Abstract
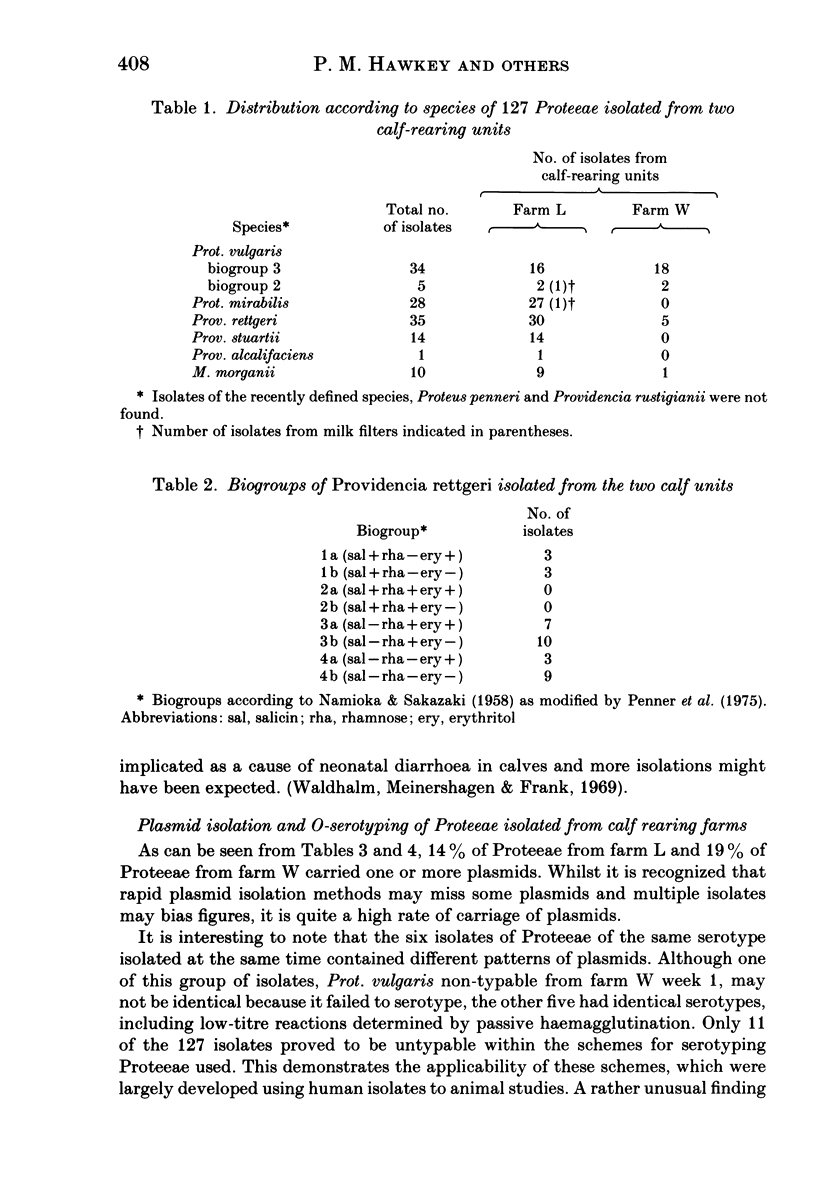
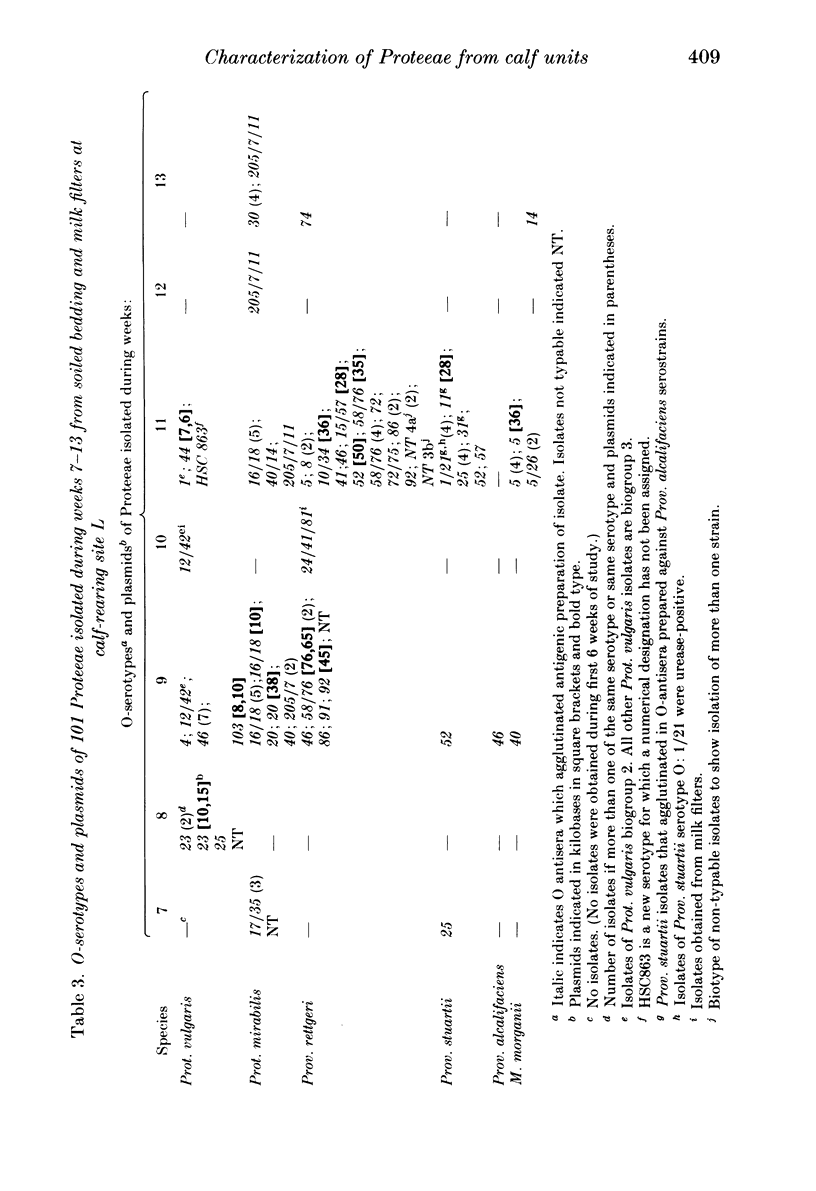
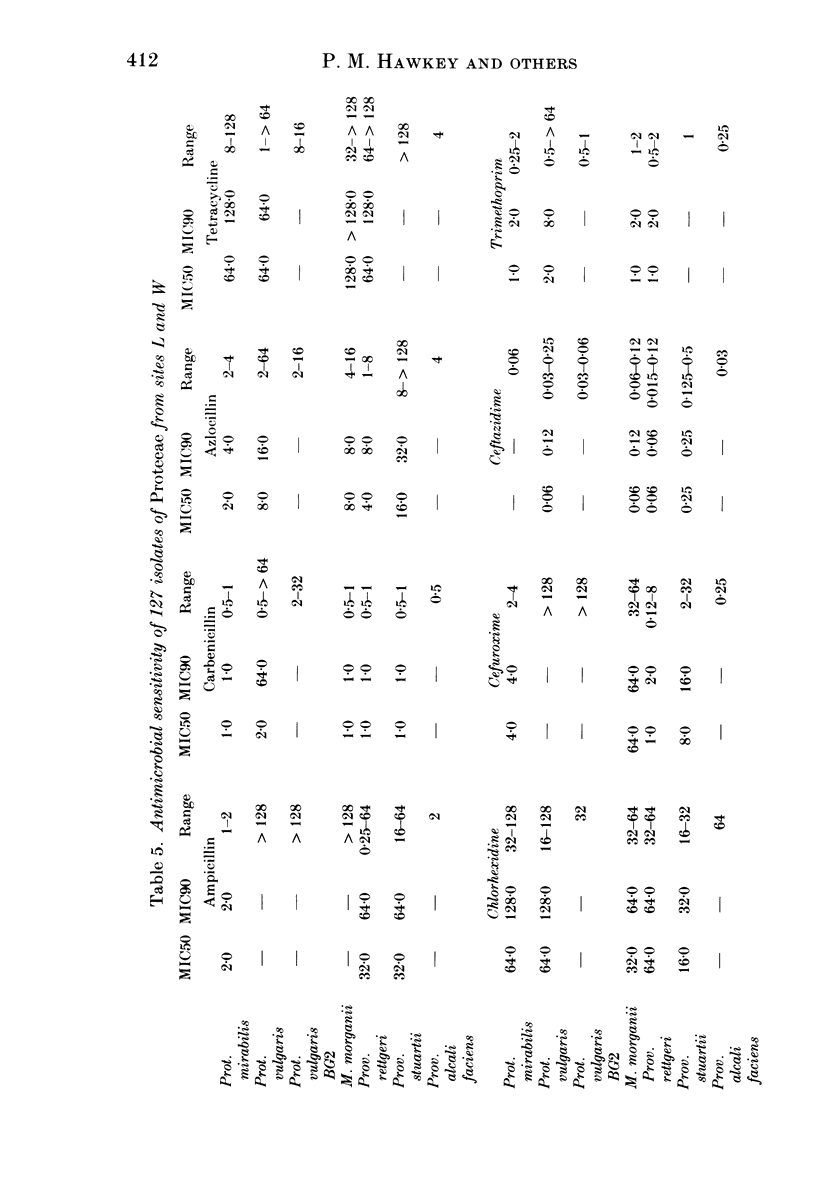
A survey was undertaken of the occurrence, serotype, antimicrobial sensitivity and plasmid content of members of the tribe Proteeae in the environment of two calf-rearing units in the county of Avon in South West England. Examples of the following species were found: Proteus mirabilis, Prot. vulgaris, Prot. vulgaris Biogroup 2, Morganella morganii, Providencia stuartii, Prov. alcalifaciens and Prov. rettgeri. A wide range of serotypes was found, many having been previously reported from nosocomial isolates. A total of 15% of isolates carried plasmids; six pairs of isolates were identified which had identical serotypes but different patterns of plasmid carriage. The antimicrobial sensitivity of the isolates was generally similar to isolates of Proteeae from humans. Although no truly aminoglycoside-resistant isolates were found, some isolates of Prov. stuartii and Prov. rettgeri had MIC's higher than the other isolates to gentamicin and netilmicin, suggesting the presence of low levels of the enzyme AAC 2'. The study demonstrates that there is a considerable diversity of species and types of Proteeae associated with calves and their environment. It seems likely that a potential cause of colonization of the human gut by Proteeae is the consumption of meat.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A. The molecular relatedness of R factors in enterobacteria of human and animal origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):376–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Taylor P. R., Yoshikawa T. T., Guze L. B. A nosocomial outbreak of infections due to multiply resistant Proteus mirabilis: role of intestinal colonization as a major reservoir. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):621–627. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Louvois J. Serotyping and the Dienes reaction on Proteus mirabilis from hospital infections. J Clin Pathol. 1969 May;22(3):263–268. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EWING W. H., TANNER K. E., DENNARD D. A. The Providence group: an intermediate group of enteric bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1954 Mar-Apr;94(2):134–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/94.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M., Bennett P. M., Hawkey C. A. Cryptic plasmids in hospital isolates of Providencia stuarti. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M., Bennett P. M., Hawkey C. A. Evolution of an R plasmid from a cryptic plasmid by transposition of two copies of Tn1 in Providencia stuartii. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):927–933. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M., Pedler S. J., Turner A. Comparative in vitro activity of semisynthetic penicillins against Proteeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):619–621. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M., Penner J. L., Potten M. R., Stephens M., Barton L. J., Speller D. C. Prospective survey of fecal, urinary tract, and environmental colonization by Providencia stuartii in two geriatric wards. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.422-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M. Providencia stuartii: a review of a multiply antibiotic-resistant bacterium. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Mar;13(3):209–226. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Brenner D. J. Identification of Proteus penneri sp. nov., formerly known as Proteus vulgaris indole negative or as Proteus vulgaris biogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1097–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1097-1102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. C., Ikeda J. S., Martin L. D., Kelly B. J., Ghazikhanian G. Y. R plasmid-mediated gentamicin resistance in salmonellae isolated from turkeys and their environment. Avian Dis. 1983 Jul-Sep;27(3):766–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollick G. E., Nolte F. S., Calnan B. J., Penner J. L., Barton L. J., Spellacy A. Characterization of endemic Providencia stuartii isolates from patients with urinary devices. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):521–525. doi: 10.1007/BF02013611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANYI B. Serological typing of proteus strains; sensitivity of serotypes to antibiotics. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1957;4(4):447–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H. Antibiotic resistance: the present situation reviewed. Vet Rec. 1977 Apr 23;100(17):354–360. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.17.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H., Whiteside E. J. The colonization of the human gut by antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from chickens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;43(3):465–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAMIOKA S., SAKAZAKI R. Etude sur les Rettgerella. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Apr;94(4):485–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS J. E. In vitro studies on Proteus organisms of animal origin. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Mar;53(1):26–31. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Fleming P. C., Whiteley G. R., Hennessy J. N. O-serotyping Providencia alcalifaciens. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):761–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.761-765.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Application of O-serotyping in a study of Providencia rettgeri (Proteus rettgeri) isolated from human and nonhuman sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):834–840. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.834-840.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. O antigen grouping of Morganella morganii (Proteus morganii) by slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):8–13. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.8-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Separate O-grouping schemes for serotyping clinical isolates of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):304–309. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.304-309.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hinton N. A., Duncan I. B., Hennessy J. N., Whiteley G. R. O serotyping of Providencia stuartii isolates collected from twelve hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):11–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.11-14.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hinton N. A., Hennessy J. N., Whiteley G. R. Reconstitution of the somatic (O-) antigenic scheme for Providencia and preparation of O-typing antisera. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):283–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hinton N. A., Hennessy J. Biotypes of Proteus rettgeri. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):136–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.136-142.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hinton N., Hennessy J. Serotyping of Proteus rettgeri on the basis of O antigens. Can J Microbiol. 1974 May;20(5):777–789. doi: 10.1139/m74-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Preston M. A., Hennessy J. N., Barton L. J., Goodbody M. M. Species differences in susceptibilities of Proteeae spp. to six cephalosporins and three aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):218–221. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. B. Face masks: which, when, where and why? J Hosp Infect. 1981 Mar;2(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(81)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustigian R., Stuart C. A. The Biochemical and Serological Relationships of the Organisms of the Genus Proteus. J Bacteriol. 1945 May;49(5):419–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.5.419-436.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER J., BAR-CHAY J. Biochemical investigation of Providence strains and their relationship to the Proteus group. J Hyg (Lond) 1954 Mar;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400027194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W. The special affinity of particular types of Proteus mirabilis for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickler D. J., Fawcett C., Chawla J. C. Providencia stuartii: a search for its natural habitat. J Hosp Infect. 1985 Jun;6(2):221–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toni M., Casewell M. W., Schito G. C. Reappraisal of the significance of multiply resistant urinary isolates of Proteus rettgeri. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):527–534. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhalm D. G., Meinershagen W. A., Frank F. W. Providencia stuartii as an etiologic agent in neonatal diarrhea in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Sep;30(9):1573–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. W., Hawkey P. M., Penner J. L., Senior B. W., Barton L. J. Serious nosocomial infection caused by Morganella morganii and Proteus mirabilis in a cardiac surgery unit. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.5-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


