Abstract
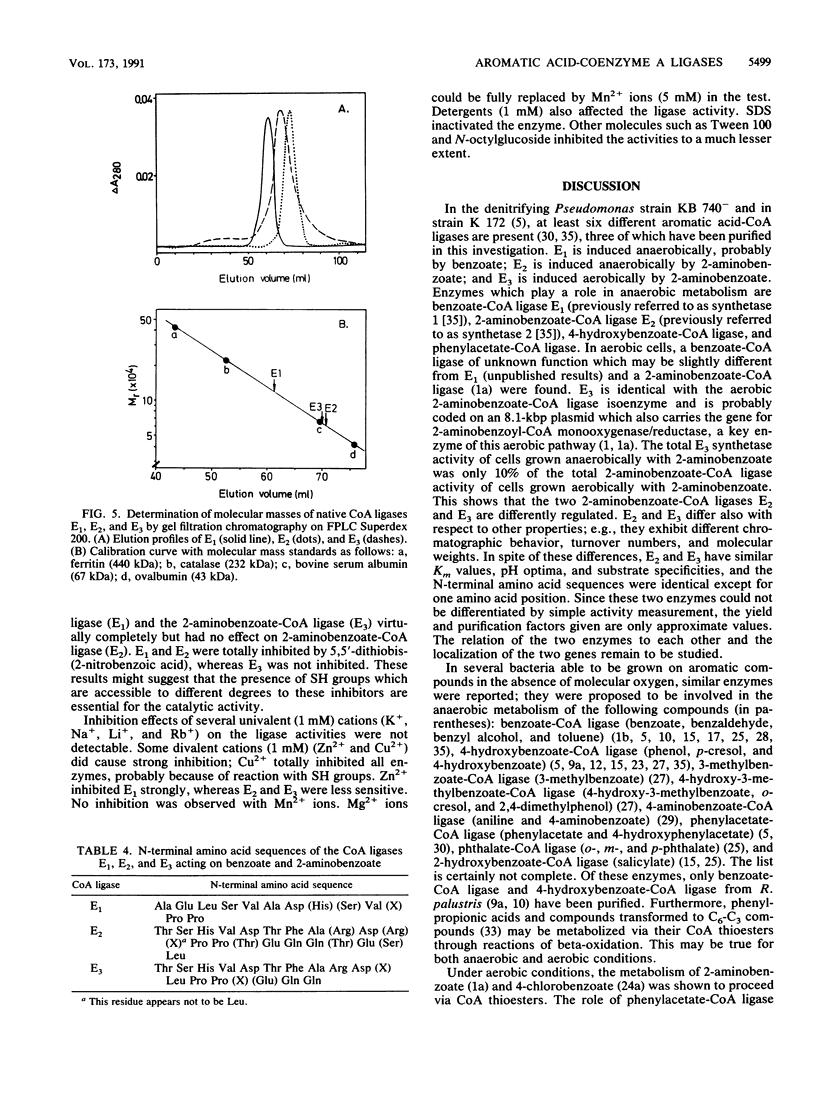
The enzymes catalyzing the formation of coenzyme A (CoA) thioesters of benzoate and 2-aminobenzoate were studied in a denitrifying Pseudomonas sp. anaerobically grown with these aromatic acids and nitrate as sole carbon and energy sources. Three different rather specific aromatic acyl-CoA ligases, E1, E2, and E3, were found which catalyze the formation of CoA thioesters of benzoate, fluorobenzoates, and 2-aminobenzoate. ATP is cleaved into AMP and pyrophosphate. The enzymes were purified, their N-terminal amino acid sequences were determined, and their catalytic and molecular properties were studied. Cells anaerobically grown on benzoate and nitrate contain one CoA ligase (AMP forming) for benzoic acid (E1). It is a homodimer of Mr 120,000 which prefers benzoate as a substrate but shows some activity also with 2-aminobenzoate and fluorobenzoates, although with lower Km. Cells anaerobically grown on 2-aminobenzoate and nitrate contain three different CoA ligases for aromatic acids. The first one is identical with benzoate-CoA ligase (E1). The second enzyme is a 2-aminobenzoate-CoA ligase (E2). It is a monomer of Mr 60,000 which prefers 2-aminobenzoate but also activates benzoate, fluorobenzoates and, less effectively, 2-methylbenzoate, with lower affinities to the latter substrates. The enzymes E1 and E2 have similar activity levels; a third minor CoA ligase activity is due to a different 2-aminobenzoate-CoA ligase. The enzyme (E3) is a monomer of Mr, 65,000 which 2-aminobenzoate pathway (U. Altenschmidt, C. Eckerskorn, and G. Fuchs, Eur. J. Biochem. 194:647-653, 1990); apparently, it is not completely repressed under anaerobic conditions and therefore also is induced to a small extent by 2-aminobenzoate under anaerobic growth conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenschmidt U., Eckerskorn C., Fuchs G. Evidence that enzymes of a novel aerobic 2-amino-benzoate metabolism in denitrifying Pseudomonas are coded on a small plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):647–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun K., Gibson D. T. Anaerobic degradation of 2-aminobenzoate (anthranilic acid) by denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):102–107. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.102-107.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buder R., Ziegler K., Fuchs G., Langkau B., Ghisla S. 2-Aminobenzoyl-CoA monooxygenase/reductase, a novel type of flavoenzyme. Studies on the stoichiometry and the course of the reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):637–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Evans W. C. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. A new, reductive, method of aromatic ring metabolism. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):525–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerskorn C., Mewes W., Goretzki H., Lottspeich F. A new siliconized-glass fiber as support for protein-chemical analysis of electroblotted proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):17–22. doi: 10.1038/270017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler J. F., Harwood C. S., Gibson J. Purification and properties of benzoate-coenzyme A ligase, a Rhodopseudomonas palustris enzyme involved in the anaerobic degradation of benzoate. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1709–1714. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1709-1714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glöckler R., Tschech A., Fuchs G. Reductive dehydroxylation of 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA to benzoyl-CoA in a denitrifying, phenol-degrading Pseudomonas species. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock J. D., Ferry J. G. Purification and properties of phloroglucinol reductase from Eubacterium oxidoreducens G-41. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4423–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Gibson J. Uptake of benzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris grown anaerobically in light. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):504–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.504-509.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumholz L. R., Crawford R. L., Hemling M. E., Bryant M. P. Metabolism of gallate and phloroglucinol in Eubacterium oxidoreducens via 3-hydroxy-5-oxohexanoate. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1886–1890. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1886-1890.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lack A., Tommasi I., Aresta M., Fuchs G. Catalytic properties of phenol carboxylase. In vitro study of CO2: 4-hydroxybenzoate isotope exchange reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Blanco H., Reglero A., Rodriguez-Aparicio L. B., Luengo J. M. Purification and biochemical characterization of phenylacetyl-CoA ligase from Pseudomonas putida. A specific enzyme for the catabolism of phenylacetic acid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7084–7090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel S. M., Eberhard A. E., Gibson J., Harwood C. S. Involvement of coenzyme A thioesters in anaerobic metabolism of 4-hydroxybenzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.1-7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa T., Maruyama Y. Anaerobic metabolism of phthalate and other aromatic compounds by a denitrifying bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5778–5784. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5778-5784.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. G., Wall J. D., Emerich D. W. Purification and properties of acetyl-CoA synthetase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):179–183. doi: 10.1042/bj2670179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolphi A., Tschech A., Fuchs G. Anaerobic degradation of cresols by denitrifying bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155(3):238–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00252207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schennen U., Braun K., Knackmuss H. J. Anaerobic degradation of 2-fluorobenzoate by benzoate-degrading, denitrifying bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):321–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.321-325.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschech A., Fuchs G. Anaerobic degradation of phenol by pure cultures of newly isolated denitrifying pseudomonads. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Sep;148(3):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00414814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster L. T., Jr, Mieyal J. J., Siddiqui U. A. Benzoyl and hydroxybenzoyl esters of coenzyme A. Ultraviolet characterization and reaction mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2641–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenk M. H., Ulbrich B., Busse J., Stöckigt J. Procedure for the enzymatic synthesis and isolation of cinnamoyl-CoA thiolesters using a bacterial system. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 1;101(1):182–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]