Abstract
Aim
To quantitatively examine the influence of study methodology and population characteristics on prevalence estimates of autism spectrum disorders.
Methods
Electronic databases and bibliographies were searched and identified papers evaluated against inclusion criteria. Two groups of studies estimated the prevalence of typical autism and all autism spectrum disorders (ASD). The extent of variation among studies and overall prevalence were estimated using meta‐analysis. The influence of methodological factors and population characteristics on estimated prevalence was investigated using meta‐regression and summarised as odds ratios (OR).
Results
Forty studies met inclusion criteria, of which 37 estimated the prevalence of typical autism, and 23 the prevalence of all ASD. A high degree of heterogeneity among studies was observed. The overall random effects estimate of prevalence across studies of typical autism was 7.1 per 10 000 (95% CI 1.6 to 30.6) and of all ASD was 20.0 per 10 000 (95% CI 4.9 to 82.1). Diagnostic criteria used (ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV versus other; OR = 3.36, 95% CI 2.07 to 5.46), age of the children screened (OR = 0.91 per year, 95% CI 0.83 to 0.99), and study location (e.g. Japan versus North America; OR = 3.60, 95% CI 1.73 to 7.46) were all significantly associated with prevalence of typical autism. Diagnostic criteria, age of the sample, and urban or rural location were associated with estimated prevalence of all ASD.
Conclusions
Sixty one per cent of the variation in prevalence estimates of typical autism was explained by these models. Diagnostic criteria used, age of children screened, and study location may be acting as proxies for other study characteristics and require further investigation.
Keywords: autism, pervasive developmental disorders, prevalence, systematic review, meta‐analysis
The prevalence of autistic disorder is now considered to be around 10 per 10 000, and the prevalence of pervasive developmental disorders, 27.5 per 10 000. These are derived from studies which have estimated prevalences of autistic disorder ranging from 0.7 to 72.6 per 10 000.1 An increase in prevalence estimates has been observed over time, the reasons for which are not clear and may include: changes in study methodology; a genuine rise in autism risk factors; increase in services available, including diagnostic; increased awareness among educational and clinical professionals; and growing acceptance that autism can coexist with a range of other conditions.1,2,3,4
True variation in prevalence could generate aetiological hypotheses for autism and it is vital to understand what underpins the variation. Accurate estimates of the true prevalence are of value in planning diagnostic and intervention services.
Several narrative reviews have been conducted. This paper uses systematic and quantitative methods to examine reasons for variation in prevalence estimates. The aims are to assess the degree of variation among prevalence studies of autism, and to provide an overall summary of prevalence diversity taking into account among‐study variance using meta‐analysis. Aspects of study methodology and population characteristics are then examined using meta‐regression to investigate their influence on prevalence estimates.
Methods
Literature searches
Two databases, MEDLINE and EMBASE, were systematically searched by the first author (box 1). In addition, bibliographies of previous reviews1,5,6 were examined to identify published prevalence studies.
Study selection
Identified papers were examined against criteria for inclusion (box 2). The paper itself was examined if the abstract was insufficiently clear. Where there was more than one paper published on a particular study, the most recent was included in the review.
Box 1: Search strategy for identifying prevalence studies
MEDLINE (PubMed) (searched 13/04/04)
Years (1966–2004):
(“Autistic‐Disorder”/all subheadings [MeSH†] OR “Asperger‐Syndrome”/all subheadings [MeSH] OR “Schizophrenia‐Childhood”/all subheadings [MeSH] and (PY = 1966–1970) OR autis* (free text term)) AND (“Prevalence‐“/all subheadings [MeSH] OR “Cross‐Sectional‐Studies”/all subheadings [MeSH] OR “Mass‐Screening”/all subheadings [MeSH] OR “Multiphasic‐Screening”/all subheadings [MeSH]).
EMBASE (Excerpta Medica Database) (searched 13/04/04)
(BIDS EMBASE, via Ovid, copyright 2003)
Years (1980–2004):
(exp‡ autism/ OR exp infantile autism/ OR exp Asperger syndrome/ OR autism.mp§ (as keyword) OR Asperger.mp (as keyword)) AND (exp prevalence/ OR exp mass screening/ OR exp screening/ OR cross‐sectional.mp (as keyword)) NOT (genetic screening/exp OR genetic screen.mp (as keyword).
†MeSH (Medical Subjects Headings), The National Library of Medicine controlled vocabulary for indexing articles in PubMed; ‡exp, explode term (search under all subheadings); §mp, uses the database thesaurus search term.
Data extraction
Methods and population characteristics reported across most studies were selected for data extraction. The first author extracted and coded the data. In studies using different diagnostic criteria, prevalence data based on the more recently published diagnostic criteria were extracted. The studies formed two groups: those that assessed the prevalence of classic autism, or autistic disorder, known here as “typical autism”; and those that assessed the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) or all pervasive developmental disorders, known here as “all ASD”. Assessments of risk of bias included reporting of refusal rates and the reliability of screen and assessment procedures.
Analysis
In the basic tables, crude prevalence estimates (number of cases/sample size) were presented, along with standard errors. For all meta‐analyses and meta‐regressions, prevalence estimates were transformed to logits
 |
to improve their statistical properties. These were later back‐transformed to prevalences and expressed as cases per 10 000 people.
Description of heterogeneity among studies and summary of prevalence
Forest plots8 were used to visualise the extent of heterogeneity among studies. Two statistical methods were used to quantify the variation. A standard test for heterogeneity examined the null hypothesis that the true prevalences are identical in every study. Since heterogeneity was expected a priori, this was supplemented with a measure of the degree of inconsistency across studies, I2.9 I2 describes the proportion of variation in prevalence estimates that is due to genuine variation in prevalences rather than sampling error. It is expressed as a percentage, with 0% indicating consistency.
The random effects model assumes the study prevalences follow a normal distribution, allowing for among‐study variation.10 The usual confidence interval for the mean in the random effects model does not take among‐study variance into account, so is deceptively narrow when there is substantial variation across studies. Instead, a 95% interval for the true prevalence was calculated as the mean of logits ± 1.96 τ, where τ is the among‐study standard deviation.11
Box 2: Inclusion criteria
Primary research
A geographically and temporally defined population
Cross‐sectional study or data, or first phase of a longitudinal study
Defined diagnostic criteria stated for autism or autism spectrum disorder
Includes individuals under 18 years old
Initial selection in a wide range of children in the general population, or in a clinical setting
Final identification of cases based on clinical or other diagnostic assessment of selected children
Published in English, or with detailed summaries in English
Peer reviewed paper or conference presentation
-
Includes prevalence data
(criteria adapted from Wing7)
Investigation of sources of heterogeneity
The potential influence of covariates on the prevalence estimates was investigated using a random effects regression model, thus taking account of among‐study variance, using the metareg command in STATA.12 The regression coefficients represent log odds ratios, which are presented as odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
A multivariate meta‐regression model was constructed to investigate which covariates were associated with prevalence estimates if there was adjustment for other study covariates. The fit of each model was assessed using the percentage of among‐study variance explained ((1−(τ2 in model/τ2 in model with no covariates))×100), together with a significance test for each introduced variable (T = coefficient/SE, related to the t‐distribution). The models were constructed using a forward stepwise procedure as described in the results section. For each model a maximum number of covariates was set at n/10 where n was the number of studies, following standard recommendations for model size relative to sample size.13
Results
Studies identified
Literature searches identified 670 papers (including duplicates). After exclusion through comparison of titles and abstracts against inclusion criteria, 77 papers were identified for detailed examination. Thirty seven papers were excluded, including ten on the basis of inclusion criterion 2 (box 2), ten on the basis of criterion 4, nine on the basis of 6, and one on the basis of 7. In addition, four papers did not have detailed English summaries, one was not peer reviewed, and two were untraceable. Of these seven potentially eligible studies, four were conducted in Japan, one in the USA, one in France, and one in Sweden.
Forty papers met inclusion criteria, of which 37 gave estimates for typical autism and 23 for all ASD (table 1). The study sample sizes ranged from 826 to 4 590 333 (median = 48 705). Only 17 (40%) studies reported the refusal rate at the screen phase of the study, and 13 (33%) at the assessment stage. Six (15%) studies reported investigating the reliability of their screen method, and 11 (26%) studies stated that the inter‐rater reliability for the diagnostic assessment had been investigated. Many studies did not report refusal rates and reliability, so these covariates could not be included in further analyses.
Table 1 Summary of prevalence studies of autism spectrum disorders (42 studies).
| Ref. | Publ. year | First author | Country | Sample size | Area | Age (years) | Sample screened§ | Screen methods¶ | Prospective(P)/retrospective (R) assessment | Typical autism | All ASD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic criteria used | Prevalence estimate (per 10 000) (SE) | Diagnostic criteria used | Prevalence estimate (per 10 000) (SE) | ||||||||||
| 14 | 1966 | Lotter | UK | 78 000 | Urban | 8–10 | P | Q | P | Kanner | 4.5 (0.76) | – | – |
| 15 | 1970 | Treffert | USA | 899 750 | Mixed | 0–12 | C | R | R | Kanner | 0.7 (0.09) | – | – |
| 16 | 1970 | Brask | Denmark | 46 500 | Urban | 2–14 | S | – | – | Kanner | 4.3 (0.96) | – | – |
| 17 | 1979 | Wing | UK | 35 000 | Urban | 0–15 | C | R | P | Kanner | 4.9 (1.18) | Triad | 21.2 (2.46) |
| 18 | 1982 | Hoshino | Japan | 609 848 | Mixed | 0–18 | P | L | P | Kanner | 2.33 (0.20) | – | – |
| 19 | 1983 | Ishii | Japan | 34 987 | Urban | 6–12 | P | L | P | Rutter | 16.0 (2.14) | – | – |
| 20 | 1983 | Bohman | Sweden | 69 000 | Mixed | 0–20 | P | L | P | Rutter | 3.0 (0.66) | Rutter | 5.6 (0.9) |
| 21 | 1984 | McCarthy | Ireland | 65 000 | Mixed | 8–10 | S | R | R | Kanner | 4.3 (0.81) | – | – |
| 22 | 1984 | Gillberg | Sweden | 128 584 | Mixed | 4–18 | P | L | P | Rutter | 2.0 (0.39) | Rutter | 3.9 (0.55) |
| 23 | 1986 | Steinhausen | Germany | 279 616 | Urban | 0–15 | S | L | R | Rutter | 1.9 (0.26) | – | – |
| 24 | 1986 | Steffenburg | Sweden | 42 886 | Mixed | 0–9 | P | L | P | DSM‐III | 4.7 (1.05) | DSM‐III | 6.9 (1.27) |
| 25 | 1987 | Burd | USA | 180 986 | Mixed | 2–18 | C | L | P | DSM‐III | 1.2 (0.26) | DSM‐III | 3.3 (0.43) |
| 26 | 1987 | Matsuishi | Japan | 32 834 | Urban | 4–12 | P | R | P | DSM‐III | 15.5 (2.17) | – | – |
| 27 | 1988 | Tanoue | Japan | 95 394 | Rural | 7 | P | C | P | DSM‐III | 13.8 (1.20) | – | – |
| 28 | 1988 | Bryson | Canada | 20 800 | Mixed | 6–14 | P | Q | P | DSM‐III | 1.9 (0.96) | Denkla Triad | 10.1 (2.2) |
| 29 | 1989 | Ritvo | USA | 526 514 | Mixed | 3–17 | P | L | P | DSM‐III | 2.92 (0.24) | – | – |
| 30 | 1989 | Sugiyama | Japan | 11 320 | Urban | 1.5 | P | C | P | DSM‐III | 13.0 (3.37) | – | – |
| 31 | 1989 | Cialdella | France | 135 180 | Urban | 5–9 | C | L | R | DSM‐III | 5.1 (0.61) | DSM‐III | 10.8 (0.89) |
| 32 | 1991 | Gillberg | Sweden | 78 102 | Mixed | 4–13 | C | L | P | DSM‐III‐R | 7.0 (0.95) | DSM‐III‐R | 9.4 (1.1) |
| 33 | 1992 | Ohtaki | Japan | 35 366 | Mixed | 6–14 | S | R | P | DSM‐III‐R | 13.9 (1.98) | – | – |
| 34 | 1992 | Fombonne | France | 274 816 | Mixed | 9 & 13 | C | R | R | ICD‐9 | 4.9 (0.42) | – | – |
| 35 | 1993 | Herder | Norway | 50 909* | – | 1–17 | C | – | – | DSM‐III‐R | 5.5 (1.04) | – | – |
| 36 | 1996 | Honda | Japan | 8 537 | Urban | 5 | P | C | P | ICD‐10 | 21.1 (4.97) | – | – |
| 37 | 1997 | Arvidsson | Sweden | 1 941 | Mixed | 3–6 | P | C | P | ICD‐10 | 31 (12.6) | ICD‐10 | 46 (15.36) |
| 38 | 1997 | Webb | UK | 73 300 | Mixed | 3–15 | P | L | P | DSM‐III‐R | 7.2 (0.98) | – | – |
| 39 | 1997 | Fombonne | France | 325 347 | Mixed | 6–16 | C | R | R | ICD‐10 | 5.35 (0.41) | ICD‐10 | 16.29 (0.71) |
| 40 | 1998 | Sponheim | Norway | 65 688 | Mixed | 3–14 | P | L | P | ICD‐10 | 3.8 (0.76) | ICD‐10 | 5.2 (0.89) |
| 41 | 1999 | Kadesjo | Sweden | 826 | Urban | 6–7 | P | L | P | ICD‐10 | 60 (26.87) | Gillberg's criteria | 121 (38.04) |
| 42 | 2000 | Powell | UK | 16 049* | Mixed | 0 to <5 | S | R | R | DSM‐III‐R or ICD‐10** | 16.2 (3.17) | ICD‐10 | 33.7 (1.48) |
| 43 | 2000 | Kielinen | Finland | 152 732 | Mixed | 3–18 | C | R | R | ICD‐10 | 5.6 (0.61) | ICD‐10 | 13.9 (0.95) |
| 44 | 2000 | Baird | UK | 16 235 | Urban | 1.5† | P | Q (CHAT) | P | ICD‐10 | 30.8 (4.35) | ICD‐10 | 57.9 (5.95) |
| 45 | 2001 | Magnusson | Iceland | 43 153 | Mixed | 5–14‡ | P | C | R | ICD‐10 | 8.6 (1.41) | ICD‐10 | 13.2 (1.75) |
| 46 | 2001 | Bertrand | USA | 8 896 | Urban | 3–10 | P | R | P (where possible) | DSM‐IV | 40.0 (6.69) | DSM‐IV | 67 (8.65) |
| 47 | 2001 | Chakrabarti | UK | 15 500 | Mixed | 2.5–6.5 | P | C | P | DSM‐IV | 16.8 (3.29) | DSM‐IV | 62.6 (6.34) |
| 48 | 2002 | Croen | USA | 4 590 333 | Mixed | 0–12 | S | R | R | DSM‐III & DSM‐IV†† | 11.0 (0.15) | – | – |
| 49 | 2003 | Lingam | UK | 186 206 | Mixed | 5–14 | S | R | R | ICD‐10 | 14.9 (0.89) | ICD‐10 | 30.4 (1.28) |
| 50 | 2004 | Tebruegge | UK | 2 536 | Mixed | 8–9 | P | R | R | ICD‐10 | 23.7 (9.7) | ICD‐10 | 82.8 (18.0) |
| ASD papers | |||||||||||||
| 51 | 2001 | Fombonne | UK | 10 438 | Mixed | 5–15 | P | Q (DAWBA) | P | – | – | DSM‐IV and ICD‐10 (excl Rett's) | 26.1 (5.0) |
| 52 | 2002 | Scott | UK | 43 472 | Mixed | 5–11 | P | L | R | – | – | ICD‐10 | 57.0 (3.61) |
| 53 | 2003 | Yeargin‐Allsopp | USA | 289 456 | Urban | 3–10 | C | R | R | – | – | DSM‐IV | 34 (1.08) |
*Estimated from number of cases and prevalence estimate; †Cohort first screened at 18 months, followed up until age 7–8 years; ‡Data from an older cohort also included in the study, but excluded from these analyses; §Sample screened: P, whole population; C, general clinical services; S, specialist clinical/educational services; ¶Screen methods: C, routine checks; L, letter to elicit referrals; Q, questionnaires/interview; R, records (CHAT, Checklist for Autism in Toddlers; DAWBA, Development and Well‐Being Assessment); **ICD‐10 used for analysis; ††DSM‐IV used for analysis.
Description of heterogeneity among studies and summary of prevalence
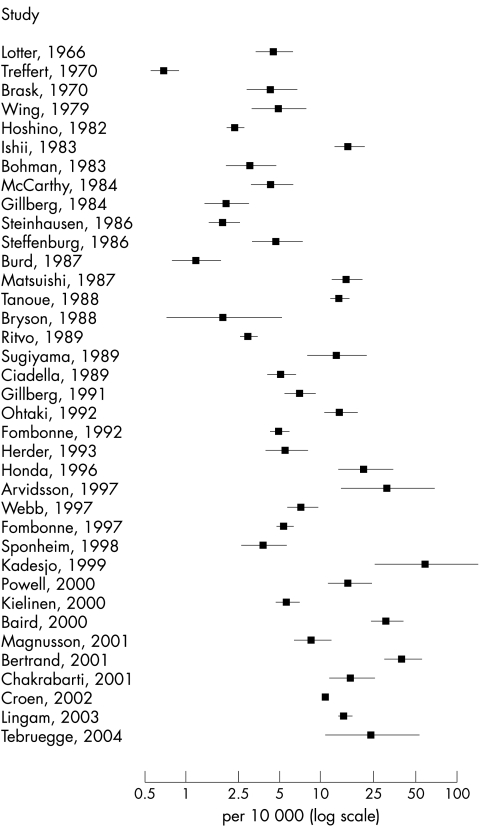
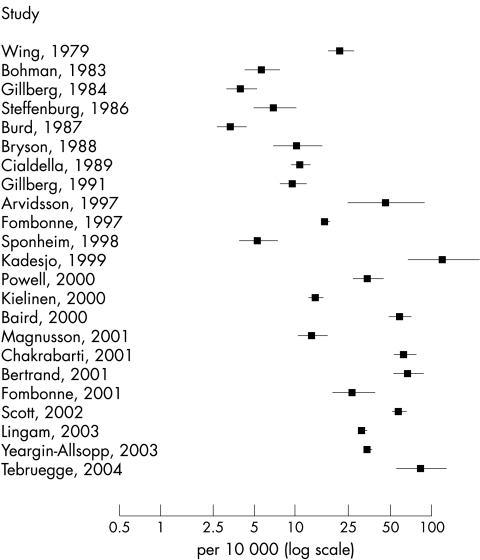
There was clearly wide variation in the prevalence estimates of typical autism (fig 1) and an increase in prevalence estimates over time. The Q statistic was very large (Q = 1947.6, df = 36, p < 0.001; I2 = 98.2%), showing that there was a great deal of variation among the studies. There was also a high degree of heterogeneity among estimates of all ASD (fig 2) (Q = 1577.7, df = 22, p < 0.001; I2 = 98.6%).
Figure 1 Forest plot of prevalence estimates and 95% confidence intervals from studies of typical autism, log transformed (n = 37).
Figure 2 Forest plot of prevalence estimates and 95% confidence intervals from studies of all ASD, log transformed (n = 23).
The back‐transformed mean of the random effects distribution for studies of typical autism was 7.1 per 10 000 (95% interval for true prevalences: 1.6 to 30.6) and for studies of all ASD was 20.0 per 10 000 (95% interval for true prevalences: 4.9 to 82.1).
Investigation of sources of heterogeneity
Two studies were excluded from the regression analyses: either the published paper was not available,16 or insufficient information on study methodology was included in the English abstract of a Swedish paper.35
Studies of typical autism
The associations between study covariates and prevalence estimates of typical autism from univariate meta‐regression analyses are shown in table 2. Taking account of the age of the children, for example, explained 23% of the among‐studies variance.
Table 2 Results of meta‐regression of studies of typical autism, univariate analyses (n = 35).
| Covariate | Categories of covariate (first listed used as baseline) | No. studies | Odds ratio | 95% CI (odds ratio) | p value | τ2 | Variance explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No covariates | 35 | – | – | – | 0.98 | – | |
| Age | Mid‐point of age range (continuous variable) | 35 | 0.84 | 0.75 to 0.93 | 0.002 | 0.75 | 23 |
| Decade | 1960s and 1970s | 3 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.58 | 41 |
| 1980s | 14 | 1.80 | 0.68 to 4.81 | 0.24 | |||
| 1990s | 9 | 4.26 | 1.52 to 11.94 | 0.006 | |||
| 2000s | 9 | 6.42 | 2.29 to 17.99 | <0.001 | |||
| Region* | N. America | 6 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.85 | 13 |
| Japan | 7 | 3.19 | 1.14 to 8.94 | 0.03 | |||
| Europe and Scandinavia | 22 | 2.05 | 0.87 to 4.85 | 0.10 | |||
| Area | Rural/mixed | 24 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.86 | 12 |
| Urban | 11 | 2.10 | 1.07 to 4.14 | 0.03 | |||
| Sample screened† | Population based | 21 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.88 | 10 |
| Clinic based | 14 | 0.54 | 0.28 to 1.03 | 0.06 | |||
| Screen method | Routine checks | 6 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.77 | 21 |
| Letter for referrals | 13 | 0.28 | 0.12 to 0.68 | 0.005 | |||
| Questionnaires | 3 | 0.45 | 0.13 to 1.62 | 0.22 | |||
| Records | 13 | 0.53 | 0.22 to 1.27 | 0.16 | |||
| Assessment | Prospective | 23 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.95 | 3 |
| Retrospective | 12 | 0.73 | 0.37 to 1.46 | 0.38 | |||
| Diagnostic criterion 1 | Not ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 21 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.64 | 35 |
| ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 14 | 3.32 | 1.89 to 5.81 | <0.001 | |||
| Diagnostic criterion 2 | Kanner | 5 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.54 | 45 |
| Rutter | 4 | 1.38 | 0.51 to 3.71 | 0.53 | |||
| DSM‐III | 8 | 1.95 | 0.84 to 4.57 | 0.12 | |||
| DSM‐III‐R | 3 | 3.29 | 1.13 to 9.58 | 0.03 | |||
| ICD‐9 | 1 | 1.82 | 0.37 to 8.85 | 0.46 | |||
| ICD‐10 | 11 | 5.10 | 2.29 to 11.47 | <0.001 | |||
| DSM‐IV | 3 | 7.17 | 2.46 to 20.91 | <0.001 |
*Region = North America: USA and Canada; Japan; Europe (UK, France, Germany, Ireland) and Scandinavia (Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, Iceland).
†Sample screened = whole population versus clinic based (general clinical services and clinic specialist services).
Diagnostic criteria and decade of publication were the covariates that explained the most variance among studies in the univariate analyses. These two covariates are collinear and it was not possible to include both in a multivariate model. The diagnostic criteria used were entered first into the multivariate model since this was considered to be more directly related to variation in prevalence estimates than decade of publication, which is a proxy for all time varying covariates. The binary categorisation of diagnostic criteria was used, as it was not possible to use multiple categories of diagnostic criteria in a multivariate analysis with so few studies. Age of the children screened also explained much among‐study variance, and was entered next into the model.
Models with three covariates were constructed which included age, diagnostic criteria, and each remaining covariate in turn. Screening method used, and whether the study was on a population or clinic based sample, were not significantly associated with prevalence. Urban location gave rise to higher prevalence estimates than studies carried out in rural or mixed locations (OR = 1.90, 95% CI 1.10 to 3.25; among‐study variance explained = 53%). Studies that drew on records of previous diagnostic assessments resulted in lower prevalence estimates than those which included a prospective diagnostic assessment (OR = 0.57, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.96; variance explained = 53%). Including region of study provided the model that explained the most among‐study variance (variance explained = 61%) (table 3). In this final model, using ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV led to prevalence estimates three times those using other diagnostic criteria. The odds ratio for age was 0.91 (95% CI 0.83 to 0.99), showing that an increase of one year in the age of the children screened led to a significant reduction in prevalence estimates. For example, when the odds ratio is taken to approximate a relative risk, if prevalence was estimated to be 10 per 10 000 in a sample of 5 year olds, it would be expected to be around 9.1 per 10 000 in a sample of 6 year olds. Studies in Japan gave rise to prevalence estimates that were 3.6 times those in North America.
Table 3 Multivariate meta‐regression results, for studies of typical autism (n = 35)*.
| Covariate | Odds ratio | 95% CI (odds ratio) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic criteria | Not ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 1.00 | – | – |
| ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 3.36 | 2.07 to 5.46 | <0.001 | |
| Age (years) | 0.91 | 0.83 to 0.99 | 0.03 | |
| Region | North America | 1.00 | – | – |
| Japan | 3.60 | 1.73 to 7.46 | 0.001 | |
| Europe and Scandinavia | 1.67 | 0.92 to 3.02 | 0.09 | |
| Intercept | 5.15×10−4 | 2.06×10−4 to 1.29×10−3 | <0.001 |
*As an example, to estimate the prevalence of typical autism in 8 year old European children using ICD‐10, take 10 000×(x/(1+x)), where x = 5.15×10−4×3.36×0.918×1.67, that is, a prevalence of 13.6 per 10 000.
Studies of all ASD
The associations between study covariates and prevalence estimates of all ASD from univariate meta‐regression analyses are shown in table 4. Only three covariates were significantly associated with the prevalence estimates: age of the children screened, urban or rural study location, and the diagnostic criteria used. The screen method used was of borderline significance. Of these, diagnostic criteria explained most among‐study variance, and was therefore included in the multivariate analyses. Each of the other covariates was introduced into the model in turn to form models with two covariates. As in the analyses of studies of typical autism, as decade and diagnostic criteria were collinear, only the covariate for diagnostic criteria was included in further analyses. When adjusting for diagnostic criteria, the only covariates that were significantly associated with the prevalence estimates were the age of the children screened (variance explained = 50%) and urban or rural study location (variance explained = 53%). Both these models are presented (table 5). Using ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV gave rise to prevalence estimates that were over twice those in studies using other diagnostic criteria. When including age in the model, an increase in the age of the sample by one year was associated with a fall in prevalence by a factor of approximately 0.85, taking the odds ratio as an approximation of a relative risk. Alternatively, when including study location, studies in urban areas gave rise to prevalence estimates over 2.5 times those in rural or mixed urban and rural areas.
Table 4 Results of meta‐regression of studies of all autism spectrum disorders, univariate analyses (n = 23).
| Covariate* | Categories of covariate (first listed used as baseline) | No. studies | Odds ratio | 95% CI (odds ratio) | p value | τ2 | Variance explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No covariates | 23 | 1.01 | |||||
| Age | Mid‐point of age range (continuous variable) | 23 | 0.82 | 0.72 to 0.94 | 0.005 | 0.74 | 27 |
| Decade | 1960s and 1970s | 1 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.43 | 57 |
| 1980s | 6 | 0.29 | 0.07 to 1.19 | 0.09 | |||
| 1990s | 5 | 0.93 | 0.22 to 3.94 | 0.92 | |||
| 2000s | 11 | 1.75 | 0.44 to 6.89 | 0.42 | |||
| Region | N. America | 4 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.77 | 24 |
| Japan | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Europe | 10 | 1.99 | 0.70 to 5.58 | 0.19 | |||
| Scandinavia | 9 | 0.72 | 0.25 to 2.05 | 0.54 | |||
| Area | Rural/mixed | 17 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.86 | 15 |
| Urban | 6 | 2.44 | 1.02 to 5.81 | 0.05 | |||
| Sample screened | Population based | 14 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.97 | 4 |
| Clinic based | 9 | 0.66 | 0.29 to 1.54 | 0.34 | |||
| Screen method | Routine checks | 3 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.72 | 29 |
| Letter for referrals | 9 | 0.31 | 0.10 to 0.98 | 0.05 | |||
| Questionnaires | 3 | 0.76 | 0.19 to 3.03 | 0.69 | |||
| Records | 8 | 0.93 | 0.30 to 2.97 | 0.91 | |||
| Assessment | Prospective | 14 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.96 | 5 |
| Retrospective | 9 | 1.52 | 0.66 to 3.49 | 0.32 | |||
| Diagnostic criterion 1 | Not ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 9 | 1.00 | – | – | 0.69 | 32 |
| ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 14 | 3.08 | 1.52 to 6.25 | 0.002 |
*Too few studies relative to the number of categories in diagnostic criterion 2 (criteria separately) were available to include this covariate in the analysis.
Table 5 Two multivariate meta‐regression models for studies of all autism spectrum disorders (n = 23).
| Covariate | Odds ratio | 95% CI (odds ratio) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1—including age | ||||
| Diagnostic criteria | Not ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 1.00 | – | – |
| ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 2.61 | 1.40 to 4.85 | 0.003 | |
| Age (years) | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.76 to 0.96 | 0.006 |
| Intercept | 1.45×10−3 | 1.45×10−3 | 3.25×10−4 to 6.45×10−3 | <0.001 |
| Model 2—including study area | ||||
| Diagnostic criteria | Not ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 1.00 | – | – |
| ICD‐10 or DSM‐IV | 3.48 | 1.92 to 6.33 | <0.001 | |
| Area | Rural/mixed | 1.00 | – | – |
| Urban | 2.85 | 1.47 to 5.53 | 0.002 | |
| Intercept | 2.03×10−4 | 7.15×10−5 to 5.73×10−4 | <0.001 |
Discussion
Main findings
As expected, a large amount of variation in prevalence across studies was found by graphical representation of estimates and by indices of heterogeneity. Despite this wide variation, pooled estimates are useful to indicate the public health burden of the disorder. The study variation is reflected in the very large intervals on the summaries of overall prevalence. The estimates of around 7.1 per 10 000 for typical autism, and 20.0 per 10 000 for all ASD are slightly lower than those estimated previously at 8.7–10.0 per 10 000 and 27.5 per 10 000 respectively.1,3
The covariate most strongly associated with prevalence estimates for typical autism and all ASD was the diagnostic criteria used. This association has been recognised previously.2,3,4 The time variation in prevalence is so closely linked to changes in diagnostic criteria, the two could not be examined separately. Furthermore, it was not possible to account entirely for the effect of the diagnostic criteria on the prevalence estimates as the ICD‐10 and DSM‐IV diagnostic schema leave some scope for variation in their interpretation and application.
The age of the children screened was strongly associated with the prevalence estimates. Manifestations of ASD may be more obvious in younger children. Alternatively, some screening methods may be more sensitive for younger children. Methods of screening were found to be significantly associated with the prevalence estimates in the univariate analyses of typical autism, but not after adjusting for the age of the children screened.
The multivariate model that explained most among‐study variance in studies of typical autism included the region studied, with studies from Japan having significantly higher estimates than North American studies. This could be due to other study factors. For example, a higher proportion of the Japanese studies were from urban areas (4/7 (57%) studies) compared to those in North America (1/6 (17%) studies). All the Japanese studies used prospective diagnostic assessments, and all but one drew on whole population rather than clinical samples. Due to the imposed limit of three covariates in the model, it was not possible to adjust for further potential effect modifiers. Countries differ in their diagnostic practice both in their theoretical background and their training procedures for healthcare workers. This may, in part, account for between‐region variation in prevalence.
In an alternative model for typical autism, when adjusting for age and diagnostic criteria, studies including prospective diagnostic assessments gave rise to higher prevalence estimates than those using retrospective records. This may be linked to the use of different diagnostic methodology at different times. Alternatively, an assessor taking part in prospective research studies might observe children more closely for symptoms of ASD.
When adjusting for diagnostic criteria, urban location was also observed to be associated with higher prevalence estimates for both typical autism and all ASD. If the screen method relied on records, these may have been more complete in urban locations. If the screen method used referrals from clinicians, it is possible that a higher proportion of children were known to services in urban locations. There may have been different diagnostic practices in urban locations where staff were more likely to be employed at specialist healthcare centres than in rural locations. It is easier to access the population in urban locations, and response rates may have been higher, but data on response were too limited to investigate this.
Limitations and recommendations for future research
Publication bias was not investigated in this review, as funnel plots were not considered appropriate due to the large degree of variation across studies. It is unlikely that the set of papers published is biased with respect to prevalence reported. However, it is possible that some studies were not identified in the searches if they were not published in mainstream journals. There may have been some time lag bias, with smaller studies, or studies with unremarkable results, coming through to publication slower than larger studies.
Of the papers identified for detailed examination, five potentially eligible studies were excluded as they did not have a detailed English summary or were not peer reviewed. There is no reason to suspect that the lack of availability of data from these studies is a direct consequence of the prevalences they might have observed.
The choice of coding of the covariates may have affected the model, such as using the midpoint of the age range or grouping diverse diagnostic criteria. Furthermore, it was only possible to assess the impact of reported covariates, or easily quantifiable covariates. Qualitative influences on prevalence such as awareness of autism in each population could not be included. As more studies are published, it may be possible to include new covariates or more precise coding of existing covariates in such a model. It would be valuable to have even more thorough recording of study characteristics in future studies to facilitate meta‐analyses of studies.
It is unlikely that it would ever be possible to measure and record all potentially important covariates. An alternative approach to investigating trends in prevalence, through ongoing monitoring of defined school aged populations using standard methodology, has been recommended.1 This would enable researchers to investigate changes in prevalence over time, and geographical variations while controlling for study methodology.
Conclusions
This review has contributed to explaining some of the influences on variation among prevalence estimates. Over half of the variation among study estimates can be explained by the age of the children screened, the diagnostic criteria used, and the country studied. Other important factors were whether the study was in a rural or urban location and whether cases were assessed prospectively or retrospectively. The impact of these identified factors on prevalence estimates should now be further investigated as they may be acting as proxies for other influences on prevalence. For example, the effect of geographical location on prevalence may be due to the services available, or variation in awareness of the disorder. By taking this quantitative approach, this review has shown that using meta‐analytic techniques can be a valuable additional tool in deepening our understanding of the influences of study and population characteristics on variation in prevalence estimates in autism spectrum disorders.
Acknowledgements
This work forms part of a PhD thesis entitled “Screening for autism spectrum disorders” (University of Cambridge, 2003). Jo Williams (née Johnson) held an MRC studentship, and subsequently received funding from the Shirley Foundation. We wish to thank Prof Patrick Bolton and Prof Simon Baron‐Cohen for their comments on an earlier draft of this paper.
Footnotes
Competing interests: none declared
References
- 1.Fombonne E. Epidemiological surveys of autism and other pervasive developmental disorders: an update. J Autism Dev Disord 200333365–382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wing L, Potter D. The epidemiology of autistic spectrum disorders: is the prevalence rising? Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Review 20028151–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fombonne E. Epidemiological trends in rates of autism. Mol Psychiatry 20027(suppl 2)S4–S6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Charman T. The prevalence of autism spectrum disorders. Recent evidence and future challenges. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 200211249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fombonne E. The epidemiology of autism: a review. Psychol Med 199929769–786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gillberg C, Wing L. Autism: not an extremely rare disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand 199999399–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wing L. The definition and prevalence of autism: a review. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 1993261–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lewis S, Clarke M. Forest plots: trying to see the wood and the trees. BMJ 20013221479–1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Higgins J P, Thompson S G, Deeks J J.et al Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. BMJ 2003327557–560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Whitehead A, Whitehead J. A general parametric approach to the meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. Stat Med 1991101665–1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Goodman S N. Meta‐analysis and evidence. Control Clin Trials 198910188–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sharp S. Meta‐analysis regression. Stata Technical Bulletin Reprints 20037(STB42)148–155. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Altman D.Practical statistics for medical research. London: Chapman & Hall, 1991349
- 14.Lotter V. Epidemiology of autistic conditions in young children. Social Psychiatry 19661124–137. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Treffert D A. Epidemiology of infantile autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 197022431–438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brask B H.A prevalence investigation of childhood psychoses. Nordic symposium on the care of psychotic children. Oslo: Barnepsychiatrist Forening, Universitetsforlagets Trykningssentral, 1970
- 17.Wing L, Gould J. Severe impairments of social interaction and associated abnormalities in children: epidemiology and classification. J Autism Dev Disord 1979911–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hoshino Y, Kumashiro H, Yashima Y.et al The epidemiological study of autism in Fukushima‐ken. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 198236115–124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ishii T, Takahashi O. The epidemiology of autistic children in Toyota, Japan: prevalence. Japanese Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 198324311–321. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bohman M, Bohman I L, Bjorck P O.et al Childhood psychosis in a northern Swedish county: some preliminary findings from an epidemiological survey. In: Schmidt M, Schmidt R, eds. Epidemiological approaches in child psychiatry. Stuttgart: George Thieme Verlag, 1983164–173.
- 21.McCarthy P, Fitzgerald M, Smith M A. Prevalence of childhood autism in Ireland. Ir Med J 198477129–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gillberg C. Infantile autism and other childhood psychoses in a Swedish urban region. Epidemiological aspects. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 19842535–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Steinhausen H C, Gobel D, Breinlinger M.et al A community survey of infantile autism. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 198625186–189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Steffenburg S, Gillberg C. Autism and autistic‐like conditions in Swedish rural and urban areas: a population study. Br J Psychiatry 198614981–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Burd L, Fisher W, Kerbeshian J. A prevalence study of pervasive developmental disorders in North Dakota. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 198726700–703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matsuishi T, Shiotsuki Y, Yoshimura K.et al High prevalence of infantile autism in Kurume City, Japan. J Child Neurol 19872268–271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tanoue Y, Oda S, Asano F.et al Epidemiology of infantile autism in southern Ibaraki, Japan: differences in prevalence in birth cohorts. J Autism Dev Disord 198818155–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bryson S E, Clark B S, Smith I M. First report of a Canadian epidemiological study of autistic syndromes. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 198829433–445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ritvo E R, Freeman B J, Pingree C.et al The UCLA–University of Utah epidemiologic survey of autism: prevalence. Am J Psychiatry 1989146194–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sugiyama T, Abe T. The prevalence of autism in Nagoya, Japan: a total population study. J Autism Dev Disord 19891987–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cialdella P, Mamelle N. An epidemiological study of infantile autism in a French department (Rhone): a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 198930165–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gillberg C, Steffenburg S, Schaumann H. Is autism more common now than ten years ago? Br J Psychiatry 1991158403–409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ohtaki E, Kawano Y, Urabe F.et al The prevalence of Rett syndrome and infantile autism in Chikugo District, the southwestern area of Fukuoka prefecture, Japan [letter]. J Autism Dev Disord 199222452–454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fombonne E, du Mazaubrun C. Prevalence of infantile autism in four French regions. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 199227203–210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Herder G A. [Infantile autism among children in the county of Nordland. Prevalence and etiology]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 19931132247–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Honda H, Shimizu Y, Misumi K.et al Cumulative incidence and prevalence of childhood autism in children in Japan. Br J Psychiatry 1996169228–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arvidsson T, Danielsson B, Forsberg P.et al Autism in 3‐6‐year‐old children in a suburb of Goteborg, Sweden. Autism 19971163–173. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Webb E V, Lobo S, Hervas A.et al The changing prevalence of autistic disorder in a Welsh health district. Dev Med Child Neurol 199739150–152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fombonne E, du Mazaubrun C, Cans C.et al Autism and associated medical disorders in a French epidemiological survey. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1997361561–1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sponheim E, Skjeldal O. Autism and related disorders: epidemiological findings in a Norwegian study using ICD‐10 diagnostic criteria. J Autism Dev Disord 199828217–227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kadesjo B, Gillberg C, Hagberg B. Brief report: autism and Asperger syndrome in seven‐year‐old children: a total population study. J Autism Dev Disord 199929327–331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Powell J E, Edwards A, Edwards M.et al Changes in the incidence of childhood autism and other autistic spectrum disorders in preschool children from two areas of the West Midlands, UK. Dev Med Child Neurol 200042624–628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kielinen M, Linna S L, Moilanen I. Autism in Northern Finland. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 20009162–167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Baird G, Charman T, Baron‐Cohen S.et al A screening instrument for autism at 18 months of age: a 6‐year follow‐ up study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 200039694–702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Magnusson P, Saemundsen E. Prevalence of autism in Iceland. J Autism Dev Disord 200131153–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bertrand J, Mars A, Boyle C.et al Prevalence of autism in a United States population: the Brick Township, New Jersey, investigation. Pediatrics 20011081155–1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chakrabarti S, Fombonne E. Pervasive developmental disorders in preschool children. JAMA 20012853093–3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Croen L A, Grether J K, Hoogstrate J.et al The changing prevalence of autism in California. J Autism Dev Disord 200232207–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lingam R, Simmons A, Andrews N.et al Prevalence of autism and parentally reported triggers in a north east London population. Arch Dis Child 200388666–670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tebruegge M, Nandini V, Ritchie J. Does routine child health surveillance contribute to the early detection of children with pervasive developmental disorders? An epidemiological study in Kent, U.K. BMC Pediatr 200444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fombonne E, Simmons H, Ford T.et al Prevalence of pervasive developmental disorders in the British nationwide survey of child mental health. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 200140820–827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Scott F, Baron‐Cohen S, Bolton P.et al Brief report: prevalence of autism spectrum conditions in children aged 5–11 years in Cambridgeshire, UK. Autism 20026231–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yeargin‐Allsopp M, Rice C, Karapurkar T.et al Prevalence of autism in a US metropolitan area. JAMA 200328949–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]