Abstract
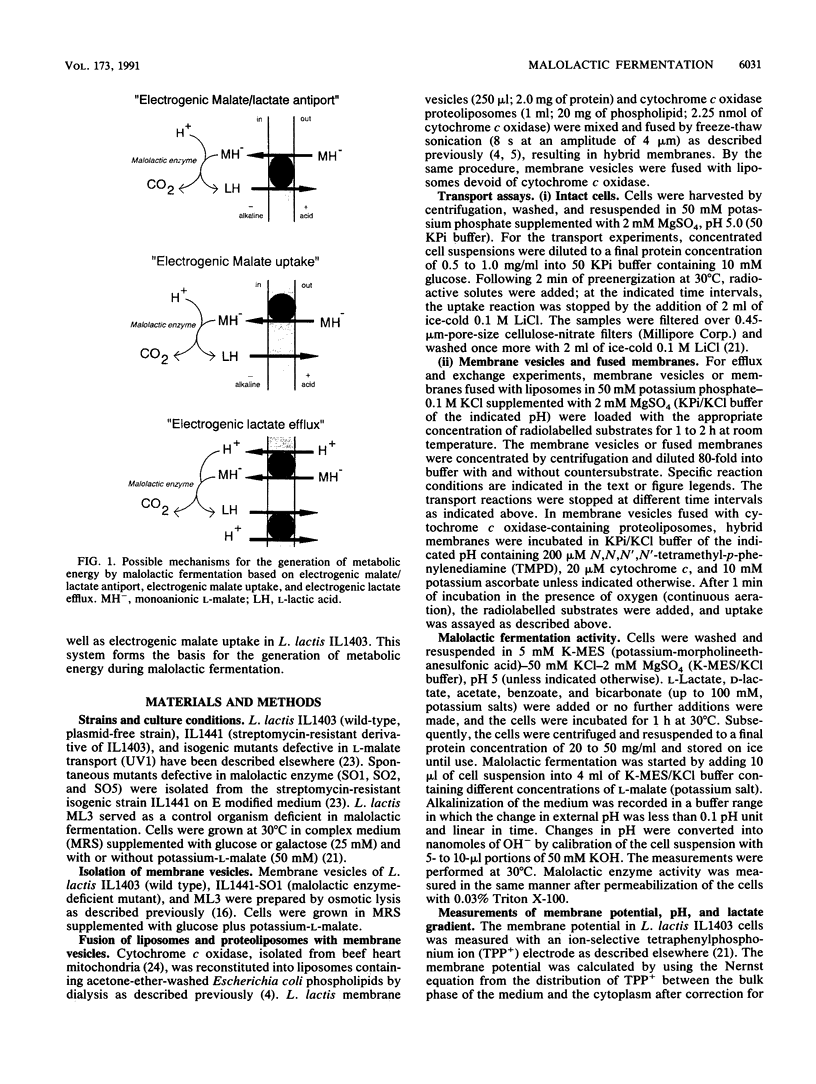
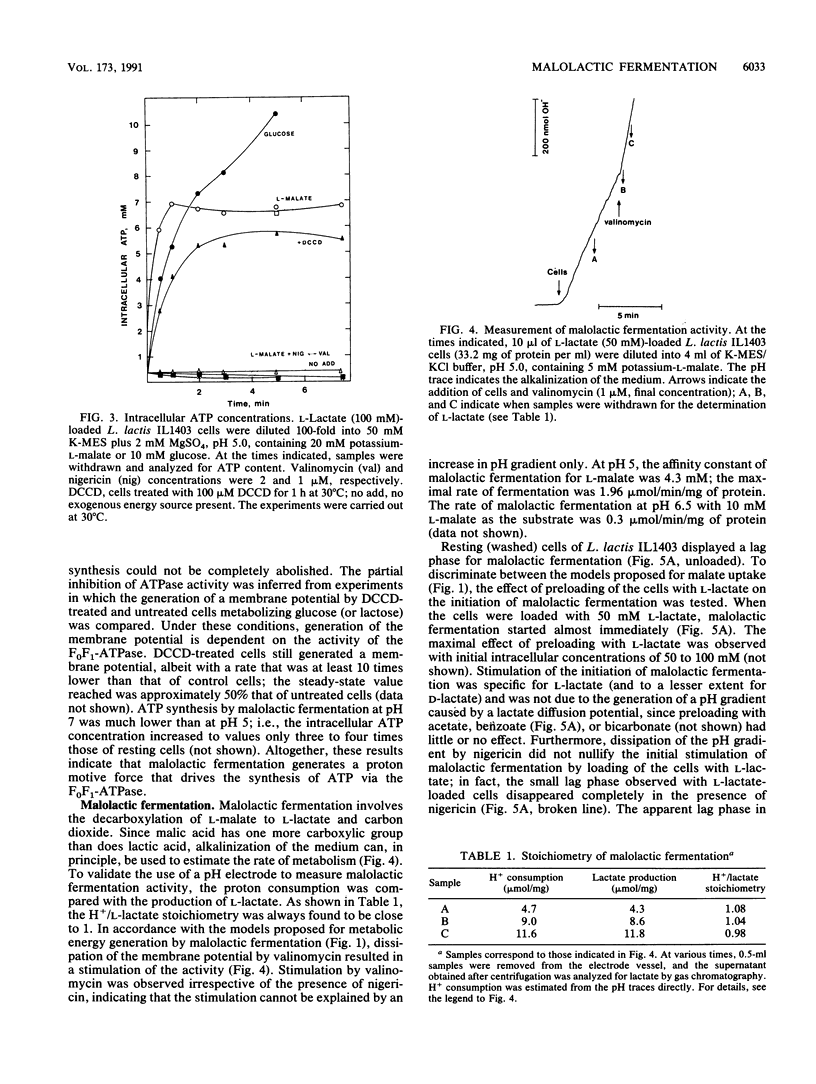
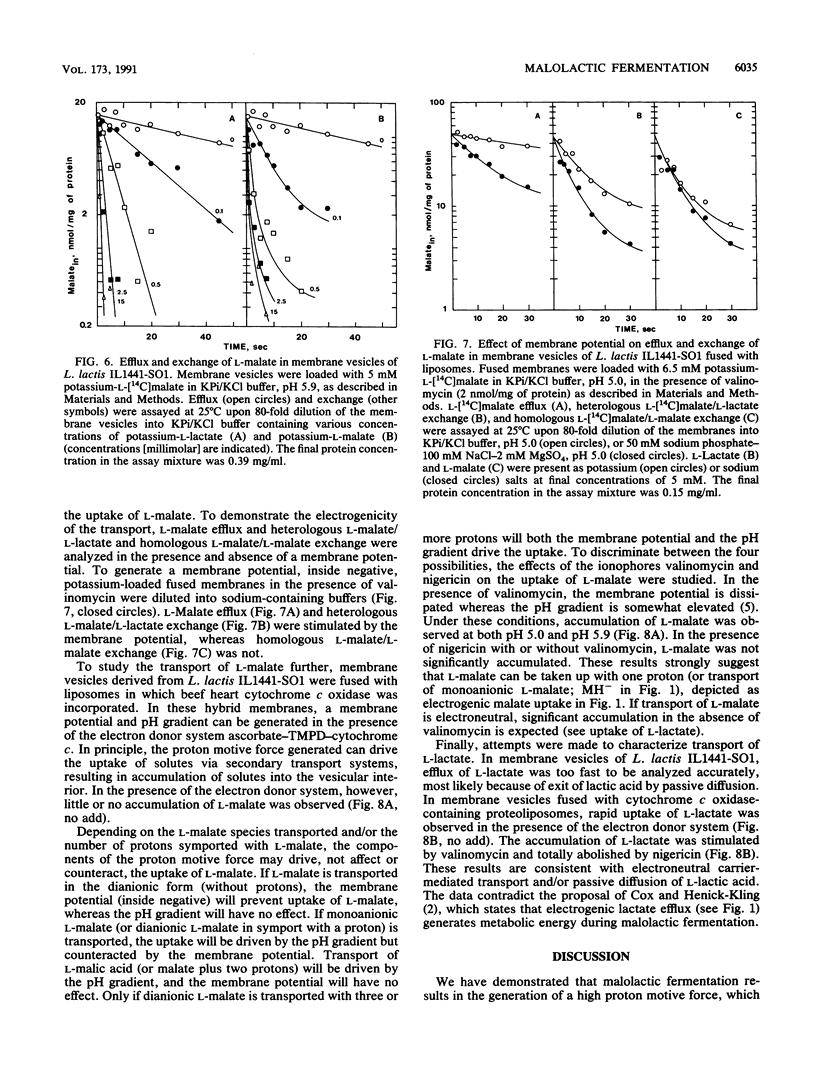
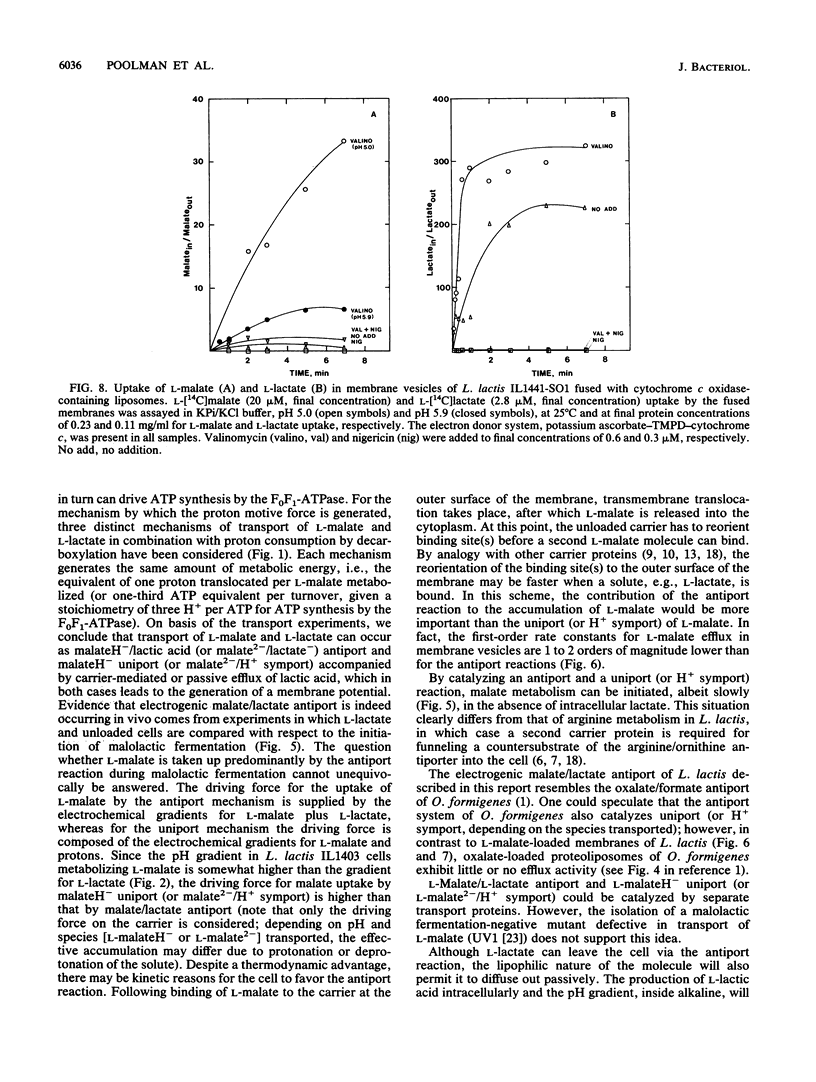
The mechanism of metabolic energy production by malolactic fermentation in Lactococcus lactis has been investigated. In the presence of L-malate, a proton motive force composed of a membrane potential and pH gradient is generated which has about the same magnitude as the proton motive force generated by the metabolism of a glycolytic substrate. Malolactic fermentation results in the synthesis of ATP which is inhibited by the ionophore nigericin and the F0F1-ATPase inhibitor N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Since substrate-level phosphorylation does not occur during malolactic fermentation, the generation of metabolic energy must originate from the uptake of L-malate and/or excretion of L-lactate. The initiation of malolactic fermentation is stimulated by the presence of L-lactate intracellularly, suggesting that L-malate is exchanged for L-lactate. Direct evidence for heterologous L-malate/L-lactate (and homologous L-malate/L-malate) antiport has been obtained with membrane vesicles of an L. lactis mutant deficient in malolactic enzyme. In membrane vesicles fused with liposomes, L-malate efflux and L-malate/L-lactate antiport are stimulated by a membrane potential (inside negative), indicating that net negative charge is moved to the outside in the efflux and antiport reaction. In membrane vesicles fused with liposomes in which cytochrome c oxidase was incorporated as a proton motive force-generating mechanism, transport of L-malate can be driven by a pH gradient alone, i.e., in the absence of L-lactate as countersubstrate. A membrane potential (inside negative) inhibits uptake of L-malate, indicating that L-malate is transported an an electronegative monoanionic species (or dianionic species together with a proton). The experiments described suggest that the generation of metabolic energy during malolactic fermentation arises from electrogenic malate/lactate antiport and electrogenic malate uptake (in combination with outward diffusion of lactic acid), together with proton consumption as result of decarboxylation of L-malate. The net energy gain would be equivalent to one proton translocated form the inside to the outside per L-malate metabolized.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anantharam V., Allison M. J., Maloney P. C. Oxalate:formate exchange. The basis for energy coupling in Oxalobacter. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7244–7250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. J., Henick-Kling T. Chemiosmotic energy from malolactic fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5750–5752. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5750-5752.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P. Sodium ion transport decarboxylases and other aspects of sodium ion cycling in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):320–340. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.320-340.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Kodde J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Neutral amino acid transport by membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris is subject to regulation by internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2748-2754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Poolman B., Kiewiet R., Konings W. Arginine transport in Streptococcus lactis is catalyzed by a cationic exchanger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6093–6097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Vrij W., Konings W. N. Incorporation of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase as a proton-motive force-generating mechanism in bacterial membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., van Leeuwen C., Konings W. N. Transport of basic amino acids by membrane vesicles of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1453–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1453-1458.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The lac carrier protein in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02000610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Poolman B., Driessen A. J. Bioenergetics and solute transport in lactococci. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(6):419–476. doi: 10.3109/10408418909104474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laanbroek H. J., Pfennig N. Oxidation of short-chain fatty acids by sulfate-reducing bacteria in freshwater and in marine sediments. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):330–335. doi: 10.1007/BF00422540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Ambudkar S. V., Anatharam V., Sonna L. A., Varadhachary A. Anion-exchange mechanisms in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):1–17. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.1-17.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of solute transport in streptococci by external and internal pH values. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):498–508. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.498-508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B. Precursor/product antiport in bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1629–1636. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Konings W. N. Kinetic properties of a phosphate-bond-driven glutamate-glutamine transport system in Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2755–2761. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2755-2761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault P. P., Heslot H. Selection of Streptococcus lactis Mutants Defective in Malolactic Fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):320–324. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.320-324.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault P., Gaillardin C., Heslot H. Role of malolactic fermentation in lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




