Abstract
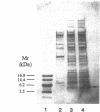
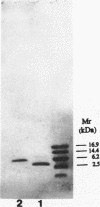
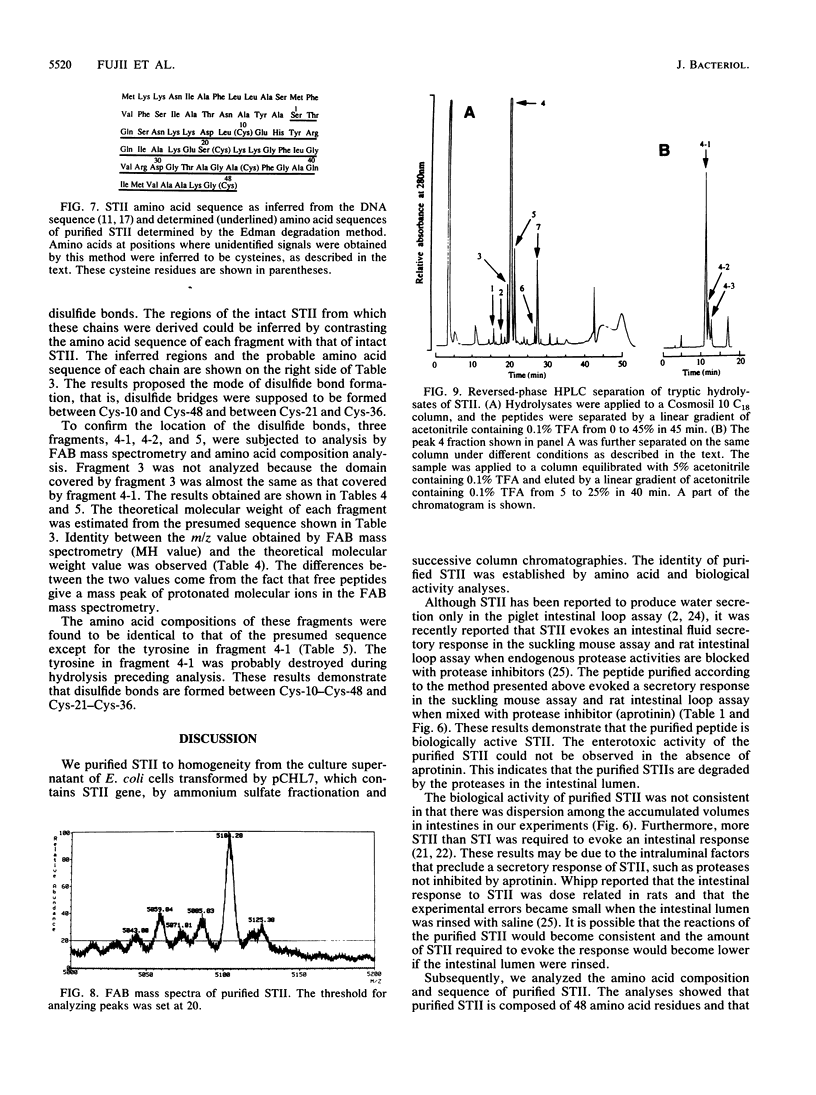
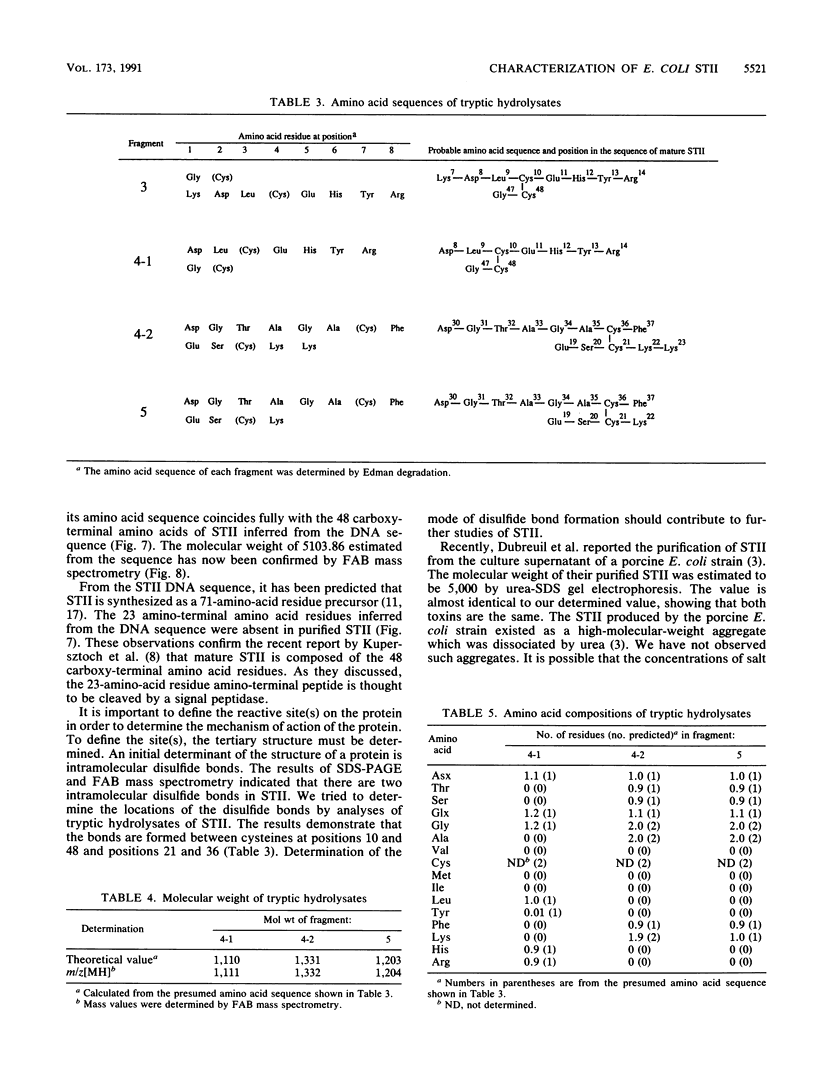
Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin II (STII) was purified to homogeneity by successive column chromatographies from the culture supernatant of a strain harboring the plasmid encoding the STII gene. The purified STII evoked a secretory response in the suckling mouse assay and ligated rat intestinal loop assay in the presence of protease inhibitor, but the response was not observed in the absence of the inhibitor. Analyses of the peptide by the Edman degradation method and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry revealed that purified STII is composed of 48 amino acid residues and that its amino acid sequence was identical to the 48 carboxy-terminal amino acids of STII predicted from the DNA sequence (C. H. Lee, S. L. Mosely, H. W. Moon, S. C. Whipp, C. L. Gyles, and M. So, Infect. Immun. 42:264-268, 1983). STII has four cysteine residues which form two intramolecular disulfide bonds. Two disulfide bonds were determined to be formed between Cys-10-Cys-48 and Cys-21-Cys-36 by analyzing tryptic hydrolysates of STII.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betley M. J., Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Fairbrother J. M., Lallier R., Larivière S. Production and purification of heat-stable enterotoxin b from a porcine Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.198-203.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Judd A. K., Schoolnik G. K. Importance of disulfide bridges in the structure and activity of Escherichia coli enterotoxin ST1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8907–8911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Lane A., Frayman F., Wilbur D., Robien W., Schoolnik G. K., Jardetzky O. Structure of the toxic domain of the Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin ST I. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7854–7866. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. J., Greenberg R. N., Dunn J. A., Abernathy R., Ryerse J. S., Guerrant R. L. Effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STb on intestines of mice, rats, rabbits, and piglets. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):639–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.639-643.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupersztoch Y. M., Tachias K., Moomaw C. R., Dreyfus L. A., Urban R., Slaughter C., Whipp S. Secretion of methanol-insoluble heat-stable enterotoxin (STB): energy- and secA-dependent conversion of pre-STB to an intermediate indistinguishable from the extracellular toxin. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2427–2432. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2427-2432.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Hu S. T., Swiatek P. J., Moseley S. L., Allen S. D., So M. Isolation of a novel transposon which carries the Escherichia coli enterotoxin STII gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.615-620.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Yukitake J., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A. Substitutions of cysteine residues of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2121–2125. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2121-2125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Yukitake J., Miyama A. Reduction of enterotoxic activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by substitution for an asparagine residue. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2144–2148. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2144-2148.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Takahara M. Synthesis of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STp as a pre-pro form and role of the pro sequence in secretion. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5260–5265. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5260-5265.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Mazaitis A. J., Maas W. K., Rey M., Heyneker H. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin II of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.269-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Smith P. L., Field M. Mode of action of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Tissue and subcellular specificities and role of cyclic GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 17;632(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonishi Y., Hidaka Y., Koizumi M., Hane M., Aimoto S., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Mode of disulfide bond formation of a heat-stable enterotoxin (STh) produced by a human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Hitouji T., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin isolated from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 18D. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikel C. S., Nellans H. N., Guerrant R. L. In vivo and in vitro effects of a novel enterotoxin, STb, produced by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):893–901. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C. Assay for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin b in rats and mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):930–934. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.930-934.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C. Protease degradation of Escherichia coli heat-stable, mouse-negative, pig-positive enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2057–2060. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2057-2060.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]