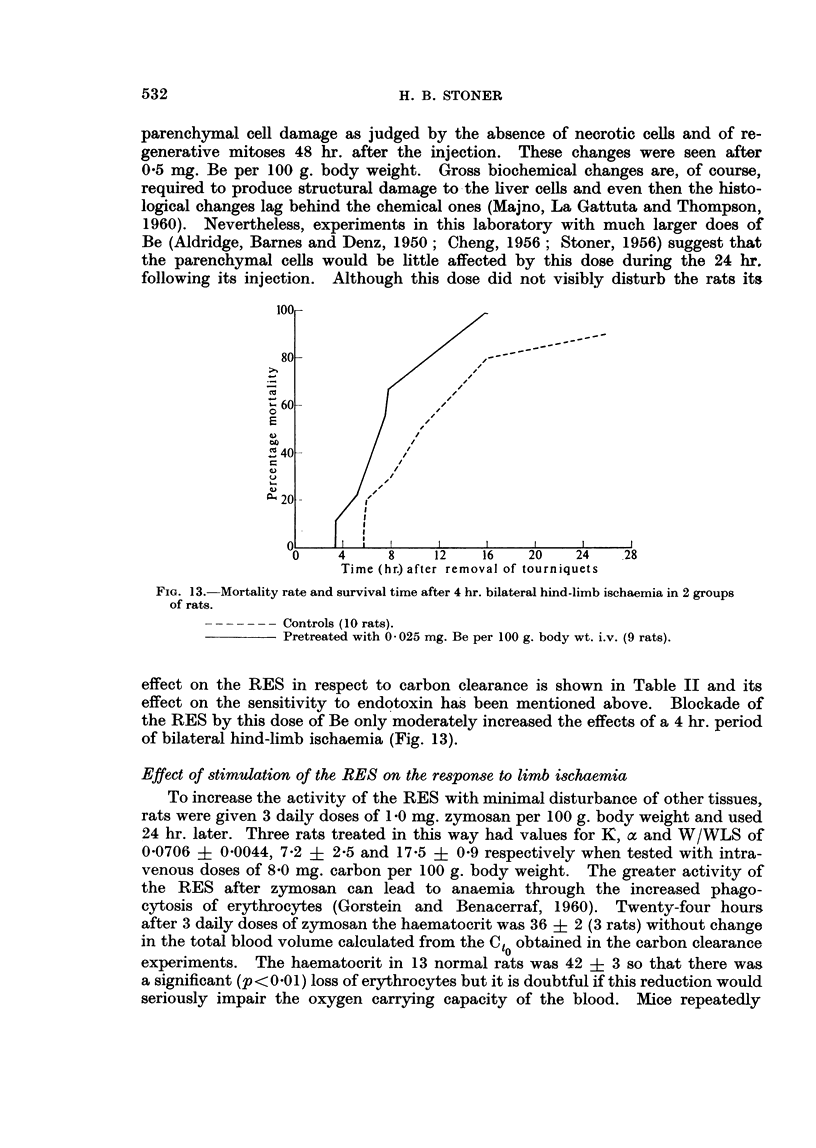

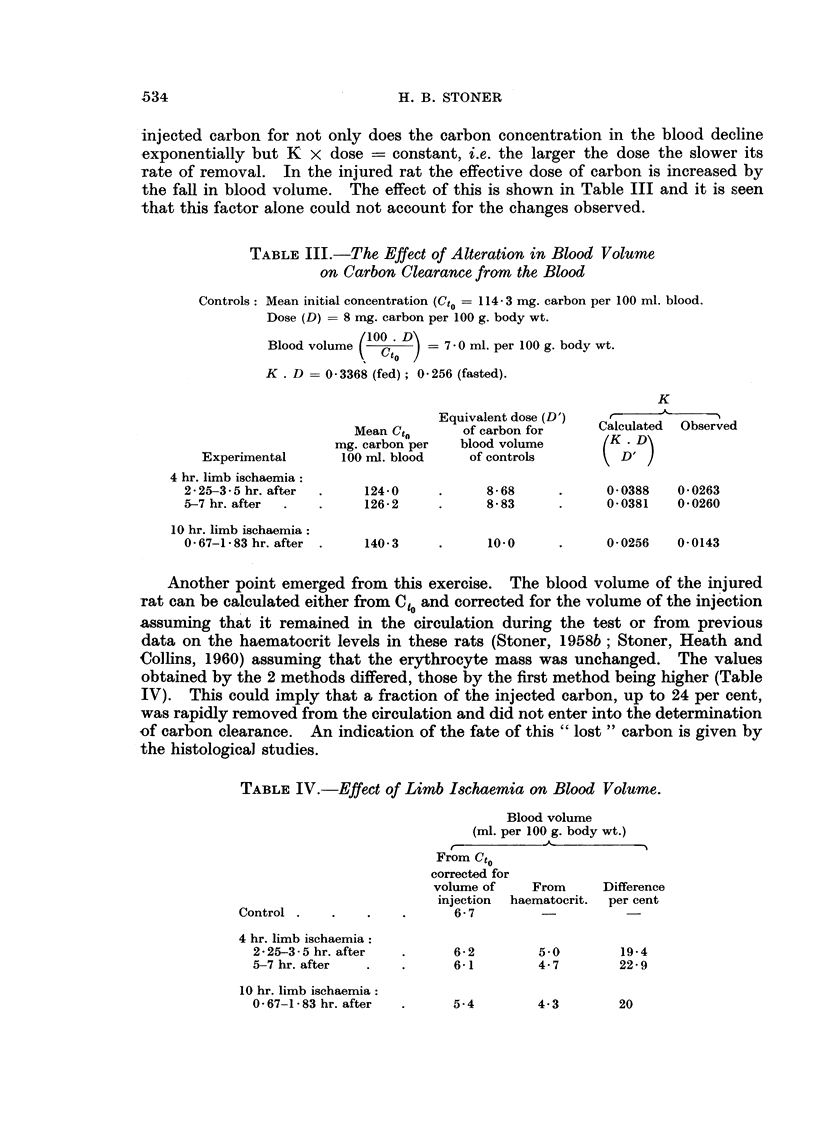




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., BARNES J. M., DENZ F. A. Biochemical changes in acute beryllium poisoning. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Aug;31(4):473–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., HALPERN B. N. Quantitative study of the granulopectic activity of the reticulo-endothelial system. II. A study of the kinetics of the R. E. S. in relation to the dose of carbon injected; relationship between the weight of the organs and their activity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Aug;34(4):441–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINE J., RUTENBURG S., SCHWEINBURG F. B. The role of the reticulo-endothelial system in hemorrhagic shock. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:547–569. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN E. W., SCHWEINBURG F. B., YASHAR J., FINE J. Bacterial factor in traumatic shock in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1957 Apr;189(1):197–202. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORSTEIN F., BENACERRAF B. Hyperactivity of the reticuloendothelial system and experimental anemia in mice. Am J Pathol. 1960 Nov;37:569–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., BIOZZI G., MENE G., BENACERRAF B. Etude quantitative de l'activité granulopexique du système réticulo-endothélial par l'injection intraveineuse d'encre de Chine chez les diverses espèces animales. I. Méthode d'étude quantitative de l'activité granulopexique du system réticuloendothélial par l'injection intraveineuse de particules de carbone de dimensions connues. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1951 Jun;80(6):582–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., DICK P., BIOZZI G., MENE G. Influence du refroidissement sur l'activité granulopexique du système réticulo-endothélial. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1951 Apr;145(7-8):503–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., LA GATTUTA M., THOMPSON T. E. Cellular death and necrosis: chemical, physical and morphologic changes in rat liver. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1960;333:421–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00955327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKENNA J. M., ZWEIFACH B. W. Reticulo-endothelial system in relation to drum shock. Am J Physiol. 1956 Nov;187(2):263–268. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEINBURG F. B., FINE J. Evidence for a lethal endotoxemia as the fundamental feature of irreversibility in three types of traumatic shock. J Exp Med. 1960 Nov 1;112:793–800. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.5.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEHBENS W. E., FLOREY H. W. The behavior of intravenously injected particles observed in chambers in rabbits' ears. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Jul;45:252–264. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONER H. B., HEATH D. F., COLLINS O. M. The metabolism of [14C]glucose, [14C]fructose and [2-14C]pyruvate after limb ischaemia in the rat. Biochem J. 1960 Jul;76:135–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0760135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THRELFALL C. J., STONER H. B. The effect of hind-limb ischaemia on the products and intermediates of glycolysis in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:553–562. doi: 10.1042/bj0790553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE H. M., Jr, KNECHT A. T., Jr, PENCE D., ONDASH B. S. Observations of the function of the liver in experimental traumatic shock. Surgery. 1959 Feb;45(2):274–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIZNITZER T., BETTER N., RACHLIN W., ATKINS N., FRANK E. D., FINE J. In vivo detoxification of endotoxin by the reticuloendothelial system. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1157–1166. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZWEIFACH B. W., BENACERRAF B., THOMAS L. The relationship between the vascular manifestations of shock produced by endotoxin, trauma, and hemorrhage. II. The possible role of the reticulo-endothelial system in resistance to each type of shock. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):403–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]